|
China – Yuan Dynasty (1280-1368 A.D.)
Xu Shouhui – Yuan Rebel Emperor: 1360-1363 A.D.
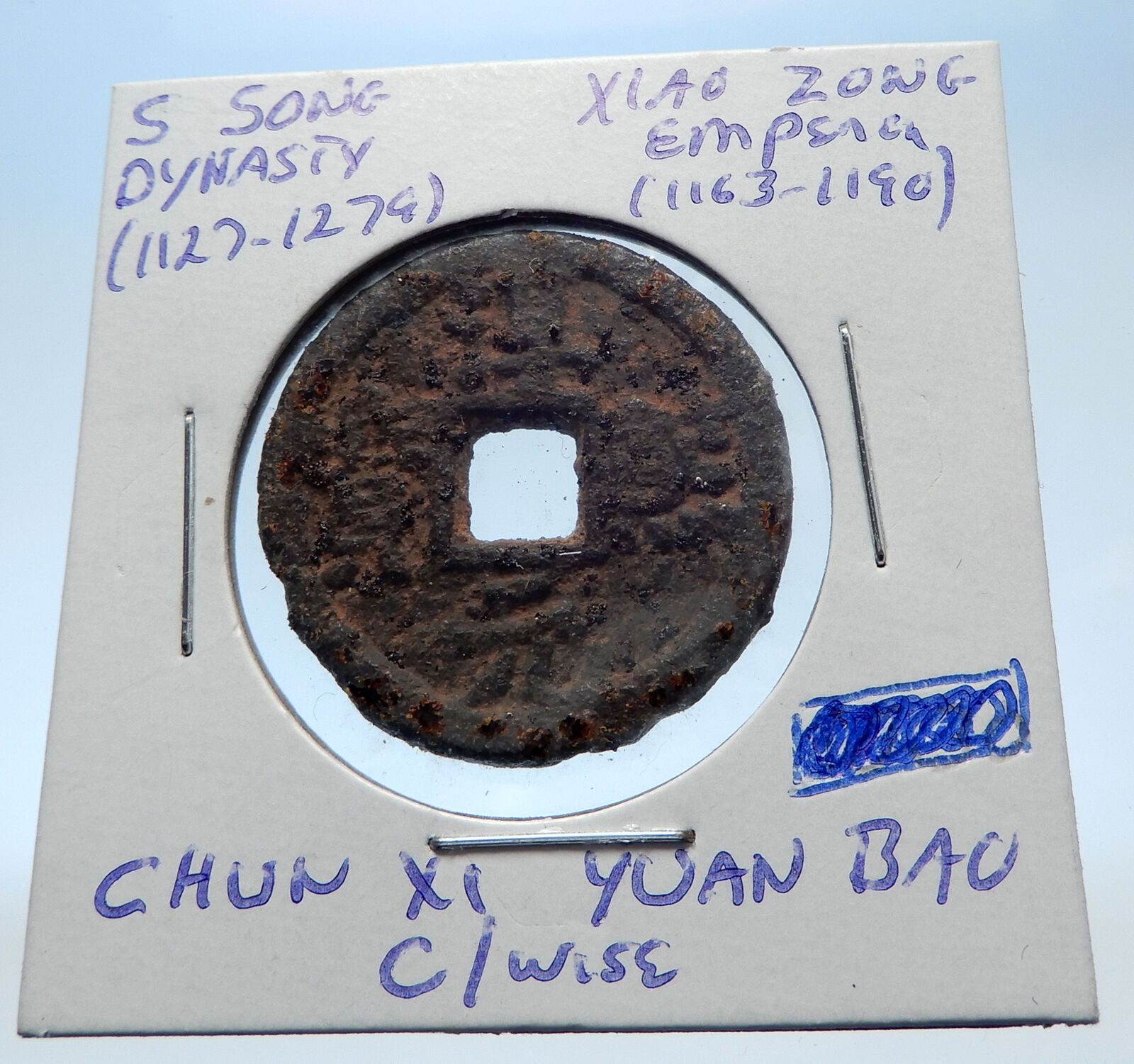
Bronze Tian Ding Tong Bao 2 Cash 32mm (8.79 grams), Struck 1360-61 AD
Reference: H# 19.143
Chinese characters, square hole within.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Xu Shouhui (simplified Chinese: 徐寿辉; traditional Chinese: 徐壽輝; pinyin: Xú Shòuhuī; Wade–Giles: Hsü Shou-hui) (died 1360) was a 14th-century Chinese rebel leader who proclaimed himself emperor of the Tianwan dynasty (天完) during the late Yuan dynasty period of China. He was also known as Xu Zhenyi (徐真一 or 徐真逸, romanized in Wade–Giles as Hsü Chen-i).
Born in Luotian (羅田, now in Hubei), Xu was a cloth vendor by profession.
In August 1351, he worked with others in Qízhōu (蘄州) to establish the rebel army of Red Turbans under the pretense of the Buddhist White Lotus Society. In the following months of the Red Turban Rebellion, they captured Qishui (蘄水) and made it the command centre of the Red Turbans and the capital of the newly declared Empire of Tianwan (天完), originally called Song (宋)[1] with himself as the emperor with the era name of Zhiping (治平).
The number of his supporters increased rapidly as he claimed to be Maitreya Buddha (彌勒佛下生) who sought to “destroy the rich to benefit the poor” (摧富益貧). In 1352, he invaded more of Hebei, and moved on to take Jiangxi, Anhui, Fujian, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and Hunan.
After being temporarily defeated by the army of the Yuan dynasty, he fled to Huangmei Mountain (黃梅山), but returned in 1355 to invade once again and move the capital to Hanyang District.
Five years later in 1360, Xu Shouhui was assassinated by his former ally, Chen Youliang, thus causing the collapse of the Tianwan Empire.
 The Yuan dynasty, officially the Great Yuan, was the empire or ruling dynasty of China established by Kublai Khan, leader of the Mongolian Borjigin clan. It followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although the Mongols had ruled territories including modern-day North China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Chinese style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279. His realm was, by this point, isolated from the other khanates and controlled most of modern-day China and its surrounding areas, including modern Mongolia. It was the first foreign dynasty to rule all of China and lasted until 1368, after which the rebuked Genghisid rulers retreated to their Mongolian homeland and continued to rule the Northern Yuan dynasty. Some of the Mongolian Emperors of the Yuan mastered the Chinese language, while others only used their native language (i.e. Mongolian) and the ‘Phags-pa script. The Yuan dynasty, officially the Great Yuan, was the empire or ruling dynasty of China established by Kublai Khan, leader of the Mongolian Borjigin clan. It followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although the Mongols had ruled territories including modern-day North China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Chinese style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279. His realm was, by this point, isolated from the other khanates and controlled most of modern-day China and its surrounding areas, including modern Mongolia. It was the first foreign dynasty to rule all of China and lasted until 1368, after which the rebuked Genghisid rulers retreated to their Mongolian homeland and continued to rule the Northern Yuan dynasty. Some of the Mongolian Emperors of the Yuan mastered the Chinese language, while others only used their native language (i.e. Mongolian) and the ‘Phags-pa script.
The Yuan dynasty was the khanate ruled by the successors of Möngke Khan after the division of the Mongol Empire. In official Chinese histories, the Yuan dynasty bore the Mandate of Heaven. The dynasty was established by Kublai Khan, yet he placed his grandfather Genghis Khan on the imperial records as the official founder of the dynasty as Taizu. In the Proclamation of the Dynastic Name, Kublai announced the name of the new dynasty as Great Yuan and claimed the succession of former Chinese dynasties from the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors to the Tang dynasty.
In addition to Emperor of China, Kublai Khan also claimed the title of Great Khan, supreme over the other successor khanates: the Chagatai, the Golden Horde, and the Ilkhanate. As such, the Yuan was also sometimes referred to as the Empire of the Great Khan. However, while the claim of supremacy by the Yuan emperors was at times recognized by the western khans, their subservience was nominal and each continued its own separate development.
|




 The Yuan dynasty, officially the Great Yuan, was the empire or ruling dynasty of China established by Kublai Khan, leader of the Mongolian Borjigin clan. It followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although the Mongols had ruled territories including modern-day North China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Chinese style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279. His realm was, by this point, isolated from the other khanates and controlled most of modern-day China and its surrounding areas, including modern Mongolia. It was the first foreign dynasty to rule all of China and lasted until 1368, after which the rebuked Genghisid rulers retreated to their Mongolian homeland and continued to rule the Northern Yuan dynasty. Some of the Mongolian Emperors of the Yuan mastered the Chinese language, while others only used their native language (i.e. Mongolian) and the ‘Phags-pa script.
The Yuan dynasty, officially the Great Yuan, was the empire or ruling dynasty of China established by Kublai Khan, leader of the Mongolian Borjigin clan. It followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although the Mongols had ruled territories including modern-day North China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Chinese style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279. His realm was, by this point, isolated from the other khanates and controlled most of modern-day China and its surrounding areas, including modern Mongolia. It was the first foreign dynasty to rule all of China and lasted until 1368, after which the rebuked Genghisid rulers retreated to their Mongolian homeland and continued to rule the Northern Yuan dynasty. Some of the Mongolian Emperors of the Yuan mastered the Chinese language, while others only used their native language (i.e. Mongolian) and the ‘Phags-pa script. 




