|
Vietnam – Nguyen Dynasty (1802-1945)
Thanh Thai – Emperor: 1889-1907
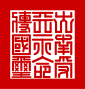
Bronze Thanh Thai Thong Bao Cash Token 24mm, Struck 1889-1907
Reference: B 107.3, H 25.40, No=13
Chinese Symbols.
Van.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
.jpg/220px-Emperor_Thanh_Thai_in_court_costume_(colored).jpg) Thành Thái (成泰; 14 March 1879 – 20 March 1954) born Nguyễn Phúc Bửu Lân (阮福寶嶙), was the son of Emperor Dục Đức and Empress Dowager Từ Minh. He reigned as emperor for 18 years, from 1889 to 1907. Thành Thái (成泰; 14 March 1879 – 20 March 1954) born Nguyễn Phúc Bửu Lân (阮福寶嶙), was the son of Emperor Dục Đức and Empress Dowager Từ Minh. He reigned as emperor for 18 years, from 1889 to 1907.
While the emperor Tự Đức was alive, Prince Quang Thái was placed under house arrest with his family for having connections with those who opposed him. When the emperor Đồng Khánh died, however, the French colonial authorities and the high-ranking mandarins decided that Quang Thái was the ideal successor and enthroned him as the new Vietnamese emperor, Emperor Thành Thái.
At the age of 10, Thành Thái was recognized as being very intelligent and was already realizing that the French were keeping watch over him through palace spies. Whereas Đồng Khánh had tried to be friendly with the French, Emperor Thành Thái took a course of passive-resistance. Although he refrained from outright rebellion (which would have been political suicide), he made his feelings clear in other ways, symbolic gestures and biting remarks. He was also a man of the people, and a monarch who cared deeply for his country. The emperor would often slip out of the Forbidden City dressed in the clothes of a commoner to talk with his people directly and see how they were being affected by government policies.
Opposing French authority
To show that he was friendly with western civilization, Thành Thái was the first Vietnamese monarch to cut his hair in the French style and learn to drive a car. He encouraged French-style education, but maintained bitter feelings over their control of his country. He also supported numerous building projects and took an interest in the everyday lives of his subjects. When traveling among his people, he would hold impromptu “town hall meetings” where the Emperor sat on a mat with his subjects in a circle around him, discussing the issues of the day and hearing their point of view.
Slowly, as the emperor began to realize how thoroughly his palace had been infiltrated with French spies, he had to feign insanity to escape their constant scrutiny. With his enemies believing he was a harmless lunatic, Thành Thái was able to push more forcefully for Vietnamese autonomy while waiting for the right time to overthrow the French colonial rule. He was on his way to join a resistance movement in China when he was arrested by French forces who declared him insane and forced the Emperor to abdicate.
In 1907, his son was installed as Emperor Duy Tân. Thành Thái was exiled first to Vũng Tàu in South Vietnam and when Duy Tân rebelled against the French they were both exiled to Réunion Island in 1916.
Unlike Hàm Nghi, the lives of Thành Thái and Duy Tân were tough. They even had no money to pay for rent. In 1925, Emperor Khải Định knew his situation and sent 1,000 piastres to him. Khải Định later occasionally gave him money.
He never gave up hope for the liberation of his country. In 1945, just after the death of Duy Tân, he was allowed to return home, but was kept under house arrest in Vũng Tàu. He died in Saigon on 24 March 1954 and was buried on the grounds of An Lang (Tomb of Duc Duc) in an old commune, Hương Thủy disctrict, Thừa Thiên Huế Province, at the age of 75.
 The Nguyễn dynasty (Chữ Nôm: 茹阮, Vietnamese: Nhà Nguyễn; Hán tự: 阮朝, Vietnamese: Nguyễn triều) was the last Vietnamese dynasty, which ruled the unified Vietnamese state largely independently from 1802 to 1884. During its existence, the empire expanded into modern-day southern Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos through a continuation of the centuries-long Nam tiến and Siamese–Vietnamese wars. After 1883, the Nguyễn emperors ruled nominally as heads of state of the French protectorates of Annam and Tonkin until the final months of WWII; they later nominally ruled over the Empire of Vietnam until the Japanese surrender. The Nguyễn dynasty (Chữ Nôm: 茹阮, Vietnamese: Nhà Nguyễn; Hán tự: 阮朝, Vietnamese: Nguyễn triều) was the last Vietnamese dynasty, which ruled the unified Vietnamese state largely independently from 1802 to 1884. During its existence, the empire expanded into modern-day southern Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos through a continuation of the centuries-long Nam tiến and Siamese–Vietnamese wars. After 1883, the Nguyễn emperors ruled nominally as heads of state of the French protectorates of Annam and Tonkin until the final months of WWII; they later nominally ruled over the Empire of Vietnam until the Japanese surrender.

The Nguyễn Phúc family established feudal rule over large amounts of territory as the Nguyễn Lords by the 16th century before defeating the Tây Sơn dynasty and establishing their own imperial rule in the 19th century. The dynastic rule began with Gia Long ascending the throne in 1802, after ending the previous Tây Sơn dynasty. The Nguyễn dynasty was gradually absorbed by France over the course of several decades in the latter half of the 19th century, beginning with the Cochinchina Campaign in 1858 which led to the occupation of the southern area of Vietnam. A series of unequal treaties followed; the occupied territory became the French colony of Cochinchina in the 1862 Treaty of Saigon, and the 1863 Treaty of Huế gave France access to Vietnamese ports and increased control of its foreign affairs. Finally, the 1883 and 1884 Treaties of Huế divided the remaining Vietnamese territory into the protectorates of Annam and Tonkin under nominal Nguyễn Phúc rule. In 1887, Cochinchina, Annam, Tonkin, and the French Protectorate of Cambodia were grouped together to form French Indochina.
The Nguyễn dynasty remained the formal emperors of Annam and Tonkin within Indochina until World War II. Japan had occupied Indochina with French collaboration in 1940, but as the war seemed increasingly lost, overthrew the French administration in March 1945 and proclaimed independence for its constituent countries. The Empire of Vietnam under Emperor Bảo Đại was a nominally independent Japanese puppet state during the last months of the war. It ended with Bảo Đại’s abdication following the surrender of Japan and August Revolution by the anti-colonial Việt Minh in the August 1945. This ended the 143-year rule of the Nguyễn dynasty. Many Vietnamese historians have a harsh and poor assessment of the Nguyễn dynasty.
|





.jpg/220px-Emperor_Thanh_Thai_in_court_costume_(colored).jpg) Thành Thái (成泰; 14 March 1879 – 20 March 1954) born Nguyễn Phúc Bửu Lân (阮福寶嶙), was the son of Emperor Dục Đức and Empress Dowager Từ Minh. He reigned as emperor for 18 years, from 1889 to 1907.
Thành Thái (成泰; 14 March 1879 – 20 March 1954) born Nguyễn Phúc Bửu Lân (阮福寶嶙), was the son of Emperor Dục Đức and Empress Dowager Từ Minh. He reigned as emperor for 18 years, from 1889 to 1907. The Nguyễn dynasty (Chữ Nôm: 茹阮, Vietnamese: Nhà Nguyễn; Hán tự: 阮朝, Vietnamese: Nguyễn triều) was the last Vietnamese dynasty, which ruled the unified Vietnamese state largely independently from 1802 to 1884. During its existence, the empire expanded into modern-day southern Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos through a continuation of the centuries-long Nam tiến and Siamese–Vietnamese wars. After 1883, the Nguyễn emperors ruled nominally as heads of state of the French protectorates of Annam and Tonkin until the final months of WWII; they later nominally ruled over the Empire of Vietnam until the Japanese surrender.
The Nguyễn dynasty (Chữ Nôm: 茹阮, Vietnamese: Nhà Nguyễn; Hán tự: 阮朝, Vietnamese: Nguyễn triều) was the last Vietnamese dynasty, which ruled the unified Vietnamese state largely independently from 1802 to 1884. During its existence, the empire expanded into modern-day southern Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos through a continuation of the centuries-long Nam tiến and Siamese–Vietnamese wars. After 1883, the Nguyễn emperors ruled nominally as heads of state of the French protectorates of Annam and Tonkin until the final months of WWII; they later nominally ruled over the Empire of Vietnam until the Japanese surrender.





