|
Portugal – 400th Anniversary of the Discovery of India
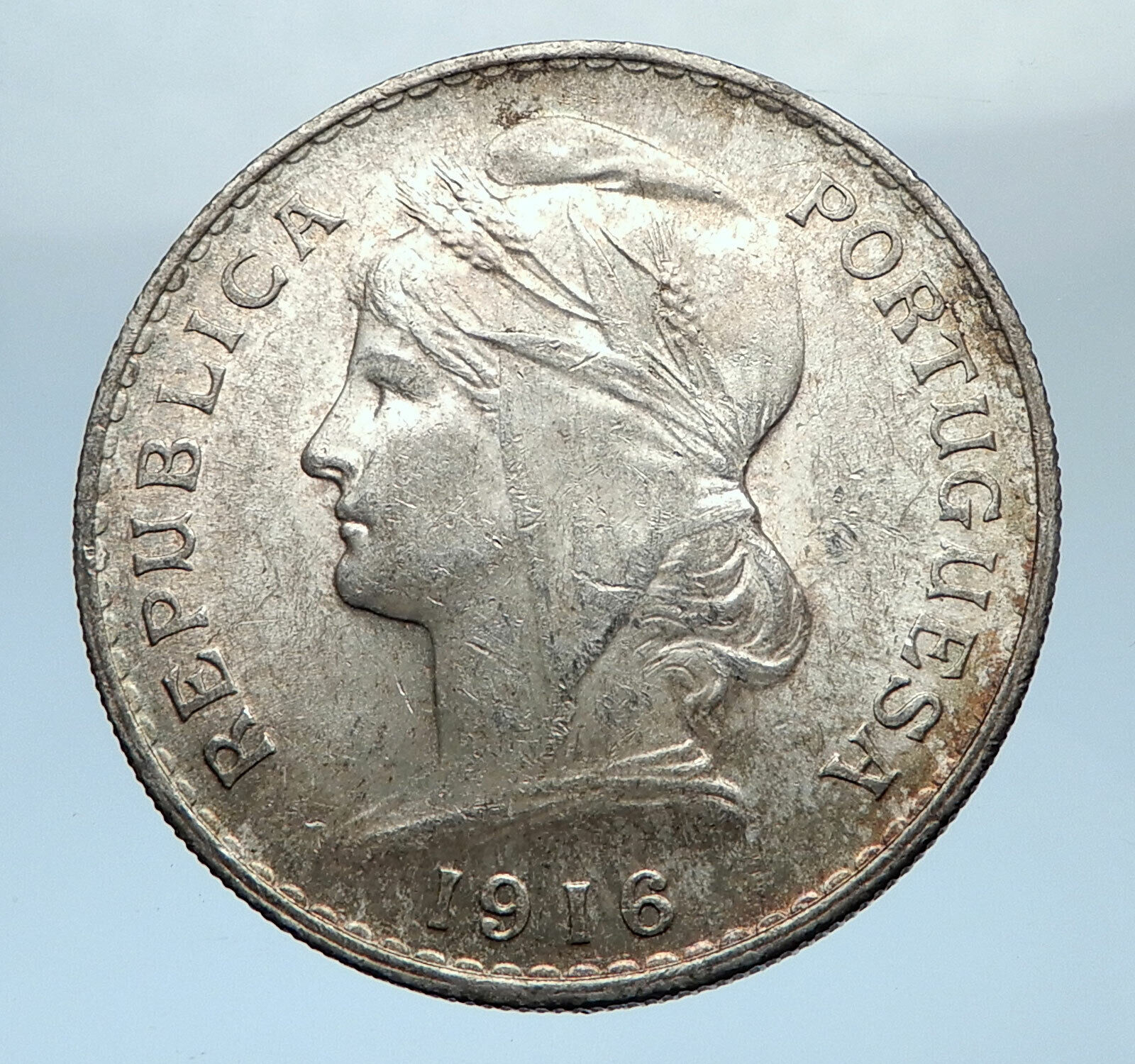
1898 Silver 200 Reis 24mm (5.00 grams) 0.917 Silver (0.1474 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 537
CARLOS I REI E AMELIA RAINHA DE PORTUGAL, Conjoined busts left.
* 4°CENTENARIO DA DESCOBERTA DA INDIA * 200 REIS IN HOC SIGNO VINCES 1498-1898, Maltese cross, rosettes in angles.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 The aim of Portugal in the Indian Ocean was to ensure the monopoly of the spice trade. Taking advantage of the rivalries that pitted Hindus against Muslims, the Portuguese established several forts and trading posts between 1500 and 1510. In East Africa, small Islamic states along the coast of Mozambique, Kilwa, Brava, Sofala and Mombasa were destroyed, or became either subjects or allies of Portugal. Pêro da Covilhã had reached Ethiopia, traveling secretly overland, as early as 1490; a diplomatic mission reached the ruler of that nation on October 19, 1520. The aim of Portugal in the Indian Ocean was to ensure the monopoly of the spice trade. Taking advantage of the rivalries that pitted Hindus against Muslims, the Portuguese established several forts and trading posts between 1500 and 1510. In East Africa, small Islamic states along the coast of Mozambique, Kilwa, Brava, Sofala and Mombasa were destroyed, or became either subjects or allies of Portugal. Pêro da Covilhã had reached Ethiopia, traveling secretly overland, as early as 1490; a diplomatic mission reached the ruler of that nation on October 19, 1520.
In 1500 the second fleet to India who came to discover Brazil explored the East African coast, where Diogo Dias discovered the island that he named St. Lawrence, later known as Madagascar. This fleet, commanded by Pedro Álvares Cabral, arrived at Calicut in September, where the first trade agreement in India was signed. For a short time a Portuguese factory was installed there, but was attacked by Muslims on December 16 and several Portuguese, including the scribe Pêro Vaz de Caminha, died. After bombarding Calicut as a retaliation, Cabral went to rival Kochi.
Profiting from the rivalry between the Maharaja of Kochi and the Zamorin of Calicut, the Portuguese were well received and seen as allies, getting a permit to build a fort (Fort Manuel) and a trading post that were the first European settlement in India. There in 1503 they built the St. Francis Church. In 1502 Vasco da Gama took the island of Kilwa on the coast of Tanzania, where in 1505 the first fort of Portuguese East Africa was built to protect ships from the East Indian trade.
In 1505 king Manuel I of Portugal appointed Francisco de Almeida first Viceroy of Portuguese India for a three-year period, starting the Portuguese government in the east, headquartered at Kochi. That year the Portuguese conquered Kannur where they founded St. Angelo Fort. Lourenço de Almeida arrived in Ceylon (modern Sri Lanka), where he discovered the source of cinnamon. Finding it divided into seven rival kingdoms, he established a defense pact with the kingdom of Kotte and extended the control in coastal areas, where in 1517 was founded the fortress of Colombo.
In 1506 a Portuguese fleet under the command of Tristão da Cunha and Afonso de Albuquerque, conquered Socotra at the entrance of the Red Sea and Muscat in 1507, having failed to conquer Ormuz, following a strategy intended to close the entrances to the Indian Ocean. That same year were built fortresses in the Island of Mozambique and Mombasa on the Kenyan coast. Madagascar was partly explored by Tristão da Cunha and in the same year Mauritius was discovered.
In 1509, the Portuguese won the sea Battle of Diu against the combined forces of the Ottoman Sultan Beyazid II, Sultan of Gujarat, Mamlûk Sultan of Cairo, Samoothiri Raja of Kozhikode, Venetian Republic, and Ragusan Republic (Dubrovnik). The Portuguese victory was critical for its strategy of control of the Indian Sea: Turks and Egyptians withdraw their navies from India, leaving the seas to the Portuguese, setting its trade dominance for almost a century, and greatly assisting the growth of the Portuguese Empire. It marked also the beginning of the European colonial dominance in the Asia. A second Battle of Diu in 1538 finally ended Ottoman ambitions in India and confirmed Portuguese hegemony in the Indian Ocean.
Under the government of Albuquerque, Goa was taken from the Bijapur sultanate in 1510 with the help of Hindu privateer Timoji. Coveted for being the best port in the region, mainly for the commerce of Arabian horses for the Deccan sultanates, it allowed to move on from the initial guest stay in Cochin. Despite constant attacks, Goa became the seat of the Portuguese government, under the name of Estado da India (State of India), with the conquest triggering compliance of neighbour kingdoms: Gujarat and Calicut sent embassies, offering alliances and grants to fortify. Albuquerque began that year in Goa the first Portuguese mint in India, taking the opportunity to announce the achievement.
  Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic (Portuguese: República Portuguesa), is a country on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe. It is the westernmost country of mainland Europe, being bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west and south and by Spain to the north and east. The Portugal-Spain border is 1,214 km (754 mi) long and considered the longest uninterrupted border within the European Union. The republic also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira, both autonomous regions with their own regional governments. Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic (Portuguese: República Portuguesa), is a country on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe. It is the westernmost country of mainland Europe, being bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west and south and by Spain to the north and east. The Portugal-Spain border is 1,214 km (754 mi) long and considered the longest uninterrupted border within the European Union. The republic also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira, both autonomous regions with their own regional governments.
 The territory of modern Portugal has been continuously settled, invaded and fought over since prehistoric times. The Pre-Celts, Celts, Phoenicians, Carthaginians and the Romans were followed by the invasions of the Visigothic and the Suebi Germanic peoples, who were themselves later invaded by the Moors. These Muslim peoples were eventually expelled during the Christian Reconquista. Portuguese nationality can be traced back to the creation of the First County of Portugal, in 868. In 1139, Afonso Henriques was proclaimed King of Portugal, thus firmly establishing Portuguese independence, under the Portuguese House of Burgundy. The territory of modern Portugal has been continuously settled, invaded and fought over since prehistoric times. The Pre-Celts, Celts, Phoenicians, Carthaginians and the Romans were followed by the invasions of the Visigothic and the Suebi Germanic peoples, who were themselves later invaded by the Moors. These Muslim peoples were eventually expelled during the Christian Reconquista. Portuguese nationality can be traced back to the creation of the First County of Portugal, in 868. In 1139, Afonso Henriques was proclaimed King of Portugal, thus firmly establishing Portuguese independence, under the Portuguese House of Burgundy.
In the 15th and 16th centuries, under the House of Aviz, which took power following the 1383-85 Crisis, Portugal expanded Western influence and established the first global empire, becoming one of the world’s major economic, political and military powers. During this time, Portuguese explorers pioneered maritime exploration in the Age of Discovery, notably under royal patronage of Prince Henry the Navigator and King João II, with such notable discoveries as Vasco da Gama’s sea route to India (1497-98), Pedro Álvares Cabral’s discovery of Brazil (1500), and Bartolomeu Dias’s reaching of the Cape of Good Hope. Portugal monopolized the spice trade during this time, under royal command of the Casa da Índia, and the Portuguese Empire expanded with military campaigns led in Asia, notably under Afonso de Albuquerque, who was known as the “Caesar of the East”.
The destruction of Lisbon in a 1755 earthquake, the country’s occupation during the Napoleonic Wars, the independence of Brazil (1822), and the Liberal Wars (1828-1834), all left Portugal crippled from war and diminished in its world power. After the 1910 revolution deposed the monarchy, the democratic but unstable Portuguese First Republic was established, later being superseded by the “Estado Novo” right-wing authoritarian regime. Democracy was restored after the Portuguese Colonial War and the Carnation Revolution in 1974. Shortly after, independence was granted to all its colonies and East Timor, with the exception of Macau, which was handed over to China in 1999. This marked the end of the longest-lived European colonial empire, leaving a profound cultural and architectural influence across the globe and a legacy of over 250 million Portuguese speakers today.
Portugal is a developed country with a high-income advanced economy and high living standards. It is the 5th most peaceful country in the world, maintaining a unitary semi-presidential republican form of government. It has the 18th highest Social Progress in the world, putting it ahead of other Western European countries like France, Spain and Italy. It is a member of numerous international organizations, including the United Nations, the European Union, the eurozone, OECD, NATO and the Community of Portuguese Language Countries. Portugal is also known for having decriminalized the usage of all common drugs in 2001, the first country in the world to do so. However, the sale and distribution of these drugs is still illegal in Portugal.
|





 The aim of Portugal in the Indian Ocean was to ensure the monopoly of the spice trade. Taking advantage of the rivalries that pitted Hindus against Muslims, the Portuguese established several forts and trading posts between 1500 and 1510. In East Africa, small Islamic states along the coast of Mozambique, Kilwa, Brava, Sofala and Mombasa were destroyed, or became either subjects or allies of Portugal. Pêro da Covilhã had reached Ethiopia, traveling secretly overland, as early as 1490; a diplomatic mission reached the ruler of that nation on October 19, 1520.
The aim of Portugal in the Indian Ocean was to ensure the monopoly of the spice trade. Taking advantage of the rivalries that pitted Hindus against Muslims, the Portuguese established several forts and trading posts between 1500 and 1510. In East Africa, small Islamic states along the coast of Mozambique, Kilwa, Brava, Sofala and Mombasa were destroyed, or became either subjects or allies of Portugal. Pêro da Covilhã had reached Ethiopia, traveling secretly overland, as early as 1490; a diplomatic mission reached the ruler of that nation on October 19, 1520. 
 Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic (Portuguese: República Portuguesa), is a country on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe. It is the westernmost country of mainland Europe, being bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west and south and by Spain to the north and east. The Portugal-Spain border is 1,214 km (754 mi) long and considered the longest uninterrupted border within the European Union. The republic also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira, both autonomous regions with their own regional governments.
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic (Portuguese: República Portuguesa), is a country on the Iberian Peninsula, in Southwestern Europe. It is the westernmost country of mainland Europe, being bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the west and south and by Spain to the north and east. The Portugal-Spain border is 1,214 km (754 mi) long and considered the longest uninterrupted border within the European Union. The republic also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira, both autonomous regions with their own regional governments. The territory of modern Portugal has been continuously settled, invaded and fought over since prehistoric times. The Pre-Celts, Celts, Phoenicians, Carthaginians and the Romans were followed by the invasions of the Visigothic and the Suebi Germanic peoples, who were themselves later invaded by the Moors. These Muslim peoples were eventually expelled during the Christian Reconquista. Portuguese nationality can be traced back to the creation of the First County of Portugal, in 868. In 1139, Afonso Henriques was proclaimed King of Portugal, thus firmly establishing Portuguese independence, under the Portuguese House of Burgundy.
The territory of modern Portugal has been continuously settled, invaded and fought over since prehistoric times. The Pre-Celts, Celts, Phoenicians, Carthaginians and the Romans were followed by the invasions of the Visigothic and the Suebi Germanic peoples, who were themselves later invaded by the Moors. These Muslim peoples were eventually expelled during the Christian Reconquista. Portuguese nationality can be traced back to the creation of the First County of Portugal, in 868. In 1139, Afonso Henriques was proclaimed King of Portugal, thus firmly establishing Portuguese independence, under the Portuguese House of Burgundy.




