|
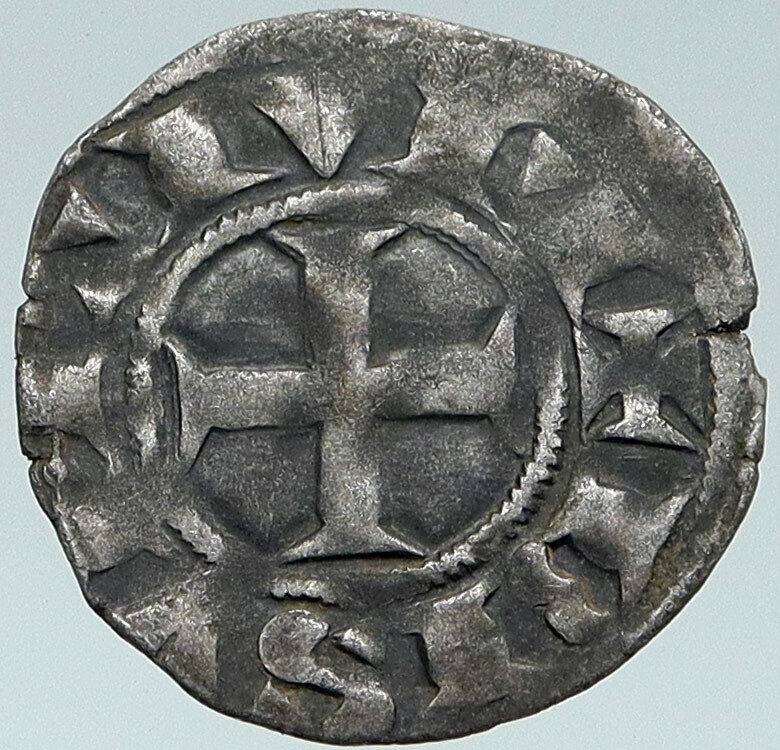
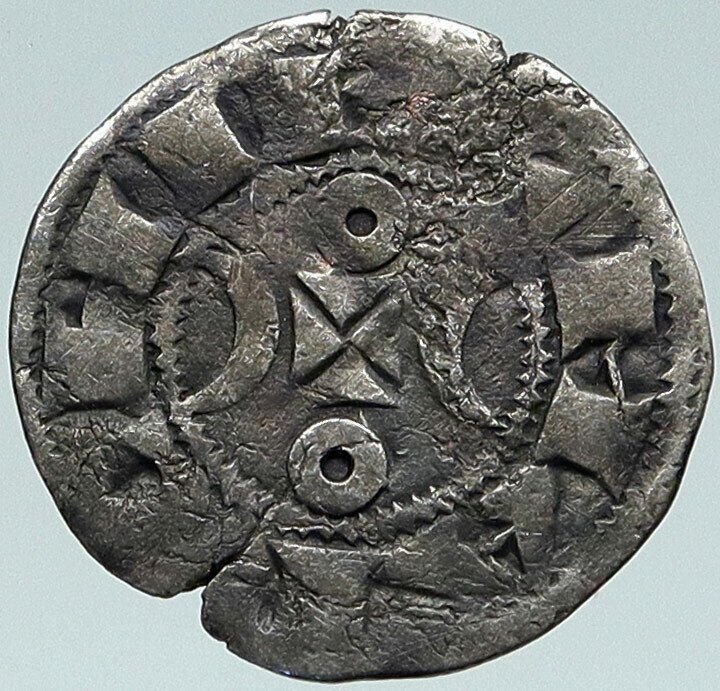
France – Fuedal – Archbishopric of Besançon
Silver Denier 18mm, (0.80 grams) Struck between 1200-1300 AD
Reference: Roberts# 4756
+ BISVNTIVM, Cross within beaded circle.
• PTHOMARTIR, Hand of benediction.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.


The Free Imperial City of Besançon was a self-governing city that was part of the Holy Roman Empire.
From 1184 until 1654 the City of Besançon was a free imperial city (Freie Reichsstadt) as shown by the coat of arms until today and called Bisanz. The city was first separated from the governance of the County of Burgundy in 1034 as a prince-bishopric, an ecclesiastical state in the Holy Roman Empire. The city was governed by the Prince-Archbishopric of Besançon, although later most of his power would devolve to a council within the town. The free imperial city enclosed only the city of Besançon in the Franche-Comté so for a large part of the time it was controlled those who controlled access across the surrounding land, first by the dukes of Burgundy, and then by the Habsburgs. Finally, it lost its imperial status but remained a free city.
Gaining independence
Besançon became part of the Holy Roman Empire in 1034, along with the rest of Franche-Comté.
In 1184, the city became the Archbishopric of Besançon, gaining autonomy as an imperial free city under the Holy Roman Emperor. The archbishop of Besançon was elevated to prince of the Holy Roman Empire in 1288. Previous bishops, such as St Hugh I, had been referred to as princes of the Empire. The close connection to the Empire is reflected in the city’s coat of arms.
In 1290, after a century of fighting against the power of the archbishops, the emperor recognised Besançon’s independence.
In August 1336, the duke of Burgundy tried to take Besançon after a dispute with the clergy of Franche-Comté. The duke sent 9,000 soldiers who set up camp at Saint-Ferjeux, near Planoise. The duke abandoned the siege after a few months.
The town fell into a number of disputes with its archbishop and sought the aid of a number of outside protectors, or captains, such as Philip the Good. In the fifteenth century, Besançon came under the influence of the dukes of Burgundy, although it never recognised their sovereignty.
Habsburg control
After the marriage of Mary of Burgundy to Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor in 1477, the city was in effect a Habsburg fief. In 1519, Charles V, King of Spain, became the Holy Roman Emperor. This made him master of Franche-Comté and Besançon, by then a francophone German city. Besançon treated the Habsburgs as their protectors in the same way they had previously treated the dukes of Burgundy.
In 1526, the city obtained the right to mint coins, which it continued to strike until 1673. Nevertheless, all coins bore the name of Charles V.
When Charles V abdicated in 1555, he gave Franche-Comté to his son, Philip II, King of Spain. Besançon remained a free imperial city under the protection of the king of Spain. In 1575, following the death of Charles IX of France, Huguenots attempted to capture Besançon in order to make it a stronghold, which meant that the city had to accept a Spanish garrison for protection – an important decline in its independent status.
In 1598, Philip II gave the province to his daughter on her marriage to an Austrian archduke. It remained formally a portion of the Empire until its cession from Austria to Spain, along with Franche-Comté, in the peace of Westphalia in 1648.<ref The city lost its status as a free city in 1651 as a reparation for other losses that the Spanish had suffered in the Thirty Years’ War. After some resistance this was finally confirmed by Besançon in 1654, although Besançon kept a high degree of internal autonomy.
Disputes with France
In 1667, Louis XIV claimed Franche-Comté as a consequence of his marriage to Maria Theresa of Spain. As part of the War of Devolution French troops arrived in the area in 1668. Besançon tried to argue that it was neutral in any hostilities as it was a Free Imperial City of the Holy Roman Empire, something that the French commander the Prince de Conde rejected as archaic. The French agreed to very generous surrender terms with the town authorities which included transferring the university from the then still recalcitrant Dole. There were also rumours that the regional Parlement may be transferred from Dole. The City also laid down that they would be left the relic of a fragment of the holy winding sheet and that Protestants should not have liberty of conscience in the same way as they then had in the rest of France.
While it was in French hands, the famed military engineer Vauban visited the city and drew up plans for its fortification. The Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle returned it to Spain within a matter of months in return for the town of Frankenthal.
The Spaniards built the main centre point of the city’s defences, “la Citadelle”, siting it on Mont St. Etienne, which closes the neck of the bend in the river that encloses the old city. In their construction, they followed Vauban’s designs.
From this time onwards a large pro-French faction grew among some of the town.
Surrender to the French
The City was to finally lose its autonomy as a result of the Franco-Dutch War starting in 1672, where the Habsburgs took the side of the Dutch and so were to lose control of Franche-Comté and Besançon. After a siege of the city, French troops occupied the city in 1674, although agreeing to allow Besançon to keep her privileges.
In 1676, the French authorities wound up the magistracy, the democratic form of government of Besançon. A baillarge court was set up in its stead. As part of the deal the city became the administrative centre for Franche-Comté, with the Parlement of Besançon administering the area, replacing the Parlement of Dole. French control was confirmed in 1678 by the Treaty of Nijmegen.
  France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories . The European part of France, called Metropolitan France , extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea , and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean . France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris , the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people. France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories . The European part of France, called Metropolitan France , extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea , and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean . France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris , the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people.
During the Iron Age , what is now Metropolitan France was inhabited by the Gauls , a Celtic people. The Gauls were conquered in 51 BC by the Roman Empire , which held Gaul until 486. The Gallo-Romans faced raids and migration from the Germanic Franks , who dominated the region for hundreds of years, eventually creating the medieval Kingdom of France . France emerged as a major European power in the Late Middle Ages , with its victory in the Hundred Years’ War (1337 to 1453) strengthening French state-building and paving the way for a future centralized absolute monarchy . During the Renaissance , France experienced a vast cultural development and established the beginning of a global colonial empire . The 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Protestants (Huguenots).
France became Europe’s dominant cultural, political, and military power under Louis XIV . French philosophers played a key role in the Age of Enlightenment during the 18th century . In 1778, France became the first and the main ally of the new United States in the American Revolutionary War . In the late 18th century, the absolute monarchy was overthrown in the French Revolution . Among its legacies was the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen , one of the earliest documents on human rights , which expresses the nation’s ideals to this day. France became one of modern history’s earliest republics until Napoleon took power and launched the First French Empire in 1804. Fighting against a complex set of coalitions during the Napoleonic Wars , he dominated European affairs for over a decade and had a long-lasting impact on Western culture. Following the collapse of the Empire, France endured a tumultuous succession of governments: the monarchy was restored , it was replaced in 1830 by a constitutional monarchy , then briefly by a Second Republic , and then by a Second Empire , until a more lasting French Third Republic was established in 1870. By the 1905 law , France adopted a strict form of secularism , called laïcité , which has become an important federative principle in the modern French society.
France reached its territorial height during the 19th and early 20th centuries, when it ultimately possessed the second-largest colonial empire in the world. In World War I , France was one of the main winners as part of the Triple Entente alliance fighting against the Central Powers . France was also one of the Allied Powers in World War II , but came under occupation by the Axis Powers in 1940. Following liberation in 1944, a Fourth Republic was established and later dissolved in the course of the Algerian War . The Fifth Republic , led by Charles de Gaulle , was formed in 1958 and remains to this day. Following World War II , most of the empire became decolonized .
Throughout its long history , France has been a leading global center of culture, making significant contributions to art , science , and philosophy . It hosts Europe’s third-largest number of cultural UNESCO World Heritage Sites (after Italy and Spain ) and receives around 83 million foreign tourists annually, the most of any country in the world. France remains a great power with significant cultural , economic , military , and political influence. It is a developed country with the world’s sixth-largest economy by nominal GDP and eight-largest by purchasing power parity . According to Credit Suisse, France is the fourth wealthiest nation in the world in terms of aggregate household wealth. It also possesses the world’s second-largest exclusive economic zone (EEZ), covering 11,035,000 square kilometres (4,261,000 sq mi).
French citizens enjoy a high standard of living , and the country performs well in international rankings of education , health care , life expectancy , civil liberties, and human development . France is a founding member of the United Nations , where it serves as one of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council . It is a member of the Group of 7 , North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the World Trade Organization (WTO), and La Francophonie . France is a founding and leading member state of the European Union (EU).
|







 France, officially the French Republic (French:
France, officially the French Republic (French: