|
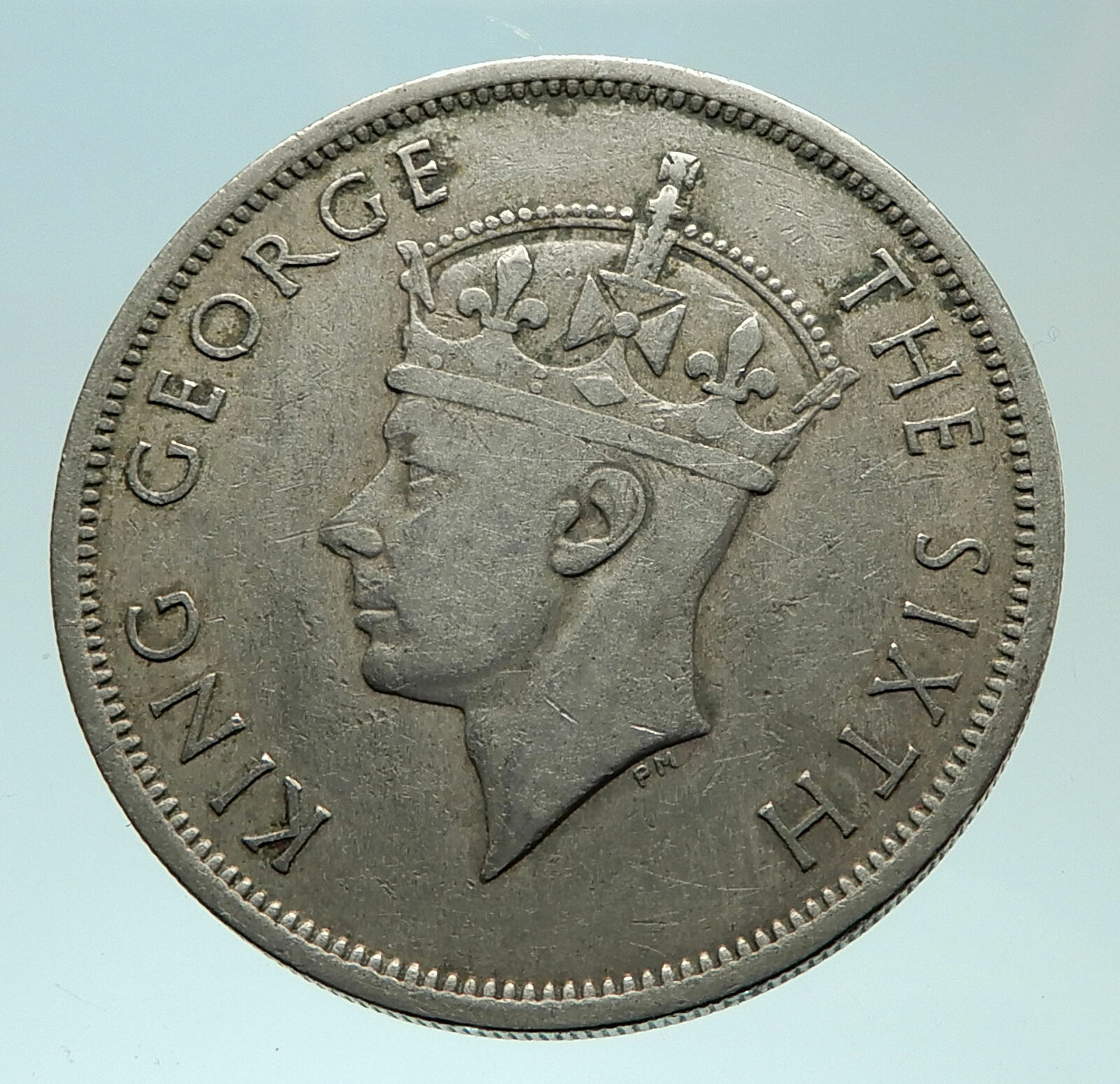
Southern Rhodesia – George V – King: 6 May 1910 – 20 January 1936
1934 Silver Half Crown 32.3mm (14.17 grams) 0.925 Silver (0.4205 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 5, Schön# 7 | Engravers: Percy Metcalfe, George Kruger Gray
GEORGE V KING EMPEROR, Crowned head of King George V facing left.
SOUTHERN·19 34·RHODESIA Gv R·I K G +HALF CROWN+, Crowned Shield with pick.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936. He was the second son of Albert Edward, Prince of Wales (later King Edward VII), and the grandson of the reigning British monarch, Queen Victoria. From the time of his birth, he was third in the line of succession behind his father and his elder brother, Prince Albert Victor, Duke of Clarence and Avondale. From 1877 to 1891, George served in the Royal Navy, until the unexpected death of his elder brother in early 1892 put him directly in line for the throne. On the death of his grandmother in 1901, George’s father became King-Emperor of the British Empire, and George was created Prince of Wales. He succeeded his father in 1910. He was the only Emperor of India to be present at his own Delhi Durbar. His reign saw the rise of socialism, communism, fascism, Irish republicanism, and the Indian independence movement, all of which radically changed the political landscape. The Parliament Act 1911 established the supremacy of the elected British House of Commons over the unelected House of Lords. As a result of the First World War (1914-18) the empires of his first cousins Tsar Nicholas II of Russia and Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany fell while the British Empire expanded to its greatest effective extent. In 1917, George became the first monarch of the House of Windsor, which he renamed from the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha as a result of anti-German public sentiment. In 1924 he appointed the first Labour ministry and in 1931 the Statute of Westminster recognised the dominions of the Empire as separate, independent states within the Commonwealth of Nations. He was plagued by illness throughout much of his later reign and at his death was succeeded by his eldest son, Edward VIII. George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936. He was the second son of Albert Edward, Prince of Wales (later King Edward VII), and the grandson of the reigning British monarch, Queen Victoria. From the time of his birth, he was third in the line of succession behind his father and his elder brother, Prince Albert Victor, Duke of Clarence and Avondale. From 1877 to 1891, George served in the Royal Navy, until the unexpected death of his elder brother in early 1892 put him directly in line for the throne. On the death of his grandmother in 1901, George’s father became King-Emperor of the British Empire, and George was created Prince of Wales. He succeeded his father in 1910. He was the only Emperor of India to be present at his own Delhi Durbar. His reign saw the rise of socialism, communism, fascism, Irish republicanism, and the Indian independence movement, all of which radically changed the political landscape. The Parliament Act 1911 established the supremacy of the elected British House of Commons over the unelected House of Lords. As a result of the First World War (1914-18) the empires of his first cousins Tsar Nicholas II of Russia and Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany fell while the British Empire expanded to its greatest effective extent. In 1917, George became the first monarch of the House of Windsor, which he renamed from the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha as a result of anti-German public sentiment. In 1924 he appointed the first Labour ministry and in 1931 the Statute of Westminster recognised the dominions of the Empire as separate, independent states within the Commonwealth of Nations. He was plagued by illness throughout much of his later reign and at his death was succeeded by his eldest son, Edward VIII.
.svg/125px-Flag_of_Rhodesia_(1964-1968).svg.png) The Colony of Southern Rhodesia was a self-governing British Crown colony in southern Africa. It was the predecessor state of what is now Zimbabwe. The Colony of Southern Rhodesia was a self-governing British Crown colony in southern Africa. It was the predecessor state of what is now Zimbabwe.
The colony was established in 1923, having earlier been administered by the British South Africa Company. In 1953, it was merged into the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland, which lasted until 1963. Southern Rhodesia then remained a de jure British colony until 1980. However, the white-minority government issued a Unilateral Declaration of Independence (UDI) in 1965 and established Rhodesia, an unrecognised state. In 1979, it reconstituted itself under indigenous African rule as Zimbabwe Rhodesia, which also failed to win overseas recognition. After a period of interim British control following the Lancaster House Agreement in December 1979, the country achieved internationally recognised independence as Zimbabwe in April 1980.
 Initially, the territory was referred to as “South Zambezia”, a reference to the River Zambezi, until the name “Rhodesia” came into use in 1895. This was in honour of Cecil Rhodes, the British empire-builder and key figure during the British expansion into southern Africa. In 1888 Rhodes obtained mineral rights from the most powerful local traditional leaders through treaties such as the Rudd Concession and the Moffat Treaty, which was signed by King Lobengula of the Ndebele people. “Southern” was first used in 1898 and dropped from normal usage in 1964, on the break-up of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland. “Rhodesia” then remained the name of the country until the creation of Zimbabwe Rhodesia in 1979. Legally, from the British perspective, the name Southern Rhodesia continued to be used until 18 April 1980, when the Republic of Zimbabwe was promulgated. Initially, the territory was referred to as “South Zambezia”, a reference to the River Zambezi, until the name “Rhodesia” came into use in 1895. This was in honour of Cecil Rhodes, the British empire-builder and key figure during the British expansion into southern Africa. In 1888 Rhodes obtained mineral rights from the most powerful local traditional leaders through treaties such as the Rudd Concession and the Moffat Treaty, which was signed by King Lobengula of the Ndebele people. “Southern” was first used in 1898 and dropped from normal usage in 1964, on the break-up of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland. “Rhodesia” then remained the name of the country until the creation of Zimbabwe Rhodesia in 1979. Legally, from the British perspective, the name Southern Rhodesia continued to be used until 18 April 1980, when the Republic of Zimbabwe was promulgated.
 The British government agreed that Rhodes’ company, the British South Africa Company (BSAC), would administer the territory stretching from the Limpopo to Lake Tanganyika under charter as a protectorate. Queen Victoria signed the charter in 1889. Rhodes used this document in 1890 to justify sending the Pioneer Column, a group of white settlers protected by well-armed British South Africa Police (BSAP) and guided by the big game hunter Frederick Selous, through Matabeleland and into Shona territory to establish Fort Salisbury (now Harare). In 1893-1894, with the help of their new Maxim guns, the BSAP defeated the Ndebele in the First Matabele War, a war which also resulted in the death of King Lobengula and the death of most of the members of the Shangani Patrol. Shortly after the disastrous BSAP Jameson Raid into the Transvaal Republic, the Ndebele were led by their spiritual leader Mlimo against the white colonials and thus began the Second Matabele War (1896-97) which resulted in the extermination of nearly half the British settlers. After months of bloodshed, Mlimo was found and shot by the American scout Frederick Russell Burnham and soon thereafter Rhodes walked unarmed into the Ndebele stronghold in Matobo Hills and persuaded the impi to lay down their arms, effectively ending the revolt. The British government agreed that Rhodes’ company, the British South Africa Company (BSAC), would administer the territory stretching from the Limpopo to Lake Tanganyika under charter as a protectorate. Queen Victoria signed the charter in 1889. Rhodes used this document in 1890 to justify sending the Pioneer Column, a group of white settlers protected by well-armed British South Africa Police (BSAP) and guided by the big game hunter Frederick Selous, through Matabeleland and into Shona territory to establish Fort Salisbury (now Harare). In 1893-1894, with the help of their new Maxim guns, the BSAP defeated the Ndebele in the First Matabele War, a war which also resulted in the death of King Lobengula and the death of most of the members of the Shangani Patrol. Shortly after the disastrous BSAP Jameson Raid into the Transvaal Republic, the Ndebele were led by their spiritual leader Mlimo against the white colonials and thus began the Second Matabele War (1896-97) which resulted in the extermination of nearly half the British settlers. After months of bloodshed, Mlimo was found and shot by the American scout Frederick Russell Burnham and soon thereafter Rhodes walked unarmed into the Ndebele stronghold in Matobo Hills and persuaded the impi to lay down their arms, effectively ending the revolt.
A Legislative Council was created in 1899 to manage the company’s civil affairs, with a minority of elected seats, through which the BSAC had to pass government measures. As the Company was a British institution in which settlers and capitalists owned most shares, and local Black African tribal chiefs the remainder, and the electorate to this council was limited to those shareholders, the electorate was almost exclusively white settlers. Over time as more settlers arrived and a growing number had less than the amount of land required to own a share in the company or where in trades supporting the company as workers, successive activism resulted in first increasing the proportion of elected seats, and eventually allowing non-share holders the right to vote in the election. Prior to about 1918, the opinion among the electorate supported continued BSAC rule but opinion changed because of the development of the country and increased settlement. In addition, a decision in the British courts that land not in private ownership belonged to the British Crown rather than the BSAC gave great impetus to the campaign for self-government. In the resulting treaty government self-government, Crown lands which were sold to settlers allowed those settlers the right to vote in the self-governing colony.
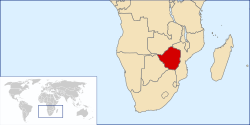
Rhodesia was a country in southern Africa from 1965 to 1979, equivalent in territory to modern Zimbabwe. Rhodesia was the de facto successor state to the British colony of Southern Rhodesia, which had been self-governing since achieving responsible government in 1923. A landlocked nation, Rhodesia was bordered by South Africa to the south, Bechuanaland (later Botswana) to the southwest, Zambia to the northwest, and Mozambique (a Portuguese province until 1975) to the east.
 In the late 19th century, the territory north of the Transvaal was chartered to the British South Africa Company, led by Cecil Rhodes. Rhodes and his Pioneer Column marched north in 1890, acquiring a huge bloc of territory that the Company would rule until the early 1920s. In 1923, the Company’s charter was revoked, and Southern Rhodesia attained self-government and established a legislature. Between 1953 and 1963, Southern Rhodesia was joined with Northern Rhodesia and Nyasaland in the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland. In the late 19th century, the territory north of the Transvaal was chartered to the British South Africa Company, led by Cecil Rhodes. Rhodes and his Pioneer Column marched north in 1890, acquiring a huge bloc of territory that the Company would rule until the early 1920s. In 1923, the Company’s charter was revoked, and Southern Rhodesia attained self-government and established a legislature. Between 1953 and 1963, Southern Rhodesia was joined with Northern Rhodesia and Nyasaland in the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland.
.svg/250px-Zimbabwe_(orthographic_projection).svg.png) The decolonisation of Africa in the early 1960s alarmed a significant proportion of Rhodesia’s white population. In an effort to delay the transition to black majority rule, Rhodesia’s predominantly white government issued its own Unilateral Declaration of Independence (UDI) from the United Kingdom on 11 November 1965. (The government of the United Kingdom supported Rhodesia’s transition to a multi-racial democracy.) The UDI administration initially sought recognition as an autonomous realm within the Commonwealth of Nations, but reconstituted itself as a republic in 1970. The Rhodesian Bush War, which pitted the government against two African nationalist organisations, ZANU and ZAPU, intensified in the 1970s, prompting Rhodesian premier Ian Smith to concede to multiracial democracy in 1978. However, a provisional government subsequently headed by Smith and his moderate colleague Abel Muzorewa failed in appeasing international critics or halting the bloodshed. By December 1979, Muzorewa had replaced Smith as Prime Minister and secured an agreement with the militant nationalists, allowing Rhodesia to briefly revert to colonial status pending elections under a universal franchise. It finally achieved internationally recognised independence in April 1980 as the Republic of Zimbabwe. The decolonisation of Africa in the early 1960s alarmed a significant proportion of Rhodesia’s white population. In an effort to delay the transition to black majority rule, Rhodesia’s predominantly white government issued its own Unilateral Declaration of Independence (UDI) from the United Kingdom on 11 November 1965. (The government of the United Kingdom supported Rhodesia’s transition to a multi-racial democracy.) The UDI administration initially sought recognition as an autonomous realm within the Commonwealth of Nations, but reconstituted itself as a republic in 1970. The Rhodesian Bush War, which pitted the government against two African nationalist organisations, ZANU and ZAPU, intensified in the 1970s, prompting Rhodesian premier Ian Smith to concede to multiracial democracy in 1978. However, a provisional government subsequently headed by Smith and his moderate colleague Abel Muzorewa failed in appeasing international critics or halting the bloodshed. By December 1979, Muzorewa had replaced Smith as Prime Minister and secured an agreement with the militant nationalists, allowing Rhodesia to briefly revert to colonial status pending elections under a universal franchise. It finally achieved internationally recognised independence in April 1980 as the Republic of Zimbabwe.
Rhodesia’s largest cities were its capital, Salisbury, and Bulawayo. The white population, which grew to nearly 300,000, dominated the country’s politics and economy, though they never made up more than eight percent of the total population. Rhodesia developed an economy largely dependent on agriculture, manufacturing, and mining. Its largest exports were chrome, tobacco, and steel. International sanctions put increasing pressure on the country as time went on. The Parliament of Rhodesia, which included the lower House of Assembly and later a senate, was predominantly white, with minority of seats reserved for blacks. After 1970, the country used a semi-presidential system, with a president, prime minister, and cabinet.
|




 George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936. He was the second son of Albert Edward, Prince of Wales (later King Edward VII), and the grandson of the reigning British monarch, Queen Victoria. From the time of his birth, he was third in the line of succession behind his father and his elder brother, Prince Albert Victor, Duke of Clarence and Avondale. From 1877 to 1891, George served in the Royal Navy, until the unexpected death of his elder brother in early 1892 put him directly in line for the throne. On the death of his grandmother in 1901, George’s father became King-Emperor of the British Empire, and George was created Prince of Wales. He succeeded his father in 1910. He was the only Emperor of India to be present at his own Delhi Durbar. His reign saw the rise of socialism, communism, fascism, Irish republicanism, and the Indian independence movement, all of which radically changed the political landscape. The Parliament Act 1911 established the supremacy of the elected British House of Commons over the unelected House of Lords. As a result of the First World War (1914-18) the empires of his first cousins Tsar Nicholas II of Russia and Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany fell while the British Empire expanded to its greatest effective extent. In 1917, George became the first monarch of the House of Windsor, which he renamed from the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha as a result of anti-German public sentiment. In 1924 he appointed the first Labour ministry and in 1931 the Statute of Westminster recognised the dominions of the Empire as separate, independent states within the Commonwealth of Nations. He was plagued by illness throughout much of his later reign and at his death was succeeded by his eldest son, Edward VIII.
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936. He was the second son of Albert Edward, Prince of Wales (later King Edward VII), and the grandson of the reigning British monarch, Queen Victoria. From the time of his birth, he was third in the line of succession behind his father and his elder brother, Prince Albert Victor, Duke of Clarence and Avondale. From 1877 to 1891, George served in the Royal Navy, until the unexpected death of his elder brother in early 1892 put him directly in line for the throne. On the death of his grandmother in 1901, George’s father became King-Emperor of the British Empire, and George was created Prince of Wales. He succeeded his father in 1910. He was the only Emperor of India to be present at his own Delhi Durbar. His reign saw the rise of socialism, communism, fascism, Irish republicanism, and the Indian independence movement, all of which radically changed the political landscape. The Parliament Act 1911 established the supremacy of the elected British House of Commons over the unelected House of Lords. As a result of the First World War (1914-18) the empires of his first cousins Tsar Nicholas II of Russia and Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany fell while the British Empire expanded to its greatest effective extent. In 1917, George became the first monarch of the House of Windsor, which he renamed from the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha as a result of anti-German public sentiment. In 1924 he appointed the first Labour ministry and in 1931 the Statute of Westminster recognised the dominions of the Empire as separate, independent states within the Commonwealth of Nations. He was plagued by illness throughout much of his later reign and at his death was succeeded by his eldest son, Edward VIII. .svg/125px-Flag_of_Rhodesia_(1964-1968).svg.png) The Colony of Southern Rhodesia was a self-governing British Crown colony in southern Africa. It was the predecessor state of what is now Zimbabwe.
The Colony of Southern Rhodesia was a self-governing British Crown colony in southern Africa. It was the predecessor state of what is now Zimbabwe.  Initially, the territory was referred to as “South Zambezia”, a reference to the River Zambezi, until the name “Rhodesia” came into use in 1895. This was in honour of Cecil Rhodes, the British empire-builder and key figure during the British expansion into southern Africa. In 1888 Rhodes obtained mineral rights from the most powerful local traditional leaders through treaties such as the Rudd Concession and the Moffat Treaty, which was signed by King Lobengula of the Ndebele people. “Southern” was first used in 1898 and dropped from normal usage in 1964, on the break-up of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland. “Rhodesia” then remained the name of the country until the creation of Zimbabwe Rhodesia in 1979. Legally, from the British perspective, the name Southern Rhodesia continued to be used until 18 April 1980, when the Republic of Zimbabwe was promulgated.
Initially, the territory was referred to as “South Zambezia”, a reference to the River Zambezi, until the name “Rhodesia” came into use in 1895. This was in honour of Cecil Rhodes, the British empire-builder and key figure during the British expansion into southern Africa. In 1888 Rhodes obtained mineral rights from the most powerful local traditional leaders through treaties such as the Rudd Concession and the Moffat Treaty, which was signed by King Lobengula of the Ndebele people. “Southern” was first used in 1898 and dropped from normal usage in 1964, on the break-up of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland. “Rhodesia” then remained the name of the country until the creation of Zimbabwe Rhodesia in 1979. Legally, from the British perspective, the name Southern Rhodesia continued to be used until 18 April 1980, when the Republic of Zimbabwe was promulgated.  The British government agreed that Rhodes’ company, the British South Africa Company (BSAC), would administer the territory stretching from the Limpopo to Lake Tanganyika under charter as a protectorate. Queen Victoria signed the charter in 1889. Rhodes used this document in 1890 to justify sending the Pioneer Column, a group of white settlers protected by well-armed British South Africa Police (BSAP) and guided by the big game hunter Frederick Selous, through Matabeleland and into Shona territory to establish Fort Salisbury (now Harare). In 1893-1894, with the help of their new Maxim guns, the BSAP defeated the Ndebele in the First Matabele War, a war which also resulted in the death of King Lobengula and the death of most of the members of the Shangani Patrol. Shortly after the disastrous BSAP Jameson Raid into the Transvaal Republic, the Ndebele were led by their spiritual leader Mlimo against the white colonials and thus began the Second Matabele War (1896-97) which resulted in the extermination of nearly half the British settlers. After months of bloodshed, Mlimo was found and shot by the American scout Frederick Russell Burnham and soon thereafter Rhodes walked unarmed into the Ndebele stronghold in Matobo Hills and persuaded the impi to lay down their arms, effectively ending the revolt.
The British government agreed that Rhodes’ company, the British South Africa Company (BSAC), would administer the territory stretching from the Limpopo to Lake Tanganyika under charter as a protectorate. Queen Victoria signed the charter in 1889. Rhodes used this document in 1890 to justify sending the Pioneer Column, a group of white settlers protected by well-armed British South Africa Police (BSAP) and guided by the big game hunter Frederick Selous, through Matabeleland and into Shona territory to establish Fort Salisbury (now Harare). In 1893-1894, with the help of their new Maxim guns, the BSAP defeated the Ndebele in the First Matabele War, a war which also resulted in the death of King Lobengula and the death of most of the members of the Shangani Patrol. Shortly after the disastrous BSAP Jameson Raid into the Transvaal Republic, the Ndebele were led by their spiritual leader Mlimo against the white colonials and thus began the Second Matabele War (1896-97) which resulted in the extermination of nearly half the British settlers. After months of bloodshed, Mlimo was found and shot by the American scout Frederick Russell Burnham and soon thereafter Rhodes walked unarmed into the Ndebele stronghold in Matobo Hills and persuaded the impi to lay down their arms, effectively ending the revolt.  In the late 19th century, the territory north of the Transvaal was chartered to the British South Africa Company, led by Cecil Rhodes. Rhodes and his Pioneer Column marched north in 1890, acquiring a huge bloc of territory that the Company would rule until the early 1920s. In 1923, the Company’s charter was revoked, and Southern Rhodesia attained self-government and established a legislature. Between 1953 and 1963, Southern Rhodesia was joined with Northern Rhodesia and Nyasaland in the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland.
In the late 19th century, the territory north of the Transvaal was chartered to the British South Africa Company, led by Cecil Rhodes. Rhodes and his Pioneer Column marched north in 1890, acquiring a huge bloc of territory that the Company would rule until the early 1920s. In 1923, the Company’s charter was revoked, and Southern Rhodesia attained self-government and established a legislature. Between 1953 and 1963, Southern Rhodesia was joined with Northern Rhodesia and Nyasaland in the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland. .svg/250px-Zimbabwe_(orthographic_projection).svg.png) The decolonisation of Africa in the early 1960s alarmed a significant proportion of Rhodesia’s white population. In an effort to delay the transition to black majority rule, Rhodesia’s predominantly white government issued its own Unilateral Declaration of Independence (UDI) from the United Kingdom on 11 November 1965. (The government of the United Kingdom supported Rhodesia’s transition to a multi-racial democracy.) The UDI administration initially sought recognition as an autonomous realm within the Commonwealth of Nations, but reconstituted itself as a republic in 1970. The Rhodesian Bush War, which pitted the government against two African nationalist organisations, ZANU and ZAPU, intensified in the 1970s, prompting Rhodesian premier Ian Smith to concede to multiracial democracy in 1978. However, a provisional government subsequently headed by Smith and his moderate colleague Abel Muzorewa failed in appeasing international critics or halting the bloodshed. By December 1979, Muzorewa had replaced Smith as Prime Minister and secured an agreement with the militant nationalists, allowing Rhodesia to briefly revert to colonial status pending elections under a universal franchise. It finally achieved internationally recognised independence in April 1980 as the Republic of Zimbabwe.
The decolonisation of Africa in the early 1960s alarmed a significant proportion of Rhodesia’s white population. In an effort to delay the transition to black majority rule, Rhodesia’s predominantly white government issued its own Unilateral Declaration of Independence (UDI) from the United Kingdom on 11 November 1965. (The government of the United Kingdom supported Rhodesia’s transition to a multi-racial democracy.) The UDI administration initially sought recognition as an autonomous realm within the Commonwealth of Nations, but reconstituted itself as a republic in 1970. The Rhodesian Bush War, which pitted the government against two African nationalist organisations, ZANU and ZAPU, intensified in the 1970s, prompting Rhodesian premier Ian Smith to concede to multiracial democracy in 1978. However, a provisional government subsequently headed by Smith and his moderate colleague Abel Muzorewa failed in appeasing international critics or halting the bloodshed. By December 1979, Muzorewa had replaced Smith as Prime Minister and secured an agreement with the militant nationalists, allowing Rhodesia to briefly revert to colonial status pending elections under a universal franchise. It finally achieved internationally recognised independence in April 1980 as the Republic of Zimbabwe. 




