|
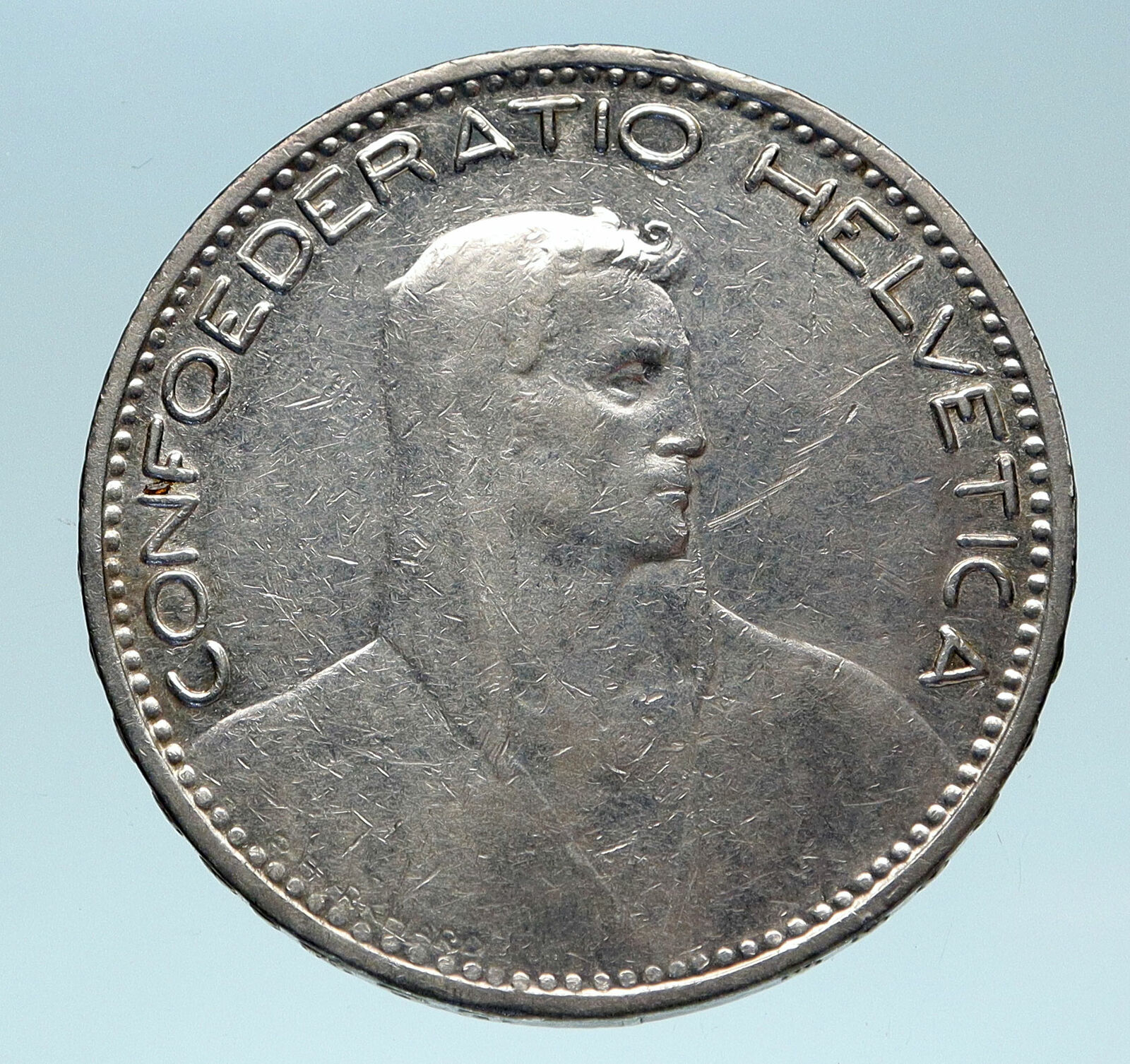
Switzerland
1966 B Silver 5 Francs Coin 31mm (15.06 grams) 0.835 Silver (0.4001 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM #40 (1931*-1969) | Designer: Paul Burkhard | Mint: Bern
CONFEDERATIO HELVETICA, Veiled draped bust of William Tell right.
Coat of arms of Switzerland flanked by sprigs; 5 FR above; year above B below.
Edge lettering: DOMINVS PROVIDEBIT (three stars) (ten stars)
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
William Tell (in the four languages of Switzerland: German: Wilhelm Tell; French: Guillaume Tell; Italian: Guglielmo Tell; Romansh: Guglielm Tell) is a folk hero of Switzerland. His legend is recorded in a late 15th-century Swiss illustrated chronicles.
It is set in the time of the original foundation of the Old Swiss Confederacy in the early 14th century. According to the legend, Tell-an expert marksman with the crossbow-assassinated Gessler, a tyrannical reeve of Habsburg Austria positioned in Altdorf, Uri.
Along with Arnold von Winkelried, Tell is a central figure in Swiss patriotism as it was constructed during the Restoration of the Confederacy after the Napoleonic era.
Legend
 Tell’s leap (Tellensprung) from the boat of his captors at the Axen cliffs 46.9326°N 8.6118°E. Study by Ernst Stückelberg (1879) for his fresco at the Tellskapelle. Tell’s leap (Tellensprung) from the boat of his captors at the Axen cliffs 46.9326°N 8.6118°E. Study by Ernst Stückelberg (1879) for his fresco at the Tellskapelle.
There are several accounts of the Tell legend. The earliest sources give an account of the apple-shot, Tell’s escape and the ensuing rebellion. The assassination of Gessler is not mentioned in the Tellenlied, but is already present in the White Book of Sarnen account.
The legend as told by Tschudi (ca. 1570) goes as follows: William Tell, who originally came from Bürglen, was known as a strong man, mountain climber, and an expert shot with the crossbow. In his time, the Habsburg emperors of Austria were seeking to dominate Uri. Albrecht (or Hermann) Gessler, the newly appointed Austrian Vogt of Altdorf, raised a pole in the village’s central square, hung his hat on top of it, and demanded that all the townsfolk bow before the hat.
On 18 November 1307, Tell visited Altdorf with his young son and passed by the hat, publicly refusing to bow to it, and so was arrested. Gessler-intrigued by Tell’s famed marksmanship, yet resentful of his defiance-devised a cruel punishment: Tell and his son would be executed, but he could redeem his life by shooting an apple off the head of his son, Walter, in a single attempt. Tell split the apple with a bolt from his crossbow.
But Gessler noticed that Tell had removed two crossbow bolts from his quiver, not one. Before releasing Tell, he asked why. Tell replied that if he had killed his son, he would have used the second bolt on Gessler himself. Gessler was angered, and had Tell bound.
Tell was brought to Gessler’s ship to be taken to his castle at Küssnacht to spend his newly won life in a dungeon. But, as a storm broke on Lake Lucerne, the soldiers were afraid that their boat would founder, and unbound Tell to steer with all his famed strength. Tell made use of the opportunity to escape, leaping from the boat at the rocky site now known as the Tellsplatte (“Tell’s slab”) and memorialized by the Tellskapelle.
Tell ran cross-country to Küssnacht. As Gessler arrived, Tell assassinated him with the second crossbow bolt along a stretch of the road cut through the rock between Immensee and Küssnacht, now known as the Hohle Gasse. Tell’s blow for liberty sparked a rebellion, in which he played a leading part. That fed the impetus for the nascent Swiss Confederation.
Tell fought again against Austria in the 1315 Battle of Morgarten. Tschudi also has an account of Tell’s death in 1354, according to which he was killed trying to save a child from drowning in the Schächenbach river in Uri.
.svg/85px-Coat_of_Arms_of_Switzerland_(Pantone).svg.png)  Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation (Latin: Confoederatio Helvetica, hence its abbreviation CH), is a federal parliamentary republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities, the so-called Bundesstadt (“federal city”). The country is situated in Western and Central Europe, where it is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland is a landlocked country geographically divided between the Alps, the Swiss Plateau and the Jura, spanning an area of 41,285 km2 (15,940 sq mi). While the Alps occupy the greater part of the territory, the Swiss population of approximately 8 million people is concentrated mostly on the Plateau, where the largest cities are to be found. Among them are the two global cities and economic centres of Zürich and Geneva. Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation (Latin: Confoederatio Helvetica, hence its abbreviation CH), is a federal parliamentary republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities, the so-called Bundesstadt (“federal city”). The country is situated in Western and Central Europe, where it is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland is a landlocked country geographically divided between the Alps, the Swiss Plateau and the Jura, spanning an area of 41,285 km2 (15,940 sq mi). While the Alps occupy the greater part of the territory, the Swiss population of approximately 8 million people is concentrated mostly on the Plateau, where the largest cities are to be found. Among them are the two global cities and economic centres of Zürich and Geneva.
The establishment of the Swiss Confederation is traditionally dated to 1 August 1291, which is celebrated annually as Swiss National Day. It has a long history of armed neutrality-it has not been in a state of war internationally since 1815-and did not join the United Nations until 2002. It pursues, however, an active foreign policy and is frequently involved in peace-building processes around the world. Switzerland is also the birthplace of the Red Cross and home to numerous international organizations, including the second largest UN office. On the European level, it is a founding member of the European Free Trade Association and is part of the Schengen Area – although it is notably not a member of the European Union, nor the European Economic Area. Switzerland comprises four main linguistic and cultural regions: German, French, Italian and the Romansh-speaking valleys. Therefore, the Swiss, although predominantly German-speaking, do not form a nation in the sense of a common ethnic or linguistic identity; rather, the strong sense of identity and community is founded on a common historical background, shared values such as federalism and direct democracy, and Alpine symbolism.
Switzerland has the highest nominal wealth per adult (financial and non-financial assets) in the world according to Credit Suisse and eighth-highest per capita gross domestic product on the IMF list. However, Switzerland is also the most expensive country in the world to live in, as measured by the price level index.
Swiss citizens have the second-highest life expectancy in the world on the UN DESA list. Switzerland is tied with the Netherlands for the top rank on the Bribe Payers Index indicating very low levels of business corruption. Moreover, for the last five years the country has been ranked first in economic and tourist competitiveness according to the Global Competitiveness Report and the Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report respectively, both developed by the World Economic Forum. Zürich and Geneva have each been ranked among the top cities with the highest quality of life in the world, with the former coming second globally according to Mercer. However, Mercer also rates those two cities as the fifth- and sixth- most expensive cities in the world to live in.
|




 Tell’s leap (Tellensprung) from the boat of his captors at the Axen cliffs 46.9326°N 8.6118°E. Study by Ernst Stückelberg (1879) for his fresco at the Tellskapelle.
Tell’s leap (Tellensprung) from the boat of his captors at the Axen cliffs 46.9326°N 8.6118°E. Study by Ernst Stückelberg (1879) for his fresco at the Tellskapelle. .svg/85px-Coat_of_Arms_of_Switzerland_(Pantone).svg.png)
 Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation (Latin: Confoederatio Helvetica, hence its abbreviation CH), is a federal parliamentary republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities, the so-called Bundesstadt (“federal city”). The country is situated in Western and Central Europe, where it is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland is a landlocked country geographically divided between the Alps, the Swiss Plateau and the Jura, spanning an area of 41,285 km2 (15,940 sq mi). While the Alps occupy the greater part of the territory, the Swiss population of approximately 8 million people is concentrated mostly on the Plateau, where the largest cities are to be found. Among them are the two global cities and economic centres of Zürich and Geneva.
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation (Latin: Confoederatio Helvetica, hence its abbreviation CH), is a federal parliamentary republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities, the so-called Bundesstadt (“federal city”). The country is situated in Western and Central Europe, where it is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland is a landlocked country geographically divided between the Alps, the Swiss Plateau and the Jura, spanning an area of 41,285 km2 (15,940 sq mi). While the Alps occupy the greater part of the territory, the Swiss population of approximately 8 million people is concentrated mostly on the Plateau, where the largest cities are to be found. Among them are the two global cities and economic centres of Zürich and Geneva.




