|
Constantius II
–
Roman Emperor
: 337-361 A.D. –
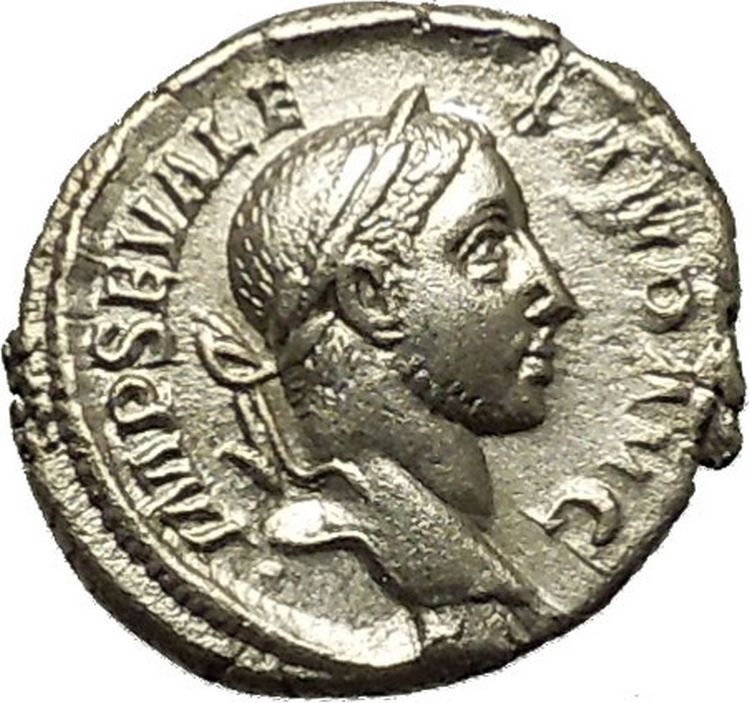
Bronze AE2 20mm (3.88 grams) Struck at the mint of Nicomedia 348-350 A.D.
Reference: RIC 67 (VIII, Nicomedia), LRBC 2289
DNCONSTANTIVSPFAVG – Diademed, draped and cuirassed bust left, holding globe.
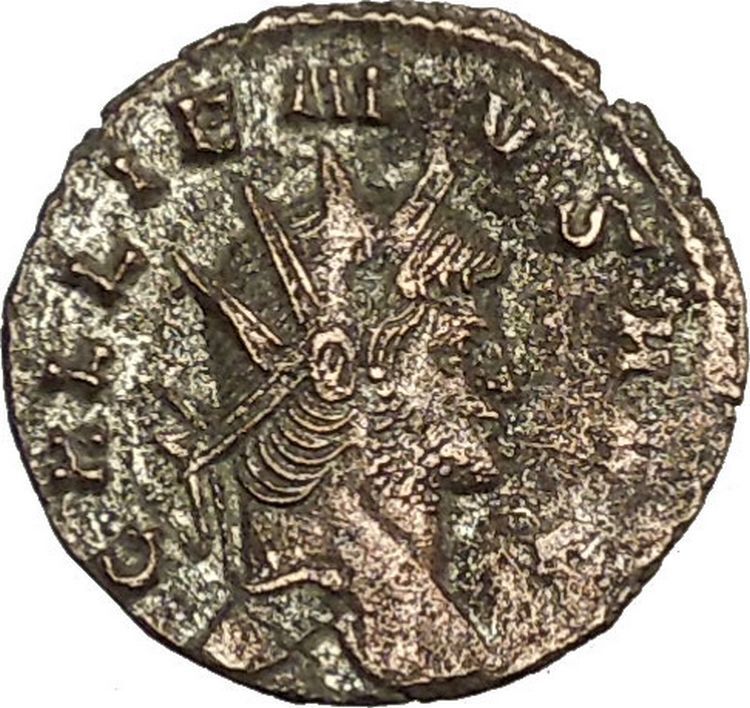
FELTEMPREPARATIO Exe: SMNЄ – Constantius II standing left, holding
labarum
and resting
hand on shield; two captives to left.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured,
provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of
Authenticity.
Royal/Imperial
symbols of power
Ruling dynasties often exploit pomp and ceremony with the use of
regalia
:
crowns
,
robes,
orb (globe) and sceptres
, some of which are reflections
of formerly practical objects. The use of language mechanisms also support this
differentiation with subjects talking of “the crown” and/or of “the
throne
” rather than referring directly to
personal names and items.

Labarum of Constantine I, displaying the “Chi-Rho” symbol above.
The labarum was a
vexillum
(military standard) that displayed
the “Chi-Rho”
symbol
☧
, formed from the first two
Greek letters
of the word “Christ”
—
Chi
and
Rho
. It was first used by the
Roman emperor
Constantine I
. Since the vexillum consisted of
a flag suspended from the crossbar of a cross, it was ideally suited to
symbolize the
crucifixion
of
Christ
.
Later usage has sometimes regarded the terms “labarum” and “Chi-Rho” as
synonyms. Ancient sources, however, draw an unambiguous distinction between the
two.
Vision of Constantine

A coin of Constantine (c.337) showing a depiction of his labarum
spearing a serpent.
On the evening of October 27, 312, with his army preparing for the
Battle of the Milvian Bridge
, the emperor
Constantine I
claimed to have had a vision
which led him to believe he was fighting under the protection of the
Christian God
.
Lactantius
states that, in the night before the
battle, Constantine was commanded in a dream to “delineate the heavenly sign on
the shields of his soldiers”. He obeyed and marked the shields with a sign
“denoting Christ”. Lactantius describes that sign as a “staurogram”, or a
Latin cross
with its upper end rounded in a
P-like fashion, rather than the better known
Chi-Rho
sign described by
Eusebius of Caesarea
. Thus, it had both the
form of a cross and the monogram of Christ’s name from the formed letters “X”
and “P”, the first letters of Christ’s name in Greek.
From Eusebius, two accounts of a battle survive. The first, shorter one in
the
Ecclesiastical History
leaves no doubt that
God helped Constantine but doesn’t mention any vision. In his later Life of
Constantine, Eusebius gives a detailed account of a vision and stresses that
he had heard the story from the emperor himself. According to this version,
Constantine with his army was marching somewhere (Eusebius doesn’t specify the
actual location of the event, but it clearly isn’t in the camp at Rome) when he
looked up to the sun and saw a cross of light above it, and with it the Greek
words
Ἐν Τούτῳ Νίκα
. The traditionally employed
Latin translation of the Greek is
in hoc signo vinces
— literally “In this
sign, you will conquer.” However, a direct translation from the original Greek
text of Eusebius into English gives the phrase “By this, conquer!”
At first he was unsure of the meaning of the apparition, but the following
night he had a dream in which Christ explained to him that he should use the
sign against his enemies. Eusebius then continues to describe the labarum, the
military standard used by Constantine in his later wars against
Licinius
, showing the Chi-Rho sign.
Those two accounts can hardly be reconciled with each other, though they have
been merged in popular notion into Constantine seeing the Chi-Rho sign on the
evening before the battle. Both authors agree that the sign was not readily
understandable as denoting Christ, which corresponds with the fact that there is
no certain evidence of the use of the letters chi and rho as a Christian sign
before Constantine. Its first appearance is on a Constantinian silver coin from
c. 317, which proves that Constantine did use the sign at that time, though not
very prominently. He made extensive use of the Chi-Rho and the labarum only
later in the conflict with Licinius.
The vision has been interpreted in a solar context (e.g. as a
solar halo
phenomenon), which would have been
reshaped to fit with the Christian beliefs of the later Constantine.
An alternate explanation of the intersecting celestial symbol has been
advanced by George Latura, which claims that Plato’s visible god in Timaeus
is in fact the intersection of the Milky Way and the Zodiacal Light, a rare
apparition important to pagan beliefs that Christian bishops reinvented as a
Christian symbol.
Iconographic career under Constantine

Coin of
Vetranio
, a soldier is holding two
labara. Interestingly they differ from the labarum of Constantine in
having the Chi-Rho depicted on the cloth rather than above it, and
in having their staves decorated with
phalerae
as were earlier Roman
military unit standards.

The emperor
Honorius
holding a variant of the
labarum – the Latin phrase on the cloth means “In the name of Christ
[rendered by the Greek letters XPI] be ever victorious.”
Among a number of standards depicted on the
Arch of Constantine
, which was erected, largely
with fragments from older monuments, just three years after the battle, the
labarum does not appear. A grand opportunity for just the kind of political
propaganda that the Arch otherwise was expressly built to present was missed.
That is if Eusebius’ oath-confirmed account of Constantine’s sudden,
vision-induced, conversion can be trusted. Many historians have argued that in
the early years after the battle the emperor had not yet decided to give clear
public support to Christianity, whether from a lack of personal faith or because
of fear of religious friction. The arch’s inscription does say that the Emperor
had saved the
res publica
INSTINCTV DIVINITATIS
MENTIS MAGNITVDINE (“by greatness of mind and by instinct [or impulse]
of divinity”). As with his predecessors, sun symbolism – interpreted as
representing
Sol Invictus
(the Unconquered Sun) or
Helios
,
Apollo
or
Mithras
– is inscribed on his coinage, but in
325 and thereafter the coinage ceases to be explicitly pagan, and Sol Invictus
disappears. In his
Historia Ecclesiae
Eusebius further reports
that, after his victorious entry into Rome, Constantine had a statue of himself
erected, “holding the sign of the Savior [the cross] in his right hand.” There
are no other reports to confirm such a monument.
Whether Constantine was the first
Christian
emperor supporting a peaceful
transition to Christianity during his rule, or an undecided pagan believer until
middle age, strongly influenced in his political-religious decisions by his
Christian mother
St. Helena
, is still in dispute among
historians.
As for the labarum itself, there is little evidence for its use before 317.In
the course of Constantine’s second war against Licinius in 324, the latter
developed a superstitious dread of Constantine’s standard. During the attack of
Constantine’s troops at the
Battle of Adrianople
the guard of the labarum
standard were directed to move it to any part of the field where his soldiers
seemed to be faltering. The appearance of this talismanic object appeared to
embolden Constantine’s troops and dismay those of Licinius.At the final battle
of the war, the
Battle of Chrysopolis
, Licinius, though
prominently displaying the images of Rome’s pagan pantheon on his own battle
line, forbade his troops from actively attacking the labarum, or even looking at
it directly.[16]
Constantine felt that both Licinius and
Arius
were agents of Satan, and associated them
with the serpent described in the
Book of Revelation
(12:9).
Constantine represented Licinius as a snake on his coins.
Eusebius stated that in addition to the singular labarum of Constantine,
other similar standards (labara) were issued to the Roman army. This is
confirmed by the two labara depicted being held by a soldier on a coin of
Vetranio
(illustrated) dating from 350.
The Chi Rho is one of the earliest
christograms
used by Christians. It is formed by superimposing the
first two letters in the Greek spelling of the word
Christ
(
Greek
: “Χριστός” ), chi = ch and rho = r, in such a way to produce
the monogram
. The Chi-Rho symbol was also used by pagan Greek scribes to
mark, in the margin, a particularly valuable or relevant passage; the
combined
letters Chi and Rho standing for chrēston, meaning “good.”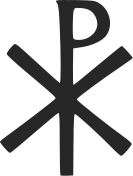
Although not technically a cross, the Chi Rho invokes the crucifixion
of Jesus as well as symbolizing his status as the Christ. There is early
evidence of the Chi Rho symbol on Christian Rings of the third century.
The labarum (Greek:
λάβαρον) was a
vexillum
(military standard) that displayed the “Chi-Rho”
symbol, formed from the first two
Greek letters
of the word “Christ”
(Greek:
ΧΡΙΣΤΟΣ, or Χριστός) — Chi (χ)
and Rho (ρ).
It was first used by the
Roman emperor
Constantine I
. Since the vexillum consisted of a flag suspended from
the crossbar of a cross, it was ideally suited to symbolize
crucifixion
. The Chi-Rho symbol was also used by Greek scribes to
mark, in the margin, a particularly valuable or relevant passage; the
combined letters Chi and Rho standing for chrēston, meaning
“good.”
Flavius Iulius Constantius, known in English as
Constantius II (7 August 317 – November 3 361) was a
Roman
Emperor
(337-361) of the
Constantinian dynasty
.
Constantius joins the lengthy list of emperors whose career
was marked by a seemingly endless series of wars both domestic and foreign. He
served as Caesar from 324 until his father’s death in 337 at which time he
shared the title of Augustus with two other brothers, Constantine II and
Constans. To make sure no more Johnny-come-latelies in his family would try
their hand at being emperor too it is thought that he engineered a bloodbath
that left nary a relative. Constantine II died in battle and Constans was
murdered by the men of Magnentius, the first of several usurpers. This left
Constantius finally as sole legitimate emperor and he moved quickly to suppress
Magnentius, an endeavor he eventually accomplished. The strife didn’t end there,
however, as he still had to deal with other revolts and wars on every corner of
the empire. Caught in these never-ending battles he died while on his way to
battle Julian II.
Flavius Iulius Constantius was born at
Sirmium
(now
Sremska Mitrovica
in
Serbia
) in
province of Pannonia
, the third son of
Constantine the Great
, and second by his second wife
Fausta
, the
daughter of Maximian
. Constantius was made
Caesar
by his father on 13 November 324.
When the elder
Constantine
died at
Constantinople
on 22 May 337, Constantius was nearest of his sons to that
city, and despite being on campaign in the eastern provinces, immediately
returned to the city to oversee his father’s funeral.
The
Massacre of 337
The role of Constantius in the massacre of his relatives
(those descended from the second marriage of his paternal grandfather
Constantius Chlorus
and
Theodora
) is unclear.
Zosimus
,
writing 498-518 claims that Constantius “caused”
the soldiers to murder his relatives, as opposed to actually ordering the
action. Eutropius
, writing between 350 and 370, writes that Constantius merely
sanctioned “the act, rather than commanding it”.
However, it must be noted that both of these sources are hostile to Constantius
– Zosimus
being a pagan,
Eutropius
a friend of
Julian
, Constantius’ cousin and, ultimately, his enemy.
Whatever the case, Constantius himself, his older brother
Constantine II
, his younger brother
Constans
and three cousins,
Gallus
, his half-brother
Julian
and
Nepotianus
,
son of
Eutropia
, were left as the only surviving males related to Constantine.
Division
of the Empire
Meeting at Sirmium not long after the massacre, the three
brothers proceeded to divide the Roman Empire among them, according to their
father’s will. Constantine II received
Britannia
, Gaul
and Hispania
;
Constans (initially under the supervision of Constantine II)
Italia
,
Africa
, Illyricum,
Thrace
,
Macedon
and
Achaea
; and Constantius the East.
Reign
in the East
There are few details of the early years of Constantius’ sole
reign in the East. He seems to have spent most of his time defending the eastern
border against invasions by the aggressive
Sassanid Empire
under
Shapur II
.
These conflicts seem to have been mainly limited to Sassanid sieges of the
various fortresses (Nisibis,
Singara
,
Constantia and
Amida
) of Roman
Mesopotamia
, which achieved little for either side.
Although Shapur II
seems to have been victorious in most of the confrontations
– except the Battle of Narasara, where one of
Shapur II
‘s
brothers, Narses, was killed
– the overall result must be considered a victory for Constantius because
Shapur
failed to make any significant gains.
In the meantime,
Constantine II
‘s desire to retain control of
Constans
‘
realm had lead Constantius’ two surviving brothers into open conflict; resulting
in the death of the elder in 340.
As a result, Constans took control of his deceased elder brother’s realms and
became sole ruler of the Western two-thirds of the Empire. This division lasted
until 350, when Constans was killed in battle by forces loyal to the
usurper
Magnentius
.
War
against Magnentius
This new state of affairs proved unacceptable to Constantius,
who felt that, as the only surviving son of
Constantine the Great
, the position of
Emperor
was his alone.
As such, he determined to march west to enforce his claims. However, feeling
that the east still required some sort of imperial control, he elevated his
cousin
Constantius Gallus
to Caesar of the East. As an extra measure to ensure the
loyalty of his cousin, he married the elder of his two sisters,
Constantina
, to
Gallus
.
Before facing
Magnentius
,
Constantius first came to terms with
Vetranio
, a
loyal Constantian general, who had previously accepted the position of Augustus
in order to retain the loyalty of his troops, and probably to stop Magnentius
from gaining more support. This action may have been carried out at the urging
of Constantius’ own sister,
Constantina
, who had since traveled east to marry
Gallus
. Constantius for his own part had previously sent
Vetranio
the imperial diadem and acknowledged the general‘s new position. However, when
Constantius arrived,
Vetranio
willingly and gladly resigned his position and accepted Constantius’ offer of a
comfortable retirement in
Bithynia
.
The following year, Constantius finally met
Magnentius
in the
Battle of Mursa Major
,
one of the bloodiest battles in Roman history. The result was a defeat for the
usurper, who withdrew back to his Gaulish domains. As a result, the cities of
Italy
switched their allegiance to Constantius and ejected all of
Magnentius
’
garrisons. Constantius spent the early months of 352 on a campaign against the
Sarmatians
,
before moving on to invade
Italy
.
When Constantius and Magnentius finally met again, at the
Battle of Mons Seleucus
in southern Gaul, Constantius once again emerged the
victor.
Soon after, Magnentius
, realising the futility of continuing his revolt, committed
suicide 10 August 353.
Sole
Ruler of the Roman Empire
Constantius spent much of the rest of 353 and early 354 on
campaign against the
Alemanni
on
the Danubian borders. The exact details of this campaign are uncertain, though
it seems to have ended with victory for Constantius.
The
Downfall of Gallus
In the meantime, Constantius had been receiving some
disturbing reports regarding the actions of his cousin,
Gallus
.
Possibly as a result of these reports, Constantius concluded a peace with the
Alemanni
,
and withdrew to Milan
.
Once there, he decided to first call
Ursicinus
, Gallus’ magister equitum, to Milan for reasons that remain
unclear.
Constantius then requested the presence of
Gallus
and
Constantina
.
Although at first
Gallus
and
Constantina
complied with this order, when
Constantina
died in
Bithynia
,
Gallus
begun to hesitate. However, after some convincing by one of
Constantius’ agents,
Gallus continued his journey west, passing through
Constantinople
and
Thrace
to Petobio in the province of
Noricum
.
It was there that
Gallus
was arrested by the soldiers of Constantius under the command of
Barbatio
.
He was then moved to Pola
, and interrogated. Once there,
Gallus
claimed that it was
Constantina
who was to blame for all the trouble that had been caused while
he was in charge of the east.
Apparently, at first, this so greatly angered Constantius that he immediately
ordered the death of
Gallus
.
However, soon after, he changed his mind, and recanted his execution order.
Unfortunately for Gallus, this order was delayed by
Eusebius
, one of Constantius‘ eunuchs, and, as a result,
Gallus
was executed.
More
Usurpers and Julian Caesar
On 11 August 355, the
magister militum
Claudius Silvanus
revolted in Gaul. Silvanus had surrendered to Constantius
after the
battle of Mursa Major
. Constantius had made him magister militum in 353,
with the purpose of blocking the German threats, a feat that Silvanus achieved
by bribing the German tribes with the money he had collected. A plot organized
by members of Constantius’ court led the emperor to recall Silvanus. After
Silvanus revolted, he received a letter by Constantius that recalled him to
Milan, but which made no reference to the revolt.
Ursicinus
, who was meant to replace Silvanus, bribed some troops, and
Silvanus was killed.
However, Constantius realised that too many threats still
faced the Empire, and he could not possibly handle all of them by himself, so on
6 November 355,
he elevated his last remaining relative, Julian, to the rank of
Caesar
.
A few days later,
Julian
was married to
Helena
, the last surviving sister of Constantius.
Not long after Constantius sent
Julian
off to Gaul.
Constantius
in the West and Return to the East
Constantius spent the next few years overseeing affairs in
the western part of the Empire primarily from his base at
Milan
. However,
he also visited Rome
– for the first and only time in his life – in 357, and, in that same year, he
forced Sarmatian
and Quadi
invaders out of
Pannonia
and Moesia Inferior
,
then led a successful campaign across the Danube against the
Sarmatians
and the Germanic Quadi
tribe.
Around 357/8, Constantius received ambassadors from
Shapur II
,
who demanded that Constantius restore the lands surrendered by
Narseh
.
Despite rejecting these terms,
Constantius still tried to avert war with the
Sassanid Empire
by sending two embassies to
Shapur II
.
As a result of Constantius’ rejection of his terms,
Shapur II
launched another invasion of Roman Mesopotamia. When news reached Constantius
that Shapur
II
had not only invaded Roman territory, but taken
Amida
[46],
destroyed Singara
and taken Bezabde
he decided to return to there to face this re-emergent threat in 360.
The
usurpation of Julian and Problems in the East
In the meantime,
Julian
had won some victories against the
Alemanni
tribe, who had once again invaded
Roman Gaul
.
As such, Constantius requested reinforcements from
Julian
for his own campaign against Shapur II. However, when he requested
reinforcements from
Julian
’s Gaulish army, the Gaulish legions revolted and proclaimed
Julian
Augustus.
However, on account of the immediate Sassanid threat,
Constantius was unable to directly respond to his cousin’s usurpation other than
by sending missives by which he tried to convince Julian to resign the title of
Augustus and be satisfied with that of Caesar.
By 361, Constantius saw no alternative but to face the
usurper with violent force; and yet the threat of the
Sassanids
remained. Constantius had already spent part of early 361
unsuccessfully attempting to take the fortress of
Bezabde
.
After a time, he had withdrawn to
Antioch
to
regroup, and prepare for a confrontation with
Shapur II
.
However, as it turned out, the campaigns of the previous year had inflicted such
heavy losses on the
Sassanids
that they did not attempt another round of engagements in 361.
This allowed Constantius to turn his full attention to facing the usurpation of
Julian
[55].
Death
As such, Constantius immediately gathered his forces and set
off west. However, by the time he reached
Mopsuestia
in Cicilia, it was clear that he was fatally ill and would not survive to face
Julian
. Apparently, realising his death was near, Constantius had himself
baptised by Euzoius
, the
Semi-Arian
bishop of
Antioch
, and
then declared that Julian was his rightful successor.
Constantius II died of fever on 3 November 361.
Marriages
and Children
Constantius II was married three times:
First to a
daughter
of his half-uncle
Julius Constantius
, whose name is unknown. She was a full-sister of Gallus
and a half-sister of Julian. She died c. 352/3.
Second, to Eusebia, a woman of
Macedonian
origin from the city of
Thessaloniki
, whom he married before Constantius’ defeat of Magnentius in
353. She died in 360.
Third and lastly, in 360, to
Faustina (empress)
, who gave birth to Constantius’ only child, a posthumous
daughter named
Flavia Maxima Constantia
, who later married Emperor
Gratian
.
Religious
Issues
Constantius seems to have had a particular interest in the
religious state of the
Roman
Empire
. As a
Christian
Roman
Emperor
, Constantius made a concerted effort to promote
Christianity
at the expense of
Roman polytheism
(‘paganism’). As such, over the course of his reign, he
issued a number of different edicts designed specifically to carry out this
agenda (see below). Constantius also took an active part in attempting to shape
the Christian
church.
Paganism
under Constantius
In spite of the some of the edicts issued by Constantius, it
should be recognised that he was not fanatically anti-pagan – he never made any
attempt to disband the various Roman priestly colleges or the
Vestal Virgins
,
he never acted against the various pagan schools, and, at times, he actually
even made some effort to protect paganism.
Also, most notably, he remained
pontifex maximus
until his death, and was actually deified by the Roman
Senate after his death. The relative moderation of Constantius’ actions toward
paganism is reflected by the fact that it was not until over 20 years after
Constantius’ death, during the reign of
Gratian
, that
any pagan senators protested their religion’s treatment.
Christianity
under Constantius
Although often considered an
Arian
,
Constantius ultimately preferred a third, compromise version that lay somewhere
in between Arianism
and the
Nicaean Creed
, retrospectively called
Semi-Arianism
[61][62].
As such, during his reign, Constantius made a concerted attempt to mold the
Christian church to follow this compromise position, and to this end, he
convened several Christian councils during his reign, the most notable of which
were one at
Rimini
and its twin at
Seleuca
,
which met in 359 and 360 respectively. “Unfortunately for his memory the
theologians whose advice he took were ultimately discredited and the malcontents
whom he pressed to conform emerged victorious,” writes the historian
A.H.M. Jones
. “The great councils of 359-60 are therefore not reckoned
ecumenical
in the tradition of the church, and Constantius II is not
remembered as a restorer of unity, but as a
heretic
who
arbitrarily imposed his will on the church.”
Judaism
under Constantius
Judaism faced some severe restrictions under Constantius, who
seems to have followed an anti-Jewish policy in line with that of his father.
Early in his reign, Constantius issued a double edict in concert with his
brothers limiting the ownership of slaves by Jewish people
and banning marriages between Jews and Christian women.
A later edict (issued by Constantius after becoming sole
Emperor
) decreed that a person who was proven to have converted from
Christianity to Judaism would have their entire property confiscated by the
state.
However, it should be noted that Constantius’ actions in this regard may not
have been so much to do with Jewish religion as Jewish business; apparently, it
was often the case that privately-owned Jewish businesses were in competition
with state-owned businesses. As such, Constantius may have sought to provide as
much of an advantage to the state-owned businesses as possible by limiting the
skilled workers and the slaves available to the Jewish businesses.
Religious
Edicts Issued by Constantius
Pagan-related edicts issued by Constantius (by himself
or with others) included:
-
The banning of sacrifices;
-
The closing of pagan temples;
-
Edicts against soothsayers and magicians.
Christian-related edicts issued by Constantius (by
himself or with others) included:
-
Exemption from compulsory public service for the clergy;
* Exemption from compulsory public service for the sons of clergy;
-
Tax exemptions for clergy and their servants,
also later for their family;
-
Clergy and the issue of private property;
-
Bishops exempted from being tried in secular courts;
-
Christian prostitutes only able to be bought by
Christians.
Jew-related edicts issued by Constantius (by himself
or with others) included:
-
Weaving women who moved from working for the government
to working for Jews, must be restored to the government; Jews may not marry
Christian women; Jews may not attempt to convert Christian women;
-
Any non-Jewish slave bought by a Jew will be confiscated
by the state; if a Jew attempts to circumcise a non-Jewish slave, the slave
will be freed and the Jew shall face capital punishment; any Christian
slaves owned by a Jew will be taken away and freed;
-
A person who is proven to have converted from
Christianity to Judaism shall have their property confiscated by the state.
Reputation
Constantius II is a particularly difficult figure to judge
properly, mainly as a result of the hostility of most every source that mentions
him.
A.H.M Jones writes that Constantius “appears in the pages of
Ammianus
as a conscientious emperor but a vain and stupid man, an easy prey
to flatterers. He was timid and suspicious, and interested persons could easily
play on his fears for their own advantage.”
However, Kent & M. and A. Hirmer suggest that Constantius
“has suffered at the hands of unsympathetic authors, ecclesiastical and civil
alike. To orthodox churchmen he was a bigoted supporter of the Arian heresy, to
Julian the Apostate and the many who have subsequently taken his part he was a
murderer, a tyrant and inept as a ruler”.
They go on to add, “Most contemporaries seem in fact to have held him in high
esteem, and he certainly inspired loyalty in a way his brother could not”.
|













