|
Byzantine Empire
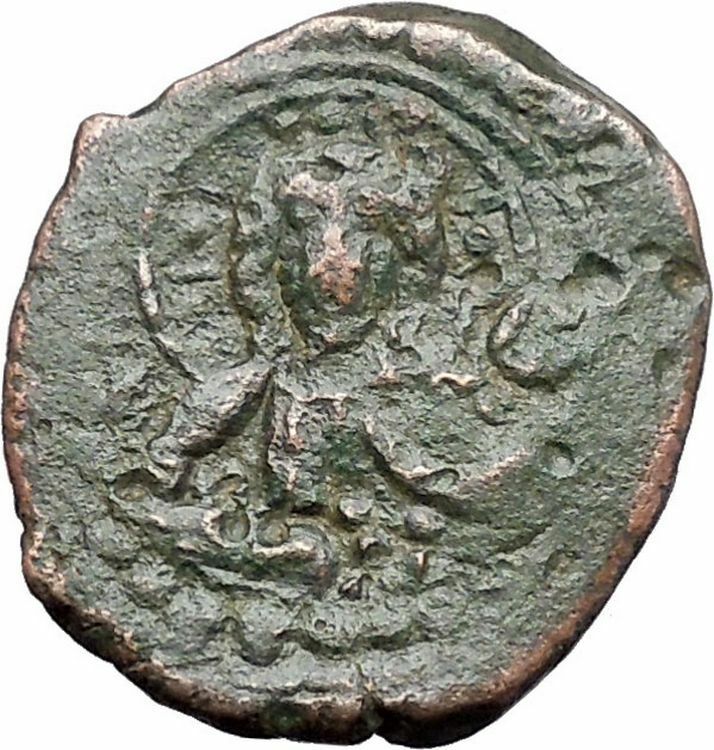
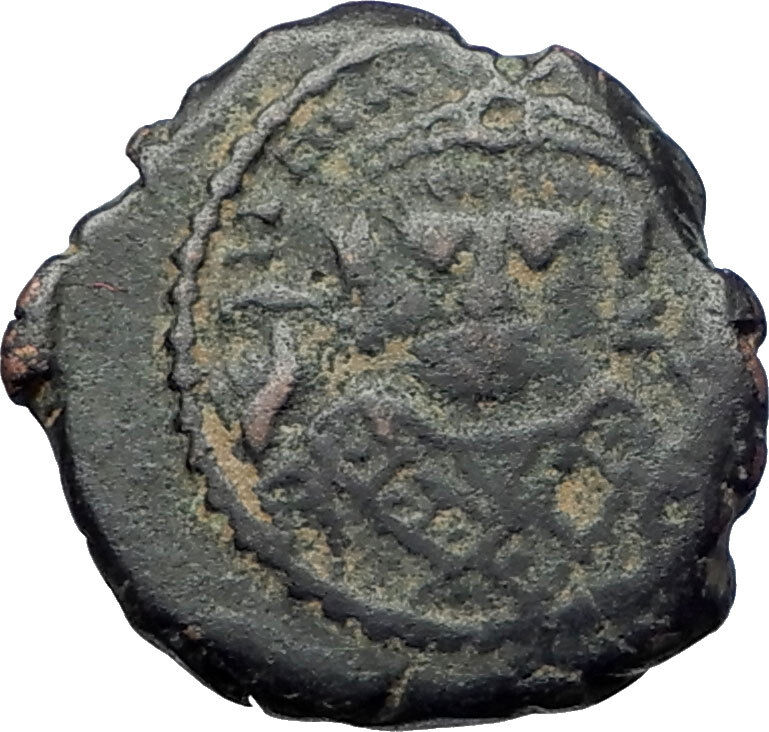
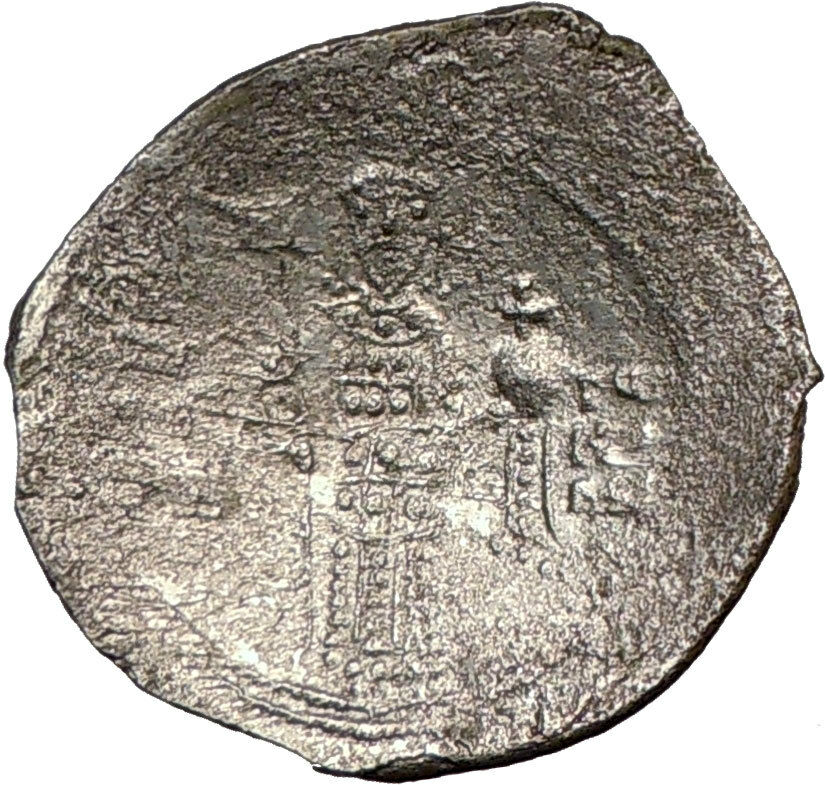
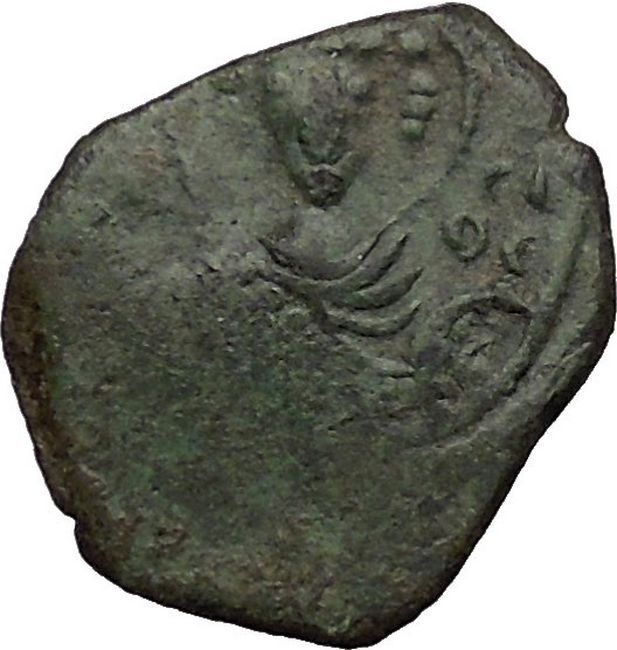
Tiberius II Constantine – Emperor: 26 September 578 – 14 August 582 A.D.
Gold Solidus 20mm (4.50 grams) Constantinople mint, 9th officina, struck 579-582 A.D.
Reference: Sear 422
Certification: NGC Ancients MS Strike: 5/5 Surface: 4/5 5743726-004
d m TIb CONS-TANT PP AVG, cuirassed bust of Tiberius II facing, wearing crown with pendilia, globus cruciger in right hand, shield decorated with horseman motif in left.
VICTORI-A AVGG Θ, cross potent set on four steps; CONOB below.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Flavius Tiberius Constantinus Augustus or Tiberius II Constantine, known in Greek as Tiberios Konstantinos (ca 520/ca 535 – August 14, 582) was a Byzantine emperor (574 – 582) of the Justinian Dynasty.
During his reign, Tiberius II Constantine gave away 7,200 pounds of gold each year for four years.
He was a friend of Justin II, who appointed Tiberius Comes of the Excubitors. He took control of the empire when Justin II went insane in 574, and to increase his popularity, he immediately began spending money that Justin had reserved in his treasury. The Empress Sophia, Justin’s wife, reproached Tiberius for having reduced the state to poverty, saying:
What I have been collecting through many years you are scattering prodigally in a short time
Tiberius replied:
I trust to the Lord that money will not be lacking in our treasury so long as the poor receive charity and captives are ransomed. For this is the great treasure, since the Lord says, ‘Lay up for yourselves treasures in heaven where neither moth nor rust doth corrupt and where thieves do not break through nor steal.’ Therefore of these things which God has furnished us let us gather treasures in heaven, and God will deign to give us increase in this world.
Justin II, Tiberius’s predecessor, had been made infirm by disease; the faculties of his mind were impaired and he subsequently lost the use of his feet. Confined to his palace, he became a stranger to the complaints of the people and the vices of the government. Conscious of his infirmity, he honorably chose to seek a successor to the Imperial throne. On the advice of his wife Sophia, he handed the diadem to one of his Excubitors, Tiberius.
“You behold,” said the emperor, “the ensigns of supreme power. You are about to receive them, not from my hand, but from the hand of God. Honor them, and from them you will derive honor. Respect the empress your mother: you are now her son; before, you were her servant. Delight not in blood; abstain from revenge; avoid those actions by which I have incurred the public hatred; and consult the experience, rather than the example, of your predecessor. As a man, I have sinned; as a sinner, even in this life, I have been severely punished: but these servants, (and we pointed to his ministers,) who have abused my confidence, and inflamed my passions, will appear with me before the tribunal of Christ. I have been dazzled by the splendor of the diadem: be thou wise and modest; remember what you have been, remember what you are. You see around us your slaves, and your children: with the authority, assume the tenderness, of a parent. Love your people like yourself; cultivate the affections, maintain the discipline, of the army; protect the fortunes of the rich, relieve the necessities of the poor.”
While Justin was still alive, Tiberius’ general Justinian fought and defeated the Persians in the East. Tiberius sent reinforcements to Italy in order to fight Lombards. He saved Rome from Lombards and allied with Childepertus, the King of the Franks, in order to defeat them, but his army, under the command of Baduarius, was defeated by the enemy and the Lombards continued their conquests in Italy.
When Tiberius became full emperor upon Justin’s death in 578, he extended his military activities into the remnants of the Western Empire, where he made peace with the Visigoths in Spain and defeated the Berbers in North Africa. He may have been the Emperor Lucius Tiberius of Arthurian legend, sending envoys to former Roman provinces after a long period without Imperial presence. Meanwhile, the Slavs began to migrate into the Balkans in 579; unfortunately, Tiberius needed the army to defend against Persian invasions, and was unable to stop the Slavic migrations.
Sophia, Justin’s wife, was persuaded that she should preserve her station and influence by marrying the new emperor Tiberius. But he refused her proposal of marriage because he was already married to Anastasia. Sophia seek revenge: a secret alliance was concluded between the dowager empress and the general Justinian. They conspired to overthrow the emperor: if the plot had been successful, Justinian would have become the new emperor. However the conspiration failed and Sophia was reduced to a modest allowance. Justinian was forgiven by Tiberius II.
In 582, Tiberius fell ill, and Maurice was named his heir. Maurice became emperor when Tiberius died in August – poisoned, it was rumored. His last words were spoken to his successor, Maurice:
Let my sovereignty be delivered to thee with this girl. Be happy in the use of it, mindful always to love equity and justice.
According to Edward Gibbon, Tiberius II was a good emperor:
With the odious name of Tiberius, he assumed the more popular appellation of Constantine, and imitated the purer virtues of the Antonines. After recording the vice or folly of so many Roman princes, it is pleasing to repose, for a moment, on a character conspicuous by the qualities of humanity, justice, temperance, and fortitude; to contemplate a sovereign affable in his palace, pious in the church, impartial on the seat of judgment, and victorious, at least by his generals, in the Persian war. The most glorious trophy of his victory consisted in a multitude of captives, whom Tiberius entertained, redeemed, and dismissed to their native homes with the charitable spirit of a Christian hero. The merit or misfortunes of his own subjects had a dearer claim to his beneficence, and he measured his bounty not so much by their expectations as by his own dignity. This maxim, however dangerous in a trustee of the public wealth, was balanced by a principle of humanity and justice, which taught him to abhor, as of the basest alloy, the gold that was extracted from the tears of the people. For their relief, as often as they had suffered by natural or hostile calamities, he was impatient to remit the arrears of the past, or the demands of future taxes: he sternly rejected the servile offerings of his ministers, which were compensated by tenfold oppression; and the wise and equitable laws of Tiberius excited the praise and regret of succeeding times. Constantinople believed that the emperor had discovered a treasure: but his genuine treasure consisted in the practice of liberal economy, and the contempt of all vain and superfluous expense. The Romans of the East would have been happy, if the best gift of Heaven, a patriot king, had been confirmed as a proper and permanent blessing. But in less than four years after the death of Justin, his worthy successor sunk into a mortal disease, which left him only sufficient time to restore the diadem, according to the tenure by which he held it, to the most deserving of his fellow-citizens.
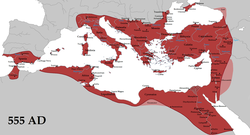 The Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire, was the predominantly Greek-speaking eastern half continuation and remainder of the Roman Empire during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. Its capital city was Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul), originally founded as Byzantium. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until it fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire was the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. Both “Byzantine Empire” and “Eastern Roman Empire” are historiographical terms created after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire (Ancient Greek: Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων, tr. Basileia Rhōmaiōn; Latin: Imperium Romanum), or Romania (Ῥωμανία), and to themselves as “Romans”. The Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire, was the predominantly Greek-speaking eastern half continuation and remainder of the Roman Empire during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. Its capital city was Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul), originally founded as Byzantium. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until it fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire was the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. Both “Byzantine Empire” and “Eastern Roman Empire” are historiographical terms created after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire (Ancient Greek: Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων, tr. Basileia Rhōmaiōn; Latin: Imperium Romanum), or Romania (Ῥωμανία), and to themselves as “Romans”.
Several events from the 4th to 6th centuries mark the transitional period during which the Roman Empire’s east and west divided. In 285, the emperor Diocletian (r. 284-305) partitioned the Roman Empire’s administration into eastern and western halves. Between 324 and 330, Constantine I (r. 306-337) transferred the main capital from Rome to Byzantium, later known as Constantinople (“City of Constantine”) and Nova Roma (“New Rome”). Under Theodosius I (r. 379-395), Christianity became the Empire’s official state religion and others such as Roman polytheism were proscribed. And finally, under the reign of Heraclius (r. 610-641), the Empire’s military and administration were restructured and adopted Greek for official use instead of Latin. Thus, although it continued the Roman state and maintained Roman state traditions, modern historians distinguish Byzantium from ancient Rome insofar as it was oriented towards Greek rather than Latin culture, and characterised by Orthodox Christianity rather than Roman polytheism.
The borders of the Empire evolved significantly over its existence, as it went through several cycles of decline and recovery. During the reign of Justinian I (r. 527-565), the Empire reached its greatest extent after reconquering much of the historically Roman western Mediterranean coast, including north Africa, Italy, and Rome itself, which it held for two more centuries. During the reign of Maurice (r. 582-602), the Empire’s eastern frontier was expanded and the north stabilised. However, his assassination caused a two-decade-long war with Sassanid Persia which exhausted the Empire’s resources and contributed to major territorial losses during the Muslim conquests of the 7th century. In a matter of years the Empire lost its richest provinces, Egypt and Syria, to the Arabs.
During the Macedonian dynasty (10th-11th centuries), the Empire again expanded and experienced a two-century long renaissance, which came to an end with the loss of much of Asia Minor to the Seljuk Turks after the Battle of Manzikert in 1071. This battle opened the way for the Turks to settle in Anatolia as a homeland.
The final centuries of the Empire exhibited a general trend of decline. It struggled to recover during the 12th century, but was delivered a mortal blow during the Fourth Crusade, when Constantinople was sacked and the Empire dissolved and divided into competing Byzantine Greek and Latin realms. Despite the eventual recovery of Constantinople and re-establishment of the Empire in 1261, Byzantium remained only one of several small rival states in the area for the final two centuries of its existence. Its remaining territories were progressively annexed by the Ottomans over the 15th century. The Fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 finally ended the Byzantine Empire.
|









 The Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire, was the predominantly Greek-speaking eastern half continuation and remainder of the Roman Empire during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. Its capital city was Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul), originally founded as Byzantium. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until it fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire was the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. Both “Byzantine Empire” and “Eastern Roman Empire” are historiographical terms created after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire (Ancient Greek: Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων, tr. Basileia Rhōmaiōn; Latin: Imperium Romanum), or Romania (Ῥωμανία), and to themselves as “Romans”.
The Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire, was the predominantly Greek-speaking eastern half continuation and remainder of the Roman Empire during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. Its capital city was Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul), originally founded as Byzantium. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until it fell to the Ottoman Turks in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire was the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. Both “Byzantine Empire” and “Eastern Roman Empire” are historiographical terms created after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire (Ancient Greek: Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων, tr. Basileia Rhōmaiōn; Latin: Imperium Romanum), or Romania (Ῥωμανία), and to themselves as “Romans”.




