|
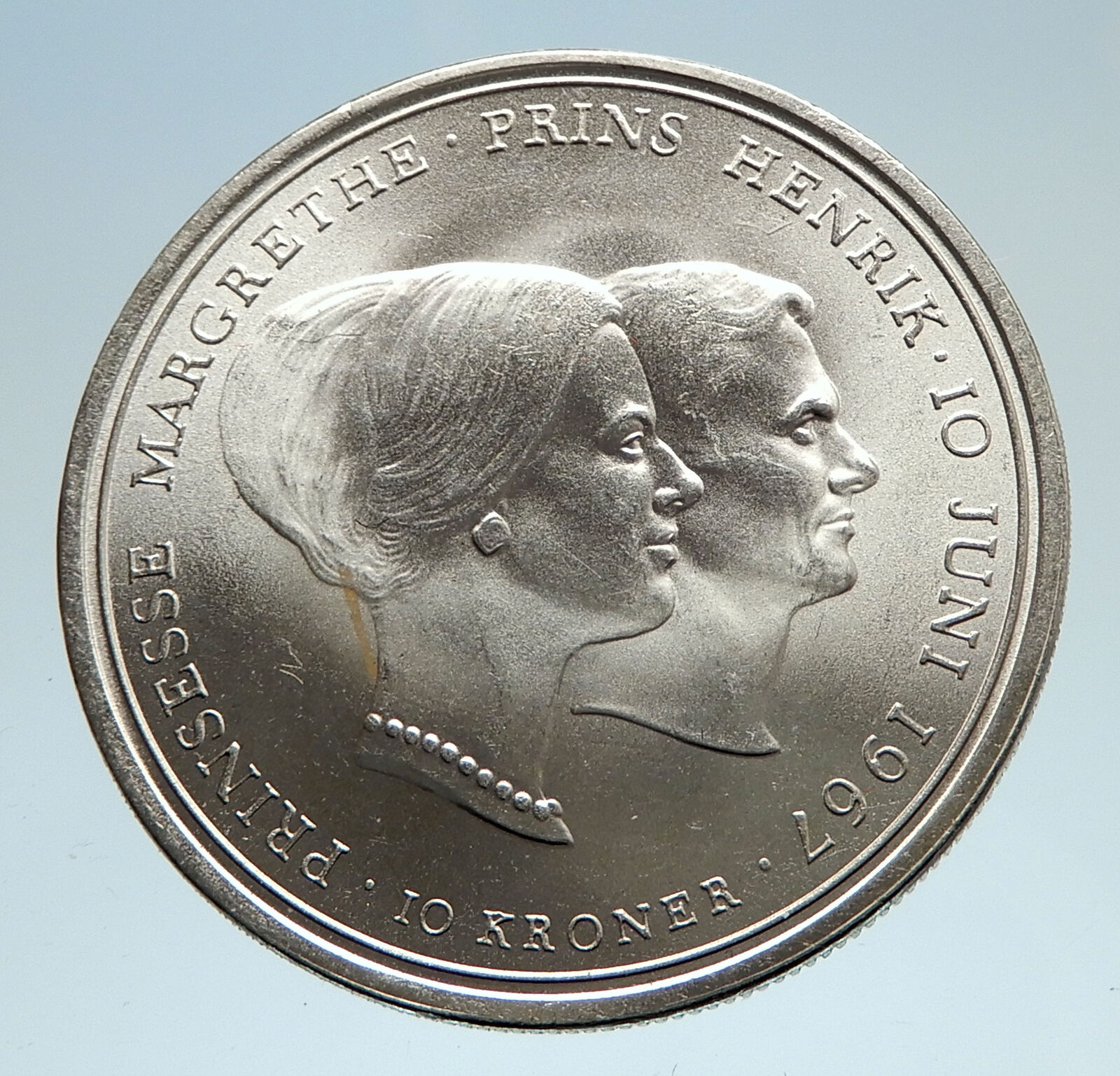
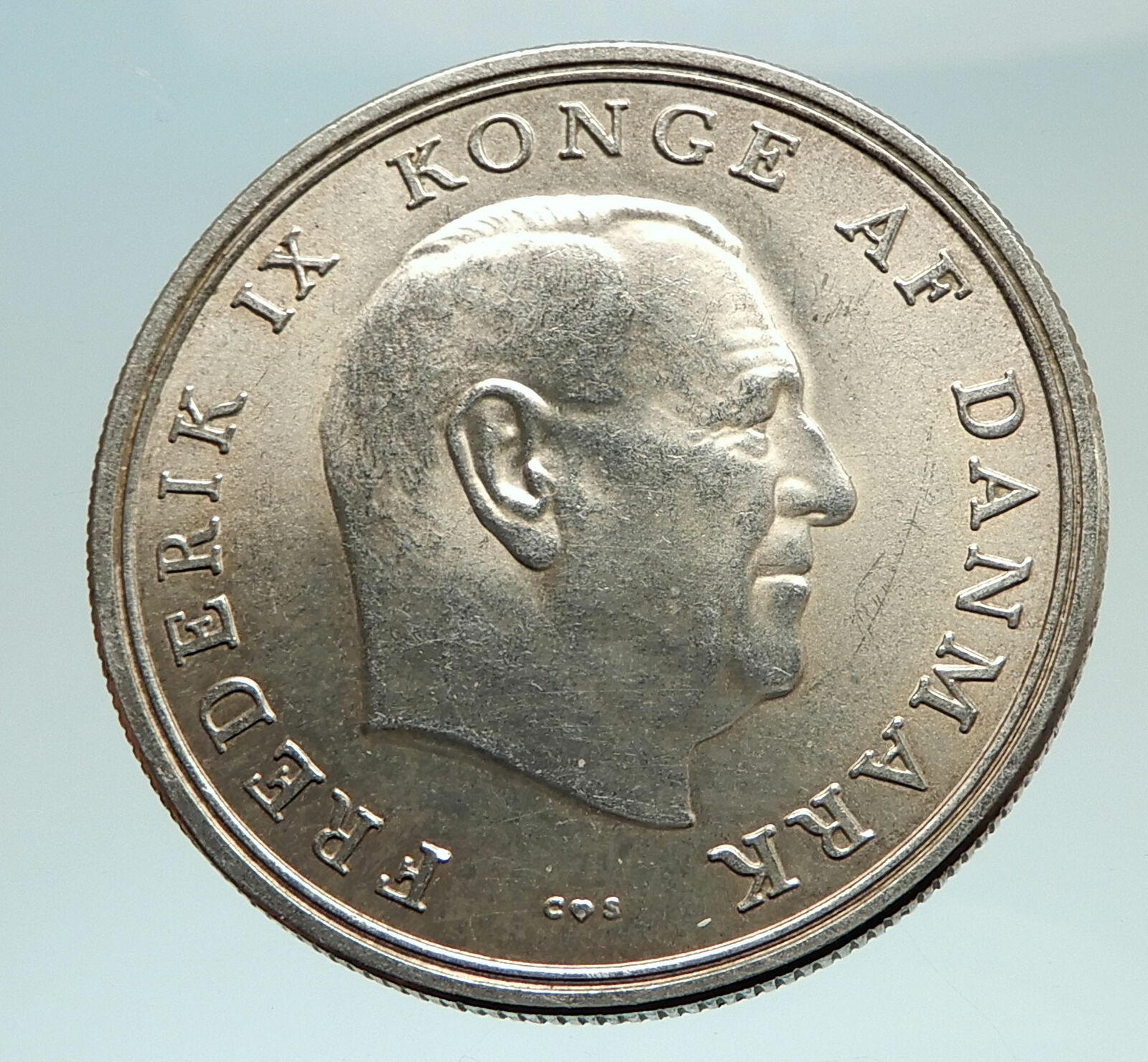
Denmark – Death of Frederik IX and accession of Margrethe II – 1972 Silver 10 Kroner 35mm (20.52 grams) 0.800 Silver (0.5247 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 858
FREDERIK IX KONGE AF DANMARK 20. APRIL 1947 14. JANUAR 1972 10 KRONER, Head of King Frederick IX right.
MARGRETHE II DANMARKS DRONNING 1972 GUDS HJÆLP. FOLKETS KÆRLIGHED. DANMARKS STYRKE, Head of Queen Margrethe II right.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 Margrethe II (born 16 April 1940) is the Queen of Denmark; as well as the supreme authority of the Church of Denmark and Commander-in-Chief of the Danish Defence. Born into the House of Glücksburg, a royal house with origins in Northern Germany, she was the eldest child of Frederick IX of Denmark and Ingrid of Sweden. She succeeded her father upon his death on 14 January 1972, having become heir presumptive to her father in 1953, when a constitutional amendment allowed women to inherit the throne. On her accession, Margrethe became the first female monarch of Denmark since Margrethe I, ruler of the Scandinavian kingdoms in 1375-1412 during the Kalmar Union. In 1967, she married Henri de Laborde de Monpezat, with whom she has two sons: Crown Prince Frederik and Prince Joachim. She has been on the Danish throne for 46 years, becoming the second-longest-reigning Danish monarch after her ancestor Christian IV. Margrethe II (born 16 April 1940) is the Queen of Denmark; as well as the supreme authority of the Church of Denmark and Commander-in-Chief of the Danish Defence. Born into the House of Glücksburg, a royal house with origins in Northern Germany, she was the eldest child of Frederick IX of Denmark and Ingrid of Sweden. She succeeded her father upon his death on 14 January 1972, having become heir presumptive to her father in 1953, when a constitutional amendment allowed women to inherit the throne. On her accession, Margrethe became the first female monarch of Denmark since Margrethe I, ruler of the Scandinavian kingdoms in 1375-1412 during the Kalmar Union. In 1967, she married Henri de Laborde de Monpezat, with whom she has two sons: Crown Prince Frederik and Prince Joachim. She has been on the Danish throne for 46 years, becoming the second-longest-reigning Danish monarch after her ancestor Christian IV.
 Frederick IX (Christian Frederik Franz Michael Carl Valdemar Georg; 11 March 1899 – 14 January 1972) was King of Denmark from 1947 to 1972. Frederick IX (Christian Frederik Franz Michael Carl Valdemar Georg; 11 March 1899 – 14 January 1972) was King of Denmark from 1947 to 1972.
Born into the House of Glücksburg, Frederick was the eldest son of King Christian X and Queen Alexandrine of Denmark. He became Crown Prince when his father succeeded as king in 1912. As a young man, he was educated at the Royal Danish Naval Academy. In 1935, he was married to Princess Ingrid of Sweden and they had three daughters, Margrethe, Benedikte and Anne-Marie. During Nazi Germany’s occupation of Denmark, Frederick acted as regent on behalf of his father from 1942 until 1943.
Frederick became king on his father’s death in early 1947. During Frederick IX’s reign, Danish society shook off the restrictions of an agrarian society and developed a welfare state. And, as a consequence of the booming economy of the 1960s, women entered the labour market. In other words, Denmark became a modern country, which meant new demands on the monarchy, and Frederick’s role as a constitutional monarch. Frederick IX died in 1972, and was succeeded by his elder daughter, Margrethe.
 Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Europe. The southernmost of the Nordic countries, it is southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. The Kingdom of Denmark is a sovereign state that comprises Denmark proper and two autonomous constituent countries in the North Atlantic Ocean: the Faroe Islands and Greenland. Denmark has an area of 42,924 square kilometres (16,573 sq mi), and a population of 5.7 million. The country consists of a peninsula, Jutland, and an archipelago of 443 named islands, of which around 70 are inhabited. The islands are characterised by flat, arable land and sandy coasts, low elevation and a temperate climate. Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Europe. The southernmost of the Nordic countries, it is southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. The Kingdom of Denmark is a sovereign state that comprises Denmark proper and two autonomous constituent countries in the North Atlantic Ocean: the Faroe Islands and Greenland. Denmark has an area of 42,924 square kilometres (16,573 sq mi), and a population of 5.7 million. The country consists of a peninsula, Jutland, and an archipelago of 443 named islands, of which around 70 are inhabited. The islands are characterised by flat, arable land and sandy coasts, low elevation and a temperate climate.
 The unified kingdom of Denmark emerged in the 10th century as a proficient seafaring nation in the struggle for control of the Baltic Sea. Denmark, Sweden and Norway were ruled together under the Kalmar Union, established in 1397 and ending with Swedish secession in 1523. Denmark and Norway remained under the same monarch until the union was dissolved by outside forces in 1814. The deterioration of the Kingdom of Norway, caused by the Black Death, made it possible for Denmark to inherit an expansive colonial empire from this union-of which the Faroe Islands and Greenland are remnants. Beginning in the 17th century, there were several cessions of territory; these culminated in the 1830s with a surge of nationalist movements, which were defeated in the 1864 Second Schleswig War. Denmark remained neutral during World War I. In April 1940, a German invasion saw brief military skirmishes while the Danish resistance movement was active from 1943 until the German surrender in May 1945. An industrialized exporter of agricultural produce in the second half of the 19th century, Denmark introduced social and labour-market reforms in the early 20th century that created the basis for the present welfare state model with a highly developed mixed economy. The unified kingdom of Denmark emerged in the 10th century as a proficient seafaring nation in the struggle for control of the Baltic Sea. Denmark, Sweden and Norway were ruled together under the Kalmar Union, established in 1397 and ending with Swedish secession in 1523. Denmark and Norway remained under the same monarch until the union was dissolved by outside forces in 1814. The deterioration of the Kingdom of Norway, caused by the Black Death, made it possible for Denmark to inherit an expansive colonial empire from this union-of which the Faroe Islands and Greenland are remnants. Beginning in the 17th century, there were several cessions of territory; these culminated in the 1830s with a surge of nationalist movements, which were defeated in the 1864 Second Schleswig War. Denmark remained neutral during World War I. In April 1940, a German invasion saw brief military skirmishes while the Danish resistance movement was active from 1943 until the German surrender in May 1945. An industrialized exporter of agricultural produce in the second half of the 19th century, Denmark introduced social and labour-market reforms in the early 20th century that created the basis for the present welfare state model with a highly developed mixed economy.
The Constitution of Denmark was signed on 5 June 1849, ending the absolute monarchy which had begun in 1660. It establishes a constitutional monarchy-the current monarch is Queen Margrethe II-organised as a parliamentary democracy. The government and national parliament are seated in Copenhagen, the nation’s capital, largest city and main commercial centre. Denmark exercises hegemonic influence in the Danish Realm, devolving powers to handle internal affairs. Denmark became a member of the European Economic Community (now the EU) in 1973, maintaining certain opt-outs; it retains its own currency, the krone. It is among the founding members of NATO, the Nordic Council, the OECD, OSCE, and the United Nations; it is also part of the Schengen Area.
Danes enjoy a high standard of living and the country ranks highly in some metrics of national performance, including education, health care, protection of civil liberties, democratic governance, prosperity and human development. The country ranks as having the world’s highest social mobility, a high level of income equality, is the least corrupt country in the world, has one of the world’s highest per capita incomes, and one of the world’s highest personal income tax rates. A large majority of Danes are members of the Lutheran State Church, though the Constitution guarantees freedom of religion.
|





 Margrethe II (born 16 April 1940) is the Queen of Denmark; as well as the supreme authority of the Church of Denmark and Commander-in-Chief of the Danish Defence. Born into the House of Glücksburg, a royal house with origins in Northern Germany, she was the eldest child of Frederick IX of Denmark and Ingrid of Sweden. She succeeded her father upon his death on 14 January 1972, having become heir presumptive to her father in 1953, when a constitutional amendment allowed women to inherit the throne. On her accession, Margrethe became the first female monarch of Denmark since Margrethe I, ruler of the Scandinavian kingdoms in 1375-1412 during the Kalmar Union. In 1967, she married Henri de Laborde de Monpezat, with whom she has two sons: Crown Prince Frederik and Prince Joachim. She has been on the Danish throne for 46 years, becoming the second-longest-reigning Danish monarch after her ancestor Christian IV.
Margrethe II (born 16 April 1940) is the Queen of Denmark; as well as the supreme authority of the Church of Denmark and Commander-in-Chief of the Danish Defence. Born into the House of Glücksburg, a royal house with origins in Northern Germany, she was the eldest child of Frederick IX of Denmark and Ingrid of Sweden. She succeeded her father upon his death on 14 January 1972, having become heir presumptive to her father in 1953, when a constitutional amendment allowed women to inherit the throne. On her accession, Margrethe became the first female monarch of Denmark since Margrethe I, ruler of the Scandinavian kingdoms in 1375-1412 during the Kalmar Union. In 1967, she married Henri de Laborde de Monpezat, with whom she has two sons: Crown Prince Frederik and Prince Joachim. She has been on the Danish throne for 46 years, becoming the second-longest-reigning Danish monarch after her ancestor Christian IV.  Frederick IX (Christian Frederik Franz Michael Carl Valdemar Georg; 11 March 1899 – 14 January 1972) was King of Denmark from 1947 to 1972.
Frederick IX (Christian Frederik Franz Michael Carl Valdemar Georg; 11 March 1899 – 14 January 1972) was King of Denmark from 1947 to 1972.
 Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Europe. The southernmost of the Nordic countries, it is southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. The Kingdom of Denmark is a sovereign state that comprises Denmark proper and two autonomous constituent countries in the North Atlantic Ocean: the Faroe Islands and Greenland. Denmark has an area of 42,924 square kilometres (16,573 sq mi), and a population of 5.7 million. The country consists of a peninsula, Jutland, and an archipelago of 443 named islands, of which around 70 are inhabited. The islands are characterised by flat, arable land and sandy coasts, low elevation and a temperate climate.
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Europe. The southernmost of the Nordic countries, it is southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. The Kingdom of Denmark is a sovereign state that comprises Denmark proper and two autonomous constituent countries in the North Atlantic Ocean: the Faroe Islands and Greenland. Denmark has an area of 42,924 square kilometres (16,573 sq mi), and a population of 5.7 million. The country consists of a peninsula, Jutland, and an archipelago of 443 named islands, of which around 70 are inhabited. The islands are characterised by flat, arable land and sandy coasts, low elevation and a temperate climate. The unified kingdom of Denmark emerged in the 10th century as a proficient seafaring nation in the struggle for control of the Baltic Sea. Denmark, Sweden and Norway were ruled together under the Kalmar Union, established in 1397 and ending with Swedish secession in 1523. Denmark and Norway remained under the same monarch until the union was dissolved by outside forces in 1814. The deterioration of the Kingdom of Norway, caused by the Black Death, made it possible for Denmark to inherit an expansive colonial empire from this union-of which the Faroe Islands and Greenland are remnants. Beginning in the 17th century, there were several cessions of territory; these culminated in the 1830s with a surge of nationalist movements, which were defeated in the 1864 Second Schleswig War. Denmark remained neutral during World War I. In April 1940, a German invasion saw brief military skirmishes while the Danish resistance movement was active from 1943 until the German surrender in May 1945. An industrialized exporter of agricultural produce in the second half of the 19th century, Denmark introduced social and labour-market reforms in the early 20th century that created the basis for the present welfare state model with a highly developed mixed economy.
The unified kingdom of Denmark emerged in the 10th century as a proficient seafaring nation in the struggle for control of the Baltic Sea. Denmark, Sweden and Norway were ruled together under the Kalmar Union, established in 1397 and ending with Swedish secession in 1523. Denmark and Norway remained under the same monarch until the union was dissolved by outside forces in 1814. The deterioration of the Kingdom of Norway, caused by the Black Death, made it possible for Denmark to inherit an expansive colonial empire from this union-of which the Faroe Islands and Greenland are remnants. Beginning in the 17th century, there were several cessions of territory; these culminated in the 1830s with a surge of nationalist movements, which were defeated in the 1864 Second Schleswig War. Denmark remained neutral during World War I. In April 1940, a German invasion saw brief military skirmishes while the Danish resistance movement was active from 1943 until the German surrender in May 1945. An industrialized exporter of agricultural produce in the second half of the 19th century, Denmark introduced social and labour-market reforms in the early 20th century that created the basis for the present welfare state model with a highly developed mixed economy.




