|
Greek city of Amorion (Amorium) in Phrygia. Pseudo-autonomous issue
Bronze 20mm (3.15 grams) Struck circa 2nd Century A.D. (circa 100-200 A.D.)
Reference: BMC –; SNG von Aulock 3394
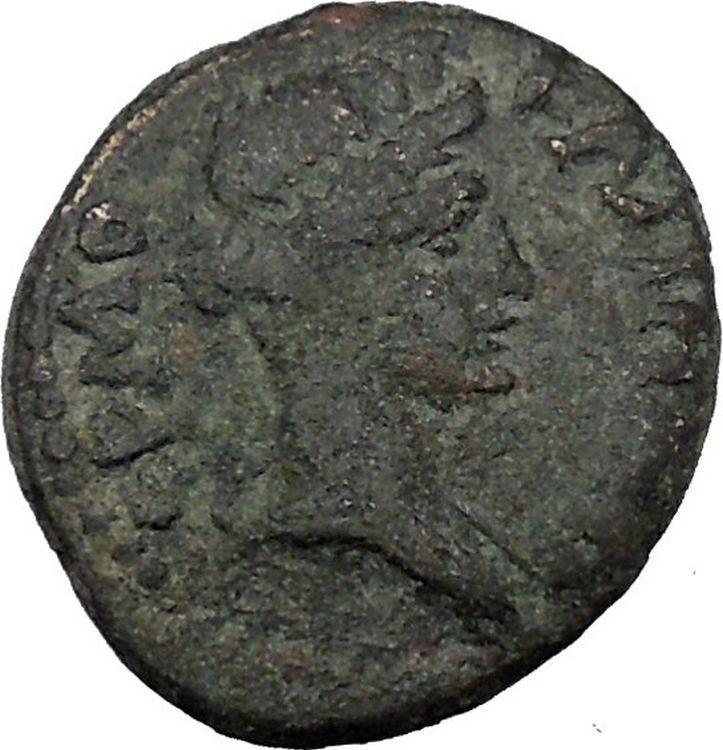
Draped bust of Serapis right, wearing calathus.
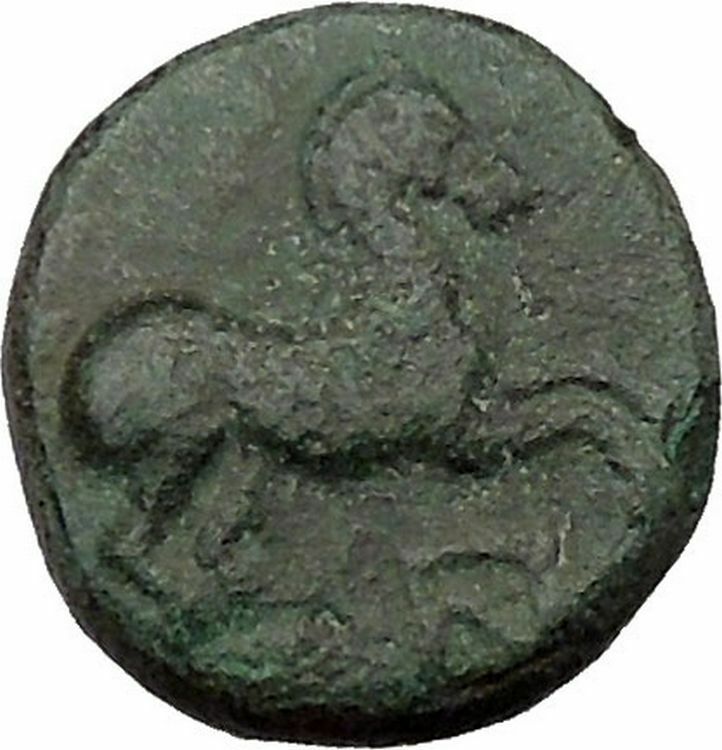
ΑΜΟΡΙΑΝΩΝ, Isis standing left, holding sistrum and situla.
Interesting Egyptian-themed issue.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity. .
 Isis or in original more likely Aset was a goddess in Ancient Egyptian religious beliefs, whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. She was worshiped as the ideal mother and wife as well as the matron of nature and magic. She was the friend of slaves, sinners, artisans, the downtrodden, as well as listening to the prayers of the wealthy, maidens, aristocrats and rulers. Isis is the Goddess of motherhood, magic and fertility. Isis or in original more likely Aset was a goddess in Ancient Egyptian religious beliefs, whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. She was worshiped as the ideal mother and wife as well as the matron of nature and magic. She was the friend of slaves, sinners, artisans, the downtrodden, as well as listening to the prayers of the wealthy, maidens, aristocrats and rulers. Isis is the Goddess of motherhood, magic and fertility.
The goddess Isis (the mother of Horus) was the first daughter of Geb, god of the Earth, and Nut, the goddess of the Overarching Sky, and was born on the fourth intercalary day. At some time Isis and Hathor had the same headdress. In later myths about Isis, she had a brother, Osiris, who became her husband, and she then was said to have conceived Horus. Isis was instrumental in the resurrection of Osiris when he was murdered by Set. Her magical skills restored his body to life after she gathered the body parts that had been strewn about the earth by Set. This myth became very important in later Egyptian religious beliefs.
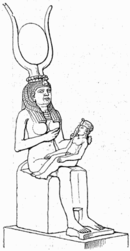
Isis nursing Horus, wearing the headdress of Hathor
Isis is also known as the goddess of simplicity, protector of the dead and goddess of children from whom all beginnings arose. In later myths, the Ancient Egyptians believed that the Nile River flooded every year because of her tears of sorrow for her dead husband, Osiris. This occurrence of his death and rebirth was relived each year through rituals. The worship of Isis eventually spread throughout the Greco-Roman world, continuing until the suppression of paganism in the Christian era.
 Serapis (Latin spelling, or Sarapis in Greek) was a syncretic Hellenistic-Egyptian god in Antiquity. His most renowned temple was the Serapeum of Alexandria. Under Ptolemy Soter, efforts were made to integrate Egyptian religion with that of their Hellenic rulers. Ptolemy’s policy was to find a deity that should win the reverence alike of both groups, despite the curses of the Egyptian priests against the gods of the previous foreign rulers (i.e Set who was lauded by the Hyksos). Alexander the Great had attempted to use Amun for this purpose, but he was more prominent in Upper Egypt, and not as popular with those in Lower Egypt, where the Greeks had stronger influence. The Greeks had little respect for animal-headed figures, and so a Greek-style anthromorphic statue was chosen as the idol, and proclaimed as the equivalent of the highly popular Apis. It was named Aser-hapi (i.e. Osiris-Apis), which became Serapis, and was said to be Osiris in full, rather than just his Ka (life force). Serapis (Latin spelling, or Sarapis in Greek) was a syncretic Hellenistic-Egyptian god in Antiquity. His most renowned temple was the Serapeum of Alexandria. Under Ptolemy Soter, efforts were made to integrate Egyptian religion with that of their Hellenic rulers. Ptolemy’s policy was to find a deity that should win the reverence alike of both groups, despite the curses of the Egyptian priests against the gods of the previous foreign rulers (i.e Set who was lauded by the Hyksos). Alexander the Great had attempted to use Amun for this purpose, but he was more prominent in Upper Egypt, and not as popular with those in Lower Egypt, where the Greeks had stronger influence. The Greeks had little respect for animal-headed figures, and so a Greek-style anthromorphic statue was chosen as the idol, and proclaimed as the equivalent of the highly popular Apis. It was named Aser-hapi (i.e. Osiris-Apis), which became Serapis, and was said to be Osiris in full, rather than just his Ka (life force).
History
The earliest mention of a Serapis is in the disputed death scene of Alexander (323 BC). Here, Serapis has a temple at Babylon, and is of such importance that he alone is named as being consulted on behalf of the dying king. His presence in Babylon would radically alter perceptions of the mythologies of this era, though fortunately it has been discovered that the unconnected Babylonian god Ea (Enki) was titled Serapsi, meaning king of the deep, and it is possibly this Serapsi which is referred to in the diaries. The significance of this Serapsi in the Hellenic psyche, due to its involvement in Alexander’s death, may have also contributed to the choice of Osiris-Apis as the chief Ptolemaic god.
According to Plutarch, Ptolemy stole the cult statue from Sinope, having been instructed in a dream by the unknown god, to bring the statue to Alexandria, where the statue was pronounced to be Serapis by two religious experts. One of the experts was of the Eumolpidae, the ancient family from whose members the hierophant of the Eleusinian Mysteries had been chosen since before history, and the other was the scholarly Egyptian priest Manetho, which gave weight to the judgement both for the Egyptians and the Greeks.
Plutarch may not however be correct, as some Egyptologists allege that the Sinope in the tale is really the hill of Sinopeion, a name given to the site of the already existing Serapeum at Memphis. Also, according to Tacitus, Serapis (i.e. Apis explicitly identified as Osiris in full) had been the god of the village of Rhakotis, before it suddenly expanded into the great capital of Alexandria.
The statue suitably depicted a figure resembling Hades or Pluto, both being kings of the Greek underworld, and was shown enthroned with the modius, a basket/grain-measure, on his head, since it was a Greek symbol for the land of the dead. He also held a sceptre in his hand indicating his rulership, with Cerberus, gatekeeper of the underworld, resting at his feet, and it also had what appeared to be a serpent at its base, fitting the Egyptian symbol of rulership, the uraeus.
With his (i.e. Osiris’) wife Isis, and their son (at this point in history) Horus (in the form of Harpocrates), Serapis won an important place in the Greek world, reaching Ancient Rome, with Anubis being identified as Cerberus. In Rome, Serapis was worshiped in the Iseum Campense, the sanctuary of the goddess Isis located in the Campus Martius and built during the Second Triumvirate. The Roman cults of Isis and Serapis gained in popularity late in the first century thanks to the god’s role in the miracles that the imperial usurper Vespasian experienced in the city of Alexandria, where he stayed prior to his return to Rome as emperor in 70 AD. From the Flavian Dynasty on, Serapis sometimes appeared on imperial coinage with the reigning emperor. The great cult survived until 385, when a Christian mob destroyed the Serapeum of Alexandria, and subsequently the cult was forbidden by the Theodosian decree.
The early Alexandrian Christian community appears to have been rather syncretic in their worship of Serapis and Jesus and would prostrate themselves without distinction between the two. A letter inserted in the Augustan History, ascribed to the Emperor Hadrian, refers to the worship of Serapis by residents of Egypt who described themselves as Christians, and Christian worship by those claiming to worship Serapis, suggesting a great confusion of the cults and practices:
The land of Egypt, the praises of which you have been recounting to me, my dear Servianus, I have found to be wholly light-minded, unstable, and blown about by every breath of rumour. There those who worship Serapis are, in fact, Christians, and those who call themselves bishops of Christ are, in fact, devotees of Serapis. There is no chief of the Jewish synagogue, no Samaritan, no Christian presbyter, who is not an astrologer, a soothsayer, or an anointer. Even the Patriarch himself, when he comes to Egypt, is forced by some to worship Serapis, by others to worship Christ.
Amorium was a city in Phrygia, Asia Minor which was founded in the Hellenistic period, flourished under the Byzantine Empire, and declined after the Arab sack of 838. It was situated on the Byzantine military road from Constantinople to Cilicia. Its ruins and höyük (‘mound, tumulus’) are located under and around the modern village of Hisarköy, 13 kilometers east of the district center, Emirdağ, Afyonkarahisar Province, Turkey. Amorium is the Latinized version of its original Greek name Amorion (Greek: Ἀμόριον). Arab/Islamic sources refer to the city as ʿAmmūriye. Under Ottoman rule the site, which never regained importance, was called Hergen Kale or Hergen Kaleh.
Antiquity
The city minted its own coins beginning between 133 BC to 27 BC until the 3rd century AD, indicating its maturity as a settlement and military importance during the pre-Byzantine period. Amorium then must have been prestigious and prosperous. But early historical records that mention the city are strictly limited to a reference by Strabo, although it is expected that new discoveries will shed light on the city’s Roman period and before.
Byzantine period
The city was fortified by the emperor Zeno in the 5th century, but did not rise to prominence until the 7th century. Its strategic location in central Asia Minor made the city a vital stronghold against the armies of the Umayyad Caliphate following the Muslim conquest of the Levant. The city was first attacked by Muawiyah I in 646. It capitulated to ‘Abd ar-Rahman ibn Khalid in 666 and was occupied by Yazid I in 669, then retaken by Constans II’s general Andreas. Over the next two centuries, it remained a frequent target of Muslim raids (razzias) into Asia Minor, especially during the great sieges of 716 and 796. It became capital of the thema of Anatolikon soon after. In 742-743, it was the main base of Emperor Constantine V against the usurper Artabasdos, and in 820, an Amorian, Michael II, ascended the Byzantine throne, establishing the Amorian dynasty. This began the period of the city’s greatest prosperity, when it became the largest city in Asia Minor. Its status however as the native city of the reigning dynasty also spelled its doom: in 838, the Caliph Al-Mu’tasim launched a campaign specifically against the city, which was captured and razed, an episode recounted in a poem of Abu Tammam.
The town was rebuilt, but was burned by Thamal al-Dulafi in 931. Nonetheless, it remained an active Byzantine city at least into the 11th century. Following the Battle of Manzikert, it was devastated by the Seljuks and a large proportion of its inhabitants were killed. Emperor Alexios I Komnenos defeated the Seljuks at Amorium in 1116, but the area was never recovered.
It remained an important place in the 12th-14th centuries according to al-Idrisi and Hamdallah Mustawfi.
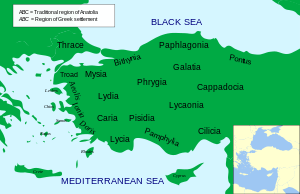 In antiquity, Phrygia was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Turkey, centered on the Sakarya River. In antiquity, Phrygia was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Turkey, centered on the Sakarya River.
During the heroic age of Greek mythology, several legendary kings were Phrygians: Gordias whose Gordian Knot would later be cut by Alexander the Great, Midas who turned whatever he touched to gold, and Mygdon who warred with the Amazons. According to Homer’s Iliad, the Phrygians were close allies of the Trojans and participants in the Trojan War against the Achaeans. Phrygian power reached its peak in the late 8th century BC under another, historical, king: Midas, who dominated most of western and central Anatolia and rivaled Assyria and Urartu for power in eastern Anatolia. This later Midas was, however, also the last independent king of Phrygia before its capital Gordium was sacked by Cimmerians around 695 BC. Phrygia then became subject to Lydia, and then successively to Persia, Alexander and his Hellenistic successors, Pergamon, Rome and Byzantium. Phrygians were gradually assimilated into other cultures by the early medieval era, and after the Turkish conquest of Anatolia the name Phrygia passed out of usage as a territorial designation.
|





 Isis or in original more likely Aset was a goddess in Ancient Egyptian religious beliefs, whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. She was worshiped as the ideal mother and wife as well as the matron of nature and magic. She was the friend of slaves, sinners, artisans, the downtrodden, as well as listening to the prayers of the wealthy, maidens, aristocrats and rulers. Isis is the Goddess of motherhood, magic and fertility.
Isis or in original more likely Aset was a goddess in Ancient Egyptian religious beliefs, whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. She was worshiped as the ideal mother and wife as well as the matron of nature and magic. She was the friend of slaves, sinners, artisans, the downtrodden, as well as listening to the prayers of the wealthy, maidens, aristocrats and rulers. Isis is the Goddess of motherhood, magic and fertility.
 Serapis (Latin spelling, or Sarapis in Greek) was a syncretic Hellenistic-Egyptian god in Antiquity. His most renowned temple was the Serapeum of Alexandria. Under Ptolemy Soter, efforts were made to integrate Egyptian religion with that of their Hellenic rulers. Ptolemy’s policy was to find a deity that should win the reverence alike of both groups, despite the curses of the Egyptian priests against the gods of the previous foreign rulers (i.e Set who was lauded by the Hyksos). Alexander the Great had attempted to use Amun for this purpose, but he was more prominent in Upper Egypt, and not as popular with those in Lower Egypt, where the Greeks had stronger influence. The Greeks had little respect for animal-headed figures, and so a Greek-style anthromorphic statue was chosen as the idol, and proclaimed as the equivalent of the highly popular Apis. It was named Aser-hapi (i.e. Osiris-Apis), which became Serapis, and was said to be Osiris in full, rather than just his Ka (life force).
Serapis (Latin spelling, or Sarapis in Greek) was a syncretic Hellenistic-Egyptian god in Antiquity. His most renowned temple was the Serapeum of Alexandria. Under Ptolemy Soter, efforts were made to integrate Egyptian religion with that of their Hellenic rulers. Ptolemy’s policy was to find a deity that should win the reverence alike of both groups, despite the curses of the Egyptian priests against the gods of the previous foreign rulers (i.e Set who was lauded by the Hyksos). Alexander the Great had attempted to use Amun for this purpose, but he was more prominent in Upper Egypt, and not as popular with those in Lower Egypt, where the Greeks had stronger influence. The Greeks had little respect for animal-headed figures, and so a Greek-style anthromorphic statue was chosen as the idol, and proclaimed as the equivalent of the highly popular Apis. It was named Aser-hapi (i.e. Osiris-Apis), which became Serapis, and was said to be Osiris in full, rather than just his Ka (life force).  In antiquity, Phrygia was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Turkey, centered on the Sakarya River.
In antiquity, Phrygia was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Turkey, centered on the Sakarya River.




