|
France under Louis XV – French King: 1 September 1715 – 10 May 1774
Academy of Sciences
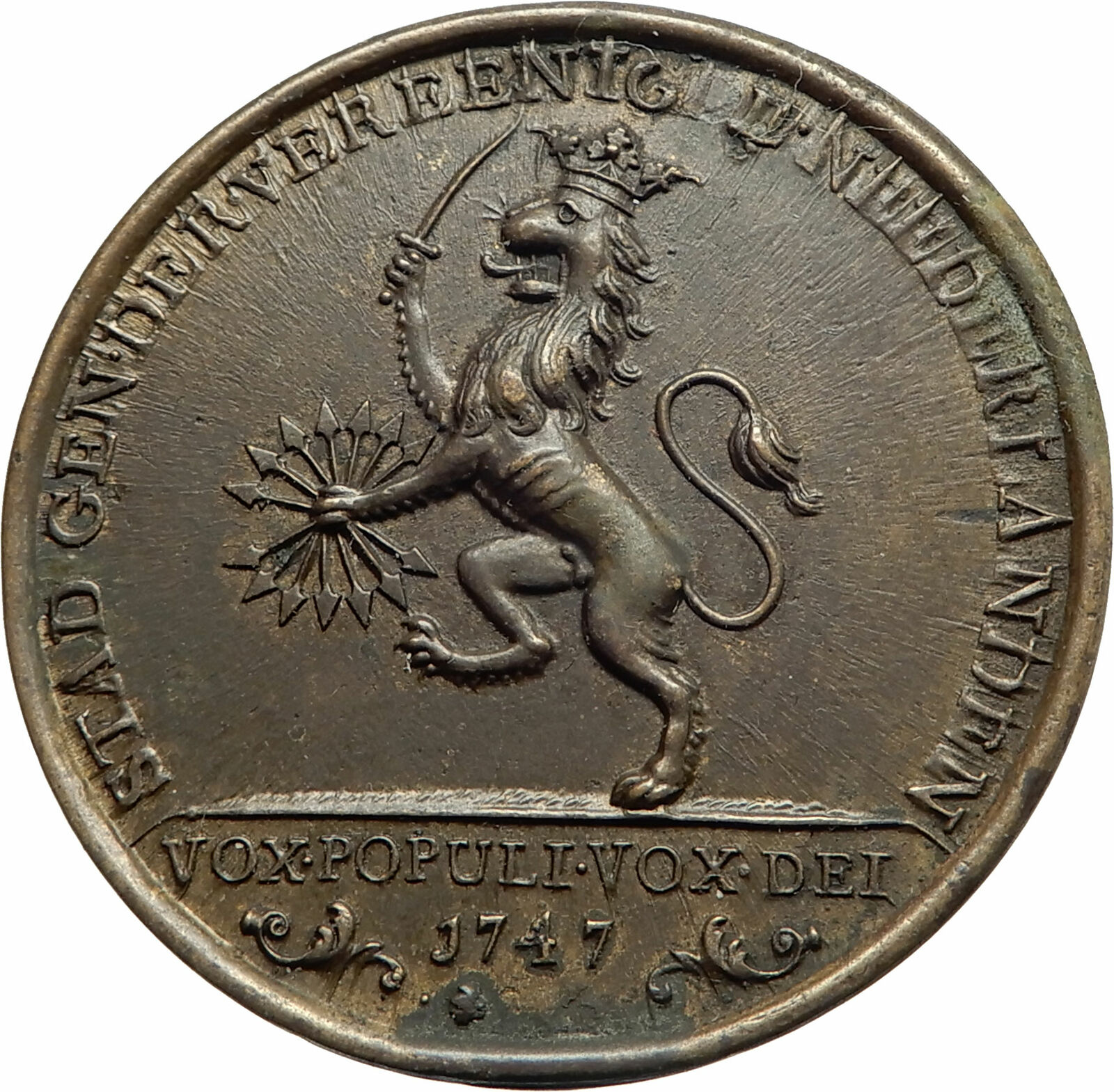
1747 Undated Silver Jeton / Token / Medal 30mm (7.75 grams)
Reference: Feu# 4407
LUD.XV.REX CHRISTIANISS, Louis facing left.
INVENIT ET PERFICIT REGIA SCIENTIARUM ACADEMIA, Athena sitting on various learning instruments.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 The French Academy of Sciences (French: Académie des sciences) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French scientific research. It was at the forefront of scientific developments in Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries, and is one of the earliest Academies of Sciences. The French Academy of Sciences (French: Académie des sciences) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French scientific research. It was at the forefront of scientific developments in Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries, and is one of the earliest Academies of Sciences.
Currently headed by Patrick Flandrin (President of the Academy), it is one of the five Academies of the Institut de France.
The Academy of Sciences traces its origin to Colbert’s plan to create a general academy. He chose a small group of scholars who met on 22 December 1666 in the King’s library, near the present-day Bibliothèque Nationals, and thereafter held twice-weekly working meetings there in the two rooms assigned to the group. The first 30 years of the Academy’s existence were relatively informal, since no statutes had as yet been laid down for the institution.
In contrast to its British counterpart, the Academy was founded as an organ of government. In Paris, there weren’t many membership openings, to fill positions there were tenacious elections. The election process was at least a 6-stage process with rules and regulations that allowed for chosen candidates to canvas other members and for current members to consider postponing certain stages of the process if the need would arise. Elections in the early days of the academy were important activities, and as such made up a large part of the proceedings at the academy, with many meetings being held regarding the election to fill a single vacancy within the academy. That is not to say that discussion of candidates and the election process as a whole was relegated to the meetings. Members that belonged to the vacancy’s respective field would continue discussion of potential candidates for the vacancy in private. Being elected into the Academy didn’t necessarily guarantee being a full member, in some cases, one would enter the academy as an associate or correspondent before being appointed as a full member of the academy.
The election process was originally only to replace members from a specific section. For example, if someone whose study was mathematics was either removed or resigned from his position, the following election process nominated only those whose focus was also mathematics in order to fill that discipline’s vacancy. This led to some periods of time where they couldn’t find specialists for specific fields of study, and had to have positions in those fields vacant, unable to fill them with people in other disciplines.
But after reform in 1987, the academy decided against the practice, favoring filling vacancies with people with new disciplines. This reform was not only aimed at further diversifying the disciplines under the academy, but also to help combat the internal aging of the academy itself. The Academy was expected to remain apolitical, and to avoid discussion of religious and social issues.
 On 20 January 1699, Louis XIV gave the Company its first rules. The Academy received the name of Royal Academy of Sciences and was installed in the Louvre in Paris. Following this reform, the Academy began publishing a volume each year with information on all the work done by its members and obituaries for members who had died. This reform also codified the method by which members of the Academy could receive pensions for their work. On 20 January 1699, Louis XIV gave the Company its first rules. The Academy received the name of Royal Academy of Sciences and was installed in the Louvre in Paris. Following this reform, the Academy began publishing a volume each year with information on all the work done by its members and obituaries for members who had died. This reform also codified the method by which members of the Academy could receive pensions for their work.
The academy was originally organized by the royal reform hierarchically into the following groups: Pensionaires, Pupils, Honoraires, and Associés.
The reform also added new groups not previously recognized, such as Vétéran. Some of these role’s member limits were expanded and some roles even removed or combined throughout the course of academy’s history. The Honoraires group establish by this reform in 1699 whose members were directly appointed by the King was recognized until its abolishment in 1793.
Membership in the academy only exceeded 100 officially recognized full members in 1976, 310 years after the academy’s inception in 1666. The membership increase came with a large-scale reorganization in 1976. Under this reorganization, 130 resident members, 160 correspondents, and 80 foreign associates could be elected.
A vacancy only opens upon the death of a member, as they serve for life. During elections, half of the vacancies are reserved for people less than 55 years old. This was created as an attempt to encourage younger members to join the academy.
The reorganization also divided the academy into 2 divisions:
One division, Division 1, covers the applications of mathematics and physical sciences,
the other, Division 2, covers the applications of chemical, natural, biological, and medical sciences.
On 8 August 1793, the National Convention abolished all the academies. On 22 August 1795, a National Institute of Sciences and Arts was put in place, bringing together the old academies of the sciences, literature and arts, among them the Académie française and the Académie des sciences.
Also in 1795, The Academy determined these 10 titles (first 4 in Division 1 and the others in Division 2) e to be their newly accepted branches of scientific study:
- Mathematics
- Mechanics
- Astronomy
- Physics
- Chemistry
- Mineralogy
- Botany
- Agriculture
- Anatomy and Zoology
- Medicine and Surgery
Jetons or jettons are tokens or coin-like medals produced across Europe from the 13th through the 17th centuries. They were produced as counters for use in calculation on a counting board, a lined board similar to an abacus. They also found use as a money substitute in games, similar to modern casino chips or poker chips.
Thousands of different jetons exist, mostly of religious and educational designs, as well as portraits, the last of which most resemble coinage, somewhat similar to modern, non-circulation commemorative coins. The spelling “jeton” is from the French; the English spell it “jetton”.
 Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved, was a monarch of the House of Bourbon who ruled as King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defined as his 13th birthday) on 15 February 1723, the kingdom was ruled by Philippe II, Duke of Orleans, as Regent of France. Cardinal Fleury was his chief minister from 1726 until the Cardinal’s death in 1743, at which time the young king took sole control of the kingdom. Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved, was a monarch of the House of Bourbon who ruled as King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defined as his 13th birthday) on 15 February 1723, the kingdom was ruled by Philippe II, Duke of Orleans, as Regent of France. Cardinal Fleury was his chief minister from 1726 until the Cardinal’s death in 1743, at which time the young king took sole control of the kingdom.
His reign of almost 59 years (from 1715-1774) was the second longest in the history of France, exceeded only by his predecessor and great-grandfather, Louis XIV who ruled for 72 years (from 1643-1715). In 1748, Louis returned the Austrian Netherlands, won at the Battle of Fontenoy of 1745. He ceded New France in North America to Spain and Great Britain at the conclusion of the disastrous Seven Years’ War in 1763. He incorporated the territories of the Duchy of Lorraine and the Corsican Republic into the Kingdom of France. He was succeeded in 1774 by his grandson Louis XVI, who was executed by guillotine during the French Revolution. Two of his other grandsons, Louis XVIII and Charles X, occupied the throne of France after the fall of Napoleon I. Historians generally give his reign very low marks, especially as wars drained the treasury and set the stage for the governmental collapse and French Revolution in the 1780s.
  France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called Metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people. France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called Metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people.
During the Iron Age, what is now Metropolitan France was inhabited by the Gauls, a Celtic people. The Gauls were conquered in 51 BC by the Roman Empire, which held Gaul until 486. The Gallo-Romans faced raids and migration from the Germanic Franks, who dominated the region for hundreds of years, eventually creating the medieval Kingdom of France. France emerged as a major European power in the Late Middle Ages, with its victory in the Hundred Years’ War (1337 to 1453) strengthening French state-building and paving the way for a future centralized absolute monarchy. During the Renaissance, France experienced a vast cultural development and established the beginning of a global colonial empire. The 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Protestants (Huguenots).
France became Europe’s dominant cultural, political, and military power under Louis XIV. French philosophers played a key role in the Age of Enlightenment during the 18th century. In 1778, France became the first and the main ally of the new United States in the American Revolutionary War. In the late 18th century, the absolute monarchy was overthrown in the French Revolution. Among its legacies was the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, one of the earliest documents on human rights, which expresses the nation’s ideals to this day. France became one of modern history’s earliest republics until Napoleon took power and launched the First French Empire in 1804. Fighting against a complex set of coalitions during the Napoleonic Wars, he dominated European affairs for over a decade and had a long-lasting impact on Western culture. Following the collapse of the Empire, France endured a tumultuous succession of governments: the monarchy was restored, it was replaced in 1830 by a constitutional monarchy, then briefly by a Second Republic, and then by a Second Empire, until a more lasting French Third Republic was established in 1870. By the 1905 law, France adopted a strict form of secularism, called laïcité, which has become an important federative principle in the modern French society.
France reached its territorial height during the 19th and early 20th centuries, when it ultimately possessed the second-largest colonial empire in the world. In World War I, France was one of the main winners as part of the Triple Entente alliance fighting against the Central Powers. France was also one of the Allied Powers in World War II, but came under occupation by the Axis Powers in 1940. Following liberation in 1944, a Fourth Republic was established and later dissolved in the course of the Algerian War. The Fifth Republic, led by Charles de Gaulle, was formed in 1958 and remains to this day. Following World War II, most of the empire became decolonized.
Throughout its long history, France has been a leading global center of culture, making significant contributions to art, science, and philosophy. It hosts Europe’s third-largest number of cultural UNESCO World Heritage Sites (after Italy and Spain) and receives around 83 million foreign tourists annually, the most of any country in the world. France remains a great power with significant cultural, economic, military, and political influence. It is a developed country with the world’s sixth-largest economy by nominal GDP and eight-largest by purchasing power parity. According to Credit Suisse, France is the fourth wealthiest nation in the world in terms of aggregate household wealth. It also possesses the world’s second-largest exclusive economic zone (EEZ), covering 11,035,000 square kilometres (4,261,000 sq mi).
French citizens enjoy a high standard of living, and the country performs well in international rankings of education, health care, life expectancy, civil liberties, and human development. France is a founding member of the United Nations, where it serves as one of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council. It is a member of the Group of 7, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the World Trade Organization (WTO), and La Francophonie. France is a founding and leading member state of the European Union (EU).
|





 The French Academy of Sciences (French: Académie des sciences) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French scientific research. It was at the forefront of scientific developments in Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries, and is one of the earliest Academies of Sciences.
The French Academy of Sciences (French: Académie des sciences) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French scientific research. It was at the forefront of scientific developments in Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries, and is one of the earliest Academies of Sciences. On 20 January 1699, Louis XIV gave the Company its first rules. The Academy received the name of Royal Academy of Sciences and was installed in the Louvre in Paris. Following this reform, the Academy began publishing a volume each year with information on all the work done by its members and obituaries for members who had died. This reform also codified the method by which members of the Academy could receive pensions for their work.
On 20 January 1699, Louis XIV gave the Company its first rules. The Academy received the name of Royal Academy of Sciences and was installed in the Louvre in Paris. Following this reform, the Academy began publishing a volume each year with information on all the work done by its members and obituaries for members who had died. This reform also codified the method by which members of the Academy could receive pensions for their work. Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved, was a monarch of the House of Bourbon who ruled as King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defined as his 13th birthday) on 15 February 1723, the kingdom was ruled by Philippe II, Duke of Orleans, as Regent of France. Cardinal Fleury was his chief minister from 1726 until the Cardinal’s death in 1743, at which time the young king took sole control of the kingdom.
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved, was a monarch of the House of Bourbon who ruled as King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defined as his 13th birthday) on 15 February 1723, the kingdom was ruled by Philippe II, Duke of Orleans, as Regent of France. Cardinal Fleury was his chief minister from 1726 until the Cardinal’s death in 1743, at which time the young king took sole control of the kingdom. 
 France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called Metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people.
France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called Metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people.





