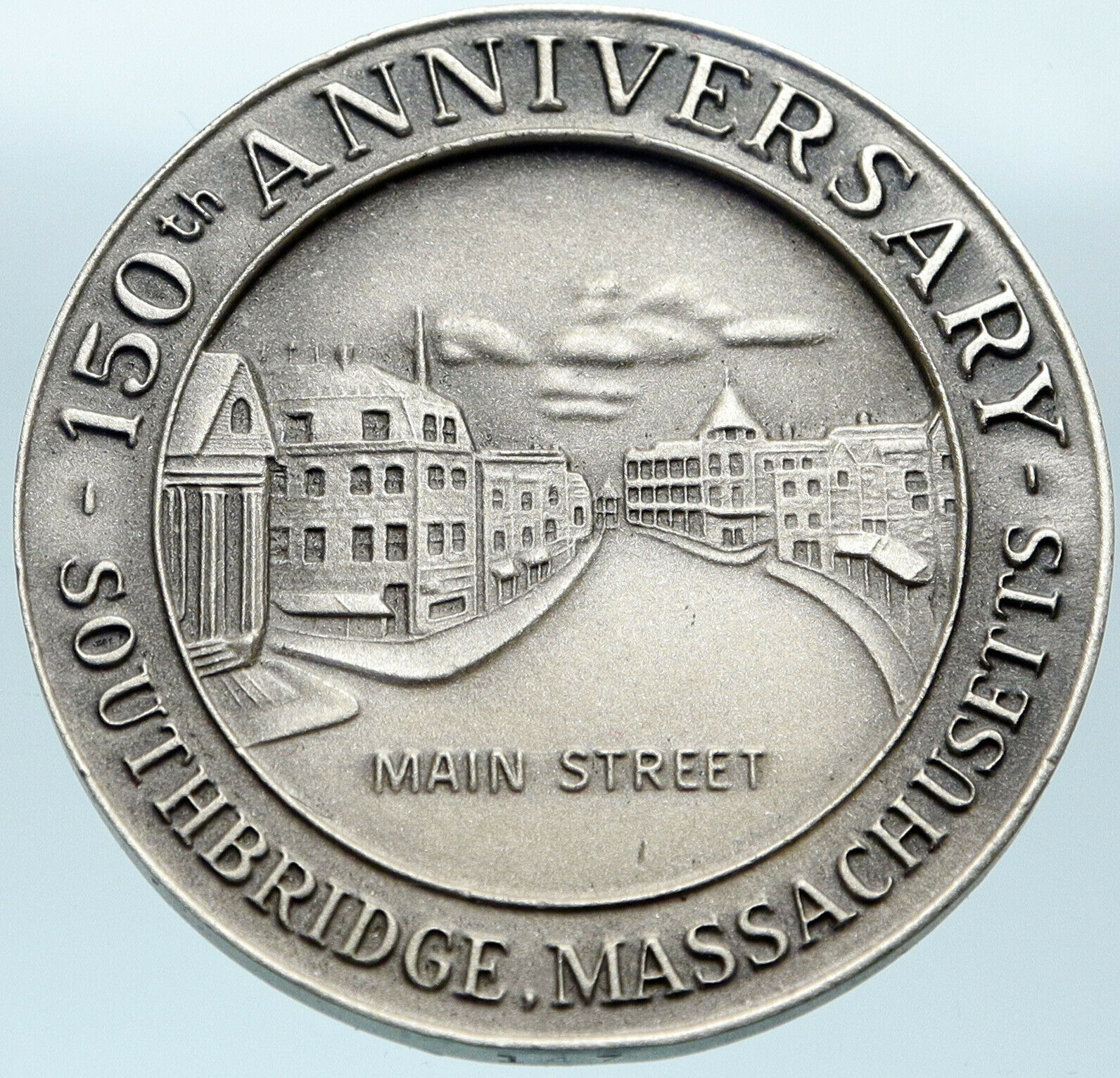|
France
– Agriculture of Clermont-Ferrand
1886 Bronze Medal 51mm (58.30 grams)
REPUBLIQUE FRANCAISE H. PONSCARME, Winged liberty head left,
star atop.
MINISTRE DE L’AGRICVLTVRE CLERMONT-FERRAND 1886 CONCOURS REGAL AGRLE E DE
CONDUCTEURS D’APPAREILS H.PONSCARME, Caduceus amid flora.
Edge Lettering:
BRONZE 1886
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Clermont-Ferrand is a city and commune of France, in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region, with a population of 143,886 (2017). Its metropolitan area (aire urbaine) had 485,315 inhabitants at the 2017 census. It is the prefecture (capital) of the Puy-de-Dôme department. Olivier Bianchi is its current mayor.
 Clermont-Ferrand sits on the plain of Limagne in the Massif Central and is surrounded by a major industrial area. The city known for the chain of volcanoes, the Chaîne des Puys surrounding it, including the dormant volcano Puy de Dôme (10 kilometres (6 miles)), one of the highest, topped by communications towers, and visible from the city, which is inscribed since July 2018 as a “tectonic hotspot” on the UNESCO World Heritage List. Clermont-Ferrand sits on the plain of Limagne in the Massif Central and is surrounded by a major industrial area. The city known for the chain of volcanoes, the Chaîne des Puys surrounding it, including the dormant volcano Puy de Dôme (10 kilometres (6 miles)), one of the highest, topped by communications towers, and visible from the city, which is inscribed since July 2018 as a “tectonic hotspot” on the UNESCO World Heritage List.
One of the oldest French cities, it has been known by Greeks as the capital of the Arvernie Tribe before developing under the Gallo-Roman era under the name of Augustonemetum in the 1st century BC. The forum of the Roman city was located on the top of the Clermont mound, on the site of the present cathedral. During the decline of the Western Roman Empire it was subjected to repeated looting by the peoples who invaded Gaul, including Vandals, Alans, Visigoths and Franks. It was later raided by Vikings during the weakening of the Carolingian Empire in the Early Middle Ages. Growing in importance under the Capetian dynasty, in 1095 it hosted the Council of Clermont, where Pope Urban II called the First Crusade. In 1551, Clermont became a royal town, and further made in 1610, inseparable property of the Crown.
Today Clermont-Ferrand hosts the Clermont-Ferrand International Short Film Festival (Festival du Court-Métrage de Clermont-Ferrand), one of the world’s leading international festivals for short films. It is also home to the corporate headquarters of Michelin, the global tyre company founded there more than 100 years ago. With a quarter of the municipal population being students, and 6,000 researchers, Clermont-Ferrand is the first city in France to join the UNESCO Learning City Network.
Along with its highly distinctive black lava stone Gothic Cathedral, Clermont-Ferrand’s most famous site includes the public square Place de Jaude, on which stands a grand statue of Vercingetorix astride a warhorse and brandishing a sword. The inscription reads: J’ai pris les armes pour la liberté de tous (I took up arms for the liberty of all). This statue was sculpted by Frédéric Bartholdi, who also created the Statue of Liberty.
  France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called Metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people. France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called Metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people.
During the Iron Age, what is now Metropolitan France was inhabited by the Gauls, a Celtic people. The Gauls were conquered in 51 BC by the Roman Empire, which held Gaul until 486. The Gallo-Romans faced raids and migration from the Germanic Franks, who dominated the region for hundreds of years, eventually creating the medieval Kingdom of France. France emerged as a major European power in the Late Middle Ages, with its victory in the Hundred Years’ War (1337 to 1453) strengthening French state-building and paving the way for a future centralized absolute monarchy. During the Renaissance, France experienced a vast cultural development and established the beginning of a global colonial empire. The 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Protestants (Huguenots).
France became Europe’s dominant cultural, political, and military power under Louis XIV. French philosophers played a key role in the Age of Enlightenment during the 18th century. In 1778, France became the first and the main ally of the new United States in the American Revolutionary War. In the late 18th century, the absolute monarchy was overthrown in the French Revolution. Among its legacies was the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, one of the earliest documents on human rights, which expresses the nation’s ideals to this day. France became one of modern history’s earliest republics until Napoleon took power and launched the First French Empire in 1804. Fighting against a complex set of coalitions during the Napoleonic Wars, he dominated European affairs for over a decade and had a long-lasting impact on Western culture. Following the collapse of the Empire, France endured a tumultuous succession of governments: the monarchy was restored, it was replaced in 1830 by a constitutional monarchy, then briefly by a Second Republic, and then by a Second Empire, until a more lasting French Third Republic was established in 1870. By the 1905 law, France adopted a strict form of secularism, called laïcité, which has become an important federative principle in the modern French society.
France reached its territorial height during the 19th and early 20th centuries, when it ultimately possessed the second-largest colonial empire in the world. In World War I, France was one of the main winners as part of the Triple Entente alliance fighting against the Central Powers. France was also one of the Allied Powers in World War II, but came under occupation by the Axis Powers in 1940. Following liberation in 1944, a Fourth Republic was established and later dissolved in the course of the Algerian War. The Fifth Republic, led by Charles de Gaulle, was formed in 1958 and remains to this day. Following World War II, most of the empire became decolonized.
Throughout its long history, France has been a leading global center of culture, making significant contributions to art, science, and philosophy. It hosts Europe’s third-largest number of cultural UNESCO World Heritage Sites (after Italy and Spain) and receives around 83 million foreign tourists annually, the most of any country in the world. France remains a great power with significant cultural, economic, military, and political influence. It is a developed country with the world’s sixth-largest economy by nominal GDP and eight-largest by purchasing power parity. According to Credit Suisse, France is the fourth wealthiest nation in the world in terms of aggregate household wealth. It also possesses the world’s second-largest exclusive economic zone (EEZ), covering 11,035,000 square kilometres (4,261,000 sq mi).
French citizens enjoy a high standard of living, and the country performs well in international rankings of education, health care, life expectancy, civil liberties, and human development. France is a founding member of the United Nations, where it serves as one of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council. It is a member of the Group of 7, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the World Trade Organization (WTO), and La Francophonie. France is a founding and leading member state of the European Union (EU).
|




 Clermont-Ferrand sits on the plain of Limagne in the Massif Central and is surrounded by a major industrial area. The city known for the chain of volcanoes, the Chaîne des Puys surrounding it, including the dormant volcano Puy de Dôme (10 kilometres (6 miles)), one of the highest, topped by communications towers, and visible from the city, which is inscribed since July 2018 as a “tectonic hotspot” on the UNESCO World Heritage List.
Clermont-Ferrand sits on the plain of Limagne in the Massif Central and is surrounded by a major industrial area. The city known for the chain of volcanoes, the Chaîne des Puys surrounding it, including the dormant volcano Puy de Dôme (10 kilometres (6 miles)), one of the highest, topped by communications towers, and visible from the city, which is inscribed since July 2018 as a “tectonic hotspot” on the UNESCO World Heritage List.
 France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called Metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people.
France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called Metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people.