|
Germany – German States – Kingdom of Bavaria (Bayern)
Otto I – King: 1886-1913
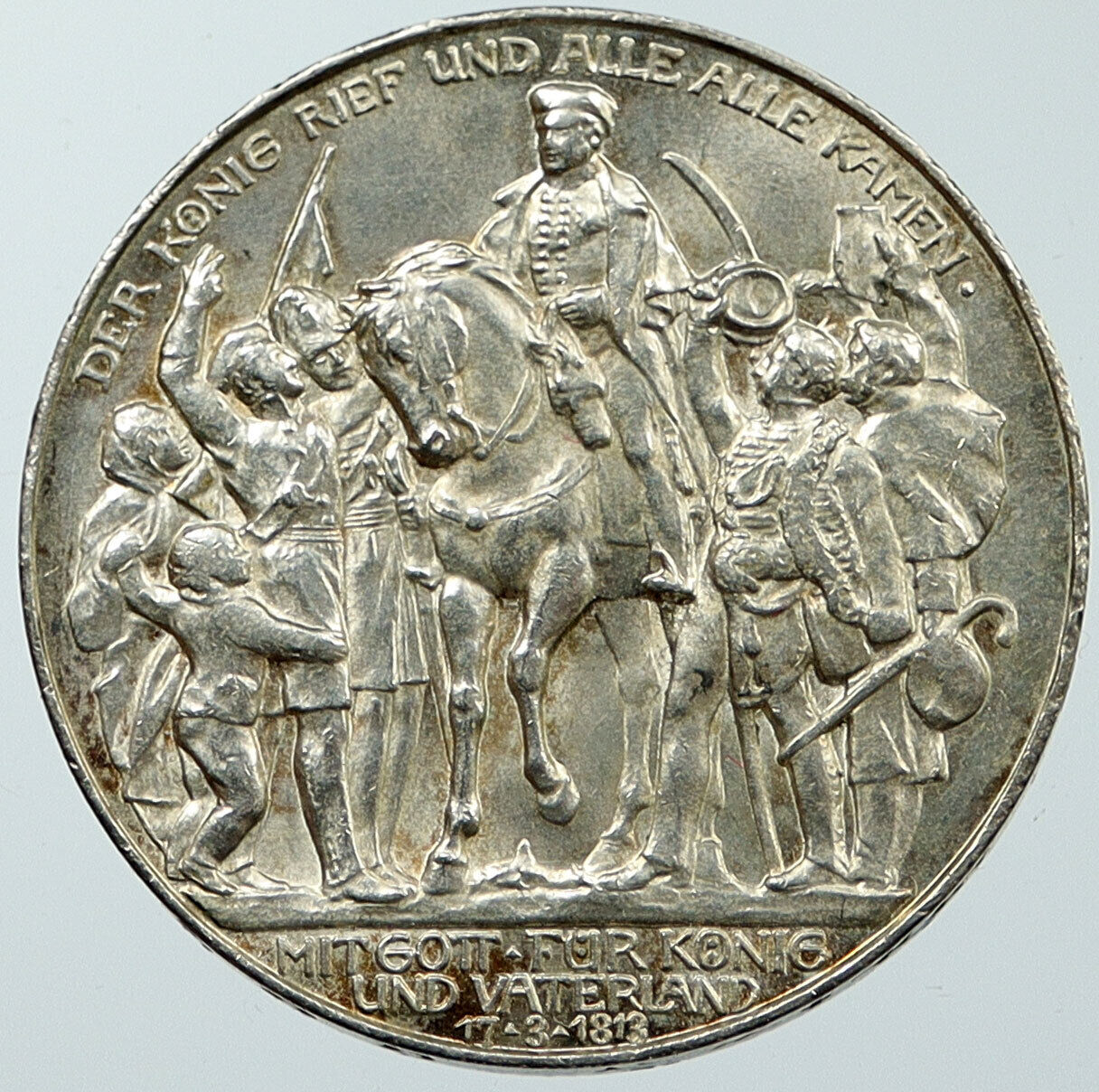
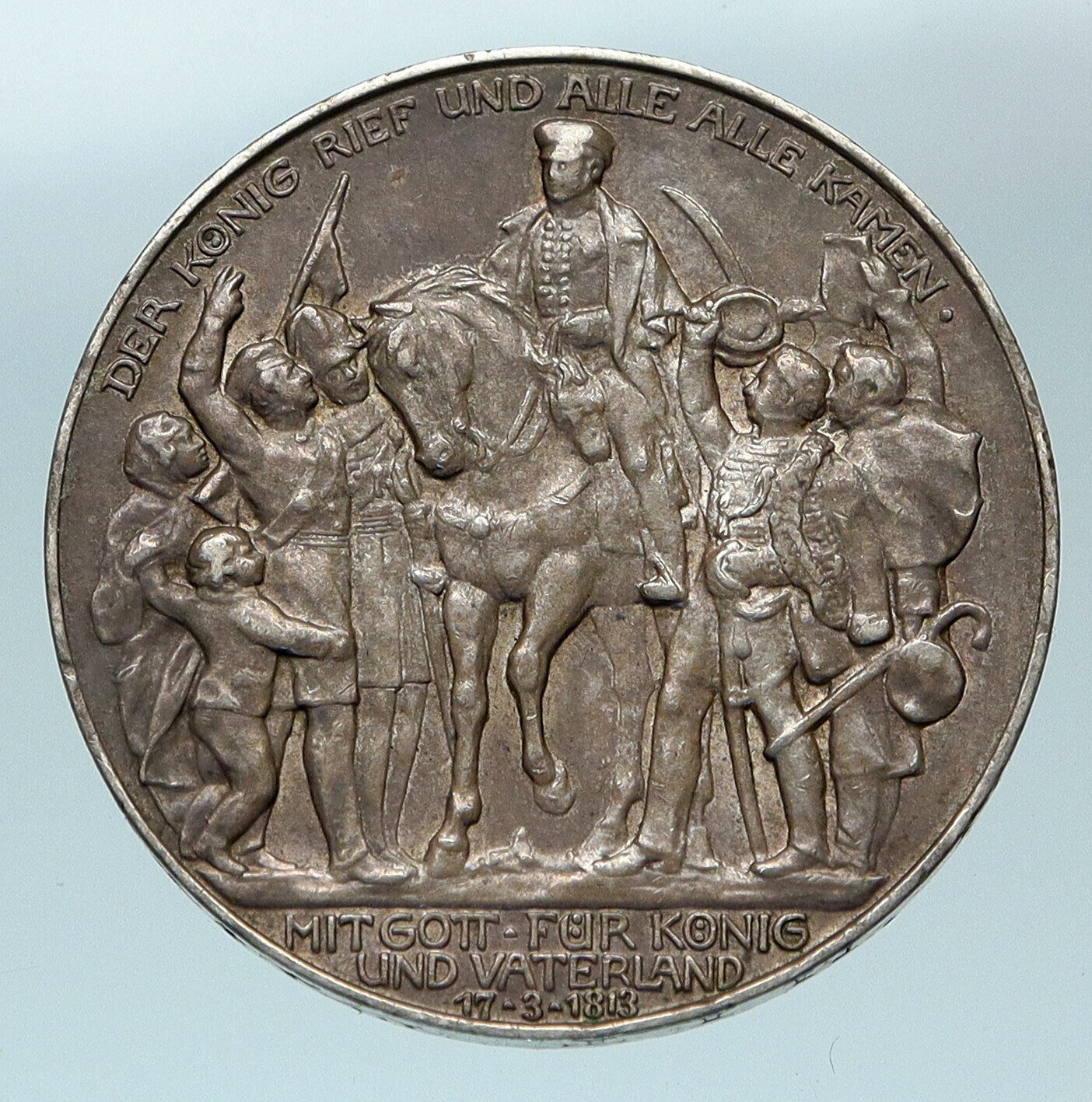
1909 D Silver 3 Mark 33mm (16.67 grams) 0.900 Silver (0.4792 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 996; J# 47; AKS# 202
Certification: NGC AU DETAILS 4657920-005
OTTO KOENIG VON BAYERN D, Head of King Otto I left.
DEUTSCHES REICH 1912 * DREI MARK *, Crowned imperial eagle, shield on breast.
Edge Lettering: GOTT MIT UNS
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 Otto (German: Otto Wilhelm Luitpold Adalbert Waldemar; 27 April 1848 – 11 October 1916), was King of Bavaria from 1886 to 1913. However, he never actively ruled due to severe mental illness; his uncle, Luitpold, and cousin, Ludwig, served as regents. Ludwig deposed him in 1913 a day after the legislature passed a law allowing him to do so, becoming king in his own right. Otto (German: Otto Wilhelm Luitpold Adalbert Waldemar; 27 April 1848 – 11 October 1916), was King of Bavaria from 1886 to 1913. However, he never actively ruled due to severe mental illness; his uncle, Luitpold, and cousin, Ludwig, served as regents. Ludwig deposed him in 1913 a day after the legislature passed a law allowing him to do so, becoming king in his own right.
He was the son of Maximilian II and his wife, Marie of Prussia, and younger brother of Ludwig II. King Otto of Bavaria is not to be confused with King Otto of Greece, who was his uncle and godfather.
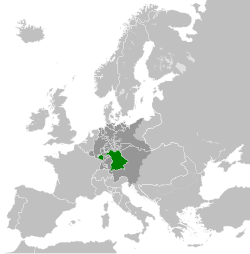 The Kingdom of Bavaria (German: Königreich Bayern; Austro-Bavarian: Kinereich Bayern) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. The Bavarian Elector Maximilian IV Joseph of the House of Wittelsbach became the first King of Bavaria in 1805 as Maximilian I Joseph. The crown would go on being held by the Wittelsbachs until the kingdom came to an end in 1918. Most of Bavaria’s present-day borders were established after 1814 with the Treaty of Paris, in which Bavaria ceded Tyrol and Vorarlberg to the Austrian Empire while receiving Aschaffenburg and Würzburg. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingdom became a federal state of the new Empire and was second in size, power, and wealth only to the leading state, the Kingdom of Prussia. In 1918 Bavaria became a republic, and the kingdom was thus succeeded by the current Free State of Bavaria. The Kingdom of Bavaria (German: Königreich Bayern; Austro-Bavarian: Kinereich Bayern) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. The Bavarian Elector Maximilian IV Joseph of the House of Wittelsbach became the first King of Bavaria in 1805 as Maximilian I Joseph. The crown would go on being held by the Wittelsbachs until the kingdom came to an end in 1918. Most of Bavaria’s present-day borders were established after 1814 with the Treaty of Paris, in which Bavaria ceded Tyrol and Vorarlberg to the Austrian Empire while receiving Aschaffenburg and Würzburg. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingdom became a federal state of the new Empire and was second in size, power, and wealth only to the leading state, the Kingdom of Prussia. In 1918 Bavaria became a republic, and the kingdom was thus succeeded by the current Free State of Bavaria.
 Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, officially the Federal Republic of  Germany is a federal parliamentary republic in western-central Europe. It includes 16 constituent states and covers an area of 357,021 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi) with a largely temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Berlin. With 81 million inhabitants, Germany is the most populous member state in the European Union. After the United States, it is the second most popular migration destination in the world. Germany is a federal parliamentary republic in western-central Europe. It includes 16 constituent states and covers an area of 357,021 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi) with a largely temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Berlin. With 81 million inhabitants, Germany is the most populous member state in the European Union. After the United States, it is the second most popular migration destination in the world.
Various Germanic tribes have occupied northern Germany since classical antiquity. A region named Germania was documented before 100 CE. During the Migration Period the Germanic tribes expanded southward. Beginning in the 10th century, German territories formed a central part of the Holy Roman Empire. During the 16th century, northern German regions became the centre of the Protestant Reformation.
The rise of Pan-Germanism inside the German Confederation resulted in the unification of most of the German states in 1871 into the Prussian-dominated German Empire. After World War I and the German Revolution of 1918-1919, the Empire was replaced by the parliamentary Weimar Republic. The establishment of the Third Reich in 1933 led to World War II and the Holocaust. After 1945, Germany split into two states, East Germany and West Germany. In 1990, the country was reunified.
 In the 21st century, Germany is a great power and has the world’s fourth-largest economy by nominal GDP, as well as the fifth-largest by PPP. As a global leader in several industrial and technological sectors, it is both the world’s third-largest exporter and importer of goods. Germany is a developed country with a very high standard of living sustained by a skilled and productive society. It upholds a social security and universal health care system, environmental protection and a tuition free university education. In the 21st century, Germany is a great power and has the world’s fourth-largest economy by nominal GDP, as well as the fifth-largest by PPP. As a global leader in several industrial and technological sectors, it is both the world’s third-largest exporter and importer of goods. Germany is a developed country with a very high standard of living sustained by a skilled and productive society. It upholds a social security and universal health care system, environmental protection and a tuition free university education.
Germany was a founding member of the European Union in 1993. It is part of the Schengen Area, and became a co-founder of the Eurozone in 1999. Germany is a member of the United Nations, NATO, the G8, the G20, and the OECD. The national military expenditure is the 9th highest in the world. Known for its rich cultural history, Germany has been continuously the home of influential artists, philosophers, musicians, sportsmen, entrepreneurs, scientists and inventors.
|









 Otto (German: Otto Wilhelm Luitpold Adalbert Waldemar; 27 April 1848 – 11 October 1916), was King of Bavaria from 1886 to 1913. However, he never actively ruled due to severe mental illness; his uncle, Luitpold, and cousin, Ludwig, served as regents. Ludwig deposed him in 1913 a day after the legislature passed a law allowing him to do so, becoming king in his own right.
Otto (German: Otto Wilhelm Luitpold Adalbert Waldemar; 27 April 1848 – 11 October 1916), was King of Bavaria from 1886 to 1913. However, he never actively ruled due to severe mental illness; his uncle, Luitpold, and cousin, Ludwig, served as regents. Ludwig deposed him in 1913 a day after the legislature passed a law allowing him to do so, becoming king in his own right. The Kingdom of Bavaria (German: Königreich Bayern; Austro-Bavarian: Kinereich Bayern) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. The Bavarian Elector Maximilian IV Joseph of the House of Wittelsbach became the first King of Bavaria in 1805 as Maximilian I Joseph. The crown would go on being held by the Wittelsbachs until the kingdom came to an end in 1918. Most of Bavaria’s present-day borders were established after 1814 with the Treaty of Paris, in which Bavaria ceded Tyrol and Vorarlberg to the Austrian Empire while receiving Aschaffenburg and Würzburg. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingdom became a federal state of the new Empire and was second in size, power, and wealth only to the leading state, the Kingdom of Prussia. In 1918 Bavaria became a republic, and the kingdom was thus succeeded by the current Free State of Bavaria.
The Kingdom of Bavaria (German: Königreich Bayern; Austro-Bavarian: Kinereich Bayern) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1805 and continued to exist until 1918. The Bavarian Elector Maximilian IV Joseph of the House of Wittelsbach became the first King of Bavaria in 1805 as Maximilian I Joseph. The crown would go on being held by the Wittelsbachs until the kingdom came to an end in 1918. Most of Bavaria’s present-day borders were established after 1814 with the Treaty of Paris, in which Bavaria ceded Tyrol and Vorarlberg to the Austrian Empire while receiving Aschaffenburg and Würzburg. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingdom became a federal state of the new Empire and was second in size, power, and wealth only to the leading state, the Kingdom of Prussia. In 1918 Bavaria became a republic, and the kingdom was thus succeeded by the current Free State of Bavaria. Germany, officially the Federal Republic of
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of  Germany is a federal parliamentary republic in western-central Europe. It includes 16 constituent states and covers an area of 357,021 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi) with a largely temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Berlin. With 81 million inhabitants, Germany is the most populous member state in the European Union. After the United States, it is the second most popular migration destination in the world.
Germany is a federal parliamentary republic in western-central Europe. It includes 16 constituent states and covers an area of 357,021 square kilometres (137,847 sq mi) with a largely temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and largest city is Berlin. With 81 million inhabitants, Germany is the most populous member state in the European Union. After the United States, it is the second most popular migration destination in the world. In the 21st century, Germany is a great power and has the world’s fourth-largest economy by nominal GDP, as well as the fifth-largest by PPP. As a global leader in several industrial and technological sectors, it is both the world’s third-largest exporter and importer of goods. Germany is a developed country with a very high standard of living sustained by a skilled and productive society. It upholds a social security and universal health care system, environmental protection and a tuition free university education.
In the 21st century, Germany is a great power and has the world’s fourth-largest economy by nominal GDP, as well as the fifth-largest by PPP. As a global leader in several industrial and technological sectors, it is both the world’s third-largest exporter and importer of goods. Germany is a developed country with a very high standard of living sustained by a skilled and productive society. It upholds a social security and universal health care system, environmental protection and a tuition free university education.




