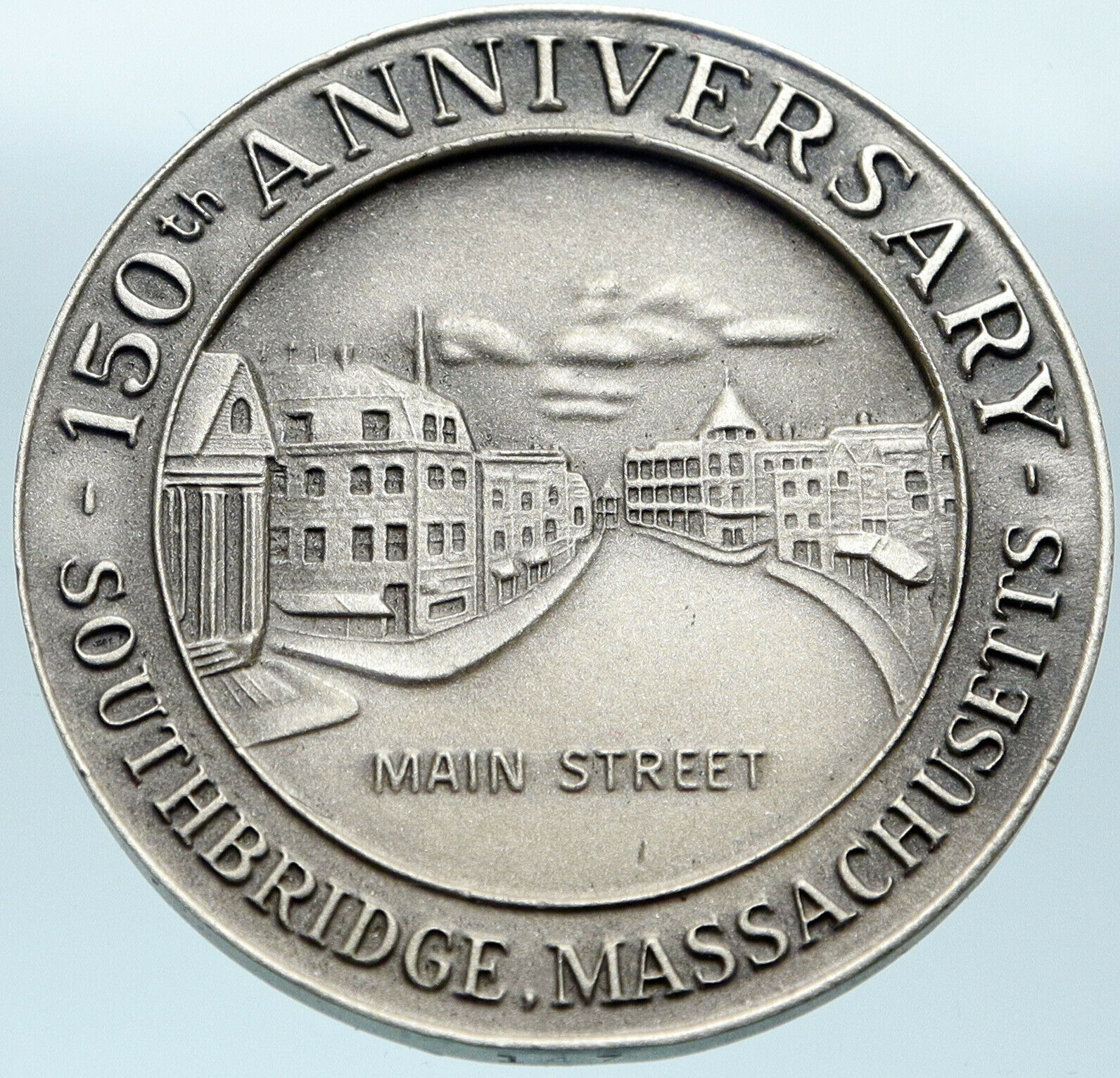|
England. Wales. Anglesey Conder Token
1791 Copper ‘Half Penny’ Conder Token 29mm (12.79 grams)
Reference: D&H 391
Certification: NGC MS 62 BN 5709572-012
Druid’s hooded head left within oak sprigs.
THE ANGLESEY MINES HALFPENNY 1971 around mouogram.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Conder Tokens, also known as 18th Century Provincial Tokens, are a form of privately minted token coinage struck and used during the latter part of the 18th Century and the early part of the 19th Century in England, Anglesey and Wales, Scotland, and Ireland.
The driving force behind the need for token coinage was the shortage of small denomination coins for everyday transactions. However, the demand was fueled by other factors such as the Industrial Revolution, population growth, and the preponderance of counterfeit circulating coins. Because the government made little effort to ameliorate this shortage, private business owners and merchants took matters into their own hands, and the first tokens of this type were issued in 1787 to pay workers at the Parys Mine Company. By 1795, millions of tokens of a few thousand varying designs had been struck and were in common use throughout Great Britain.
Collecting Conder tokens has been popular since shortly after they were first manufactured, resulting in the availability today of many highly preserved examples for collectors. The demarcation of what is or is not considered a Conder token is somewhat unclear; however, most collectors consider Conder tokens to include those indexed originally by James Conder or later by Dalton & Hamer.
 Anglesey is an island situated on the north coast of Wales with an area of 276 square miles (715 km2). Anglesey is by far the largest island in Wales and the seventh largest in the British Isles. Anglesey is also the largest island in the Irish Sea by area, and the second most populous island (after the Isle of Man). The ferry port of Holyhead handles more than 2 million passengers each year. The Menai Suspension Bridge, designed by Thomas Telford in 1826, and the Britannia Bridge span the Menai Strait to connect Anglesey with the mainland. Anglesey is an island situated on the north coast of Wales with an area of 276 square miles (715 km2). Anglesey is by far the largest island in Wales and the seventh largest in the British Isles. Anglesey is also the largest island in the Irish Sea by area, and the second most populous island (after the Isle of Man). The ferry port of Holyhead handles more than 2 million passengers each year. The Menai Suspension Bridge, designed by Thomas Telford in 1826, and the Britannia Bridge span the Menai Strait to connect Anglesey with the mainland.
 Anglesey, one of the historic counties of Wales was administered as part of Gwynedd, but along with Holy Island and other smaller islands, it is now governed by the Isle of Anglesey County Council. The majority of Anglesey’s inhabitants are Welsh speakers and Ynys Môn, the Welsh name for the island, is used for the UK Parliament and National Assembly constituencies. The population at the 2011 census was 69,751. Anglesey, one of the historic counties of Wales was administered as part of Gwynedd, but along with Holy Island and other smaller islands, it is now governed by the Isle of Anglesey County Council. The majority of Anglesey’s inhabitants are Welsh speakers and Ynys Môn, the Welsh name for the island, is used for the UK Parliament and National Assembly constituencies. The population at the 2011 census was 69,751.
 A druid (Welsh: derwydd; Old Irish: druí; Scottish Gaelic: draoidh) was a member of the high-ranking professional class in ancient Celtic cultures. Perhaps best remembered as religious leaders, they were also legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals, and political advisors. While the druids are reported to have been literate, they are believed to have been prevented by doctrine from recording their knowledge in written form, thus they left no written accounts of themselves. They are however attested in some detail by their contemporaries from other cultures, such as the Romans and the Greeks. A druid (Welsh: derwydd; Old Irish: druí; Scottish Gaelic: draoidh) was a member of the high-ranking professional class in ancient Celtic cultures. Perhaps best remembered as religious leaders, they were also legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals, and political advisors. While the druids are reported to have been literate, they are believed to have been prevented by doctrine from recording their knowledge in written form, thus they left no written accounts of themselves. They are however attested in some detail by their contemporaries from other cultures, such as the Romans and the Greeks.
The earliest known references to the druids date to the fourth century BCE and the oldest detailed description comes from Julius Caesar’s Commentarii de Bello Gallico (50s BCE). They were also described by later Greco-Roman writers such as Cicero, Tacitus, and Pliny the Elder. Following the Roman invasion of Gaul, the druid orders were suppressed by the Roman government under the 1st century CE emperors Tiberius and Claudius, and had disappeared from the written record by the 2nd century.
In about 750 CE the word druid appears in a poem by Blathmac, who wrote about Jesus, saying that he was “… better than a prophet, more knowledgeable than every druid, a king who was a bishop and a complete sage.” The druids then also appear in some of the medieval tales from Christianized Ireland like the “Táin Bó Cúailnge”, where they are largely portrayed as sorcerers who opposed the coming of Christianity. In the wake of the Celtic revival during the 18th and 19th centuries, fraternal and neopagan groups were founded based on ideas about the ancient druids, a movement known as Neo-Druidism. Many popular notions about druids, based on misconceptions of 18th century scholars, have been largely superseded by more recent study.
|









 Anglesey is an island situated on the north coast of Wales with an area of 276 square miles (715 km2). Anglesey is by far the largest island in Wales and the seventh largest in the British Isles. Anglesey is also the largest island in the Irish Sea by area, and the second most populous island (after the Isle of Man). The ferry port of Holyhead handles more than 2 million passengers each year. The Menai Suspension Bridge, designed by Thomas Telford in 1826, and the Britannia Bridge span the Menai Strait to connect Anglesey with the mainland.
Anglesey is an island situated on the north coast of Wales with an area of 276 square miles (715 km2). Anglesey is by far the largest island in Wales and the seventh largest in the British Isles. Anglesey is also the largest island in the Irish Sea by area, and the second most populous island (after the Isle of Man). The ferry port of Holyhead handles more than 2 million passengers each year. The Menai Suspension Bridge, designed by Thomas Telford in 1826, and the Britannia Bridge span the Menai Strait to connect Anglesey with the mainland.  Anglesey, one of the historic counties of Wales was administered as part of Gwynedd, but along with Holy Island and other smaller islands, it is now governed by the Isle of Anglesey County Council. The majority of Anglesey’s inhabitants are Welsh speakers and Ynys Môn, the Welsh name for the island, is used for the UK Parliament and National Assembly constituencies. The population at the 2011 census was 69,751.
Anglesey, one of the historic counties of Wales was administered as part of Gwynedd, but along with Holy Island and other smaller islands, it is now governed by the Isle of Anglesey County Council. The majority of Anglesey’s inhabitants are Welsh speakers and Ynys Môn, the Welsh name for the island, is used for the UK Parliament and National Assembly constituencies. The population at the 2011 census was 69,751.  A druid (Welsh: derwydd; Old Irish: druí; Scottish Gaelic: draoidh) was a member of the high-ranking professional class in ancient Celtic cultures. Perhaps best remembered as religious leaders, they were also legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals, and political advisors. While the druids are reported to have been literate, they are believed to have been prevented by doctrine from recording their knowledge in written form, thus they left no written accounts of themselves. They are however attested in some detail by their contemporaries from other cultures, such as the Romans and the Greeks.
A druid (Welsh: derwydd; Old Irish: druí; Scottish Gaelic: draoidh) was a member of the high-ranking professional class in ancient Celtic cultures. Perhaps best remembered as religious leaders, they were also legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals, and political advisors. While the druids are reported to have been literate, they are believed to have been prevented by doctrine from recording their knowledge in written form, thus they left no written accounts of themselves. They are however attested in some detail by their contemporaries from other cultures, such as the Romans and the Greeks.