|
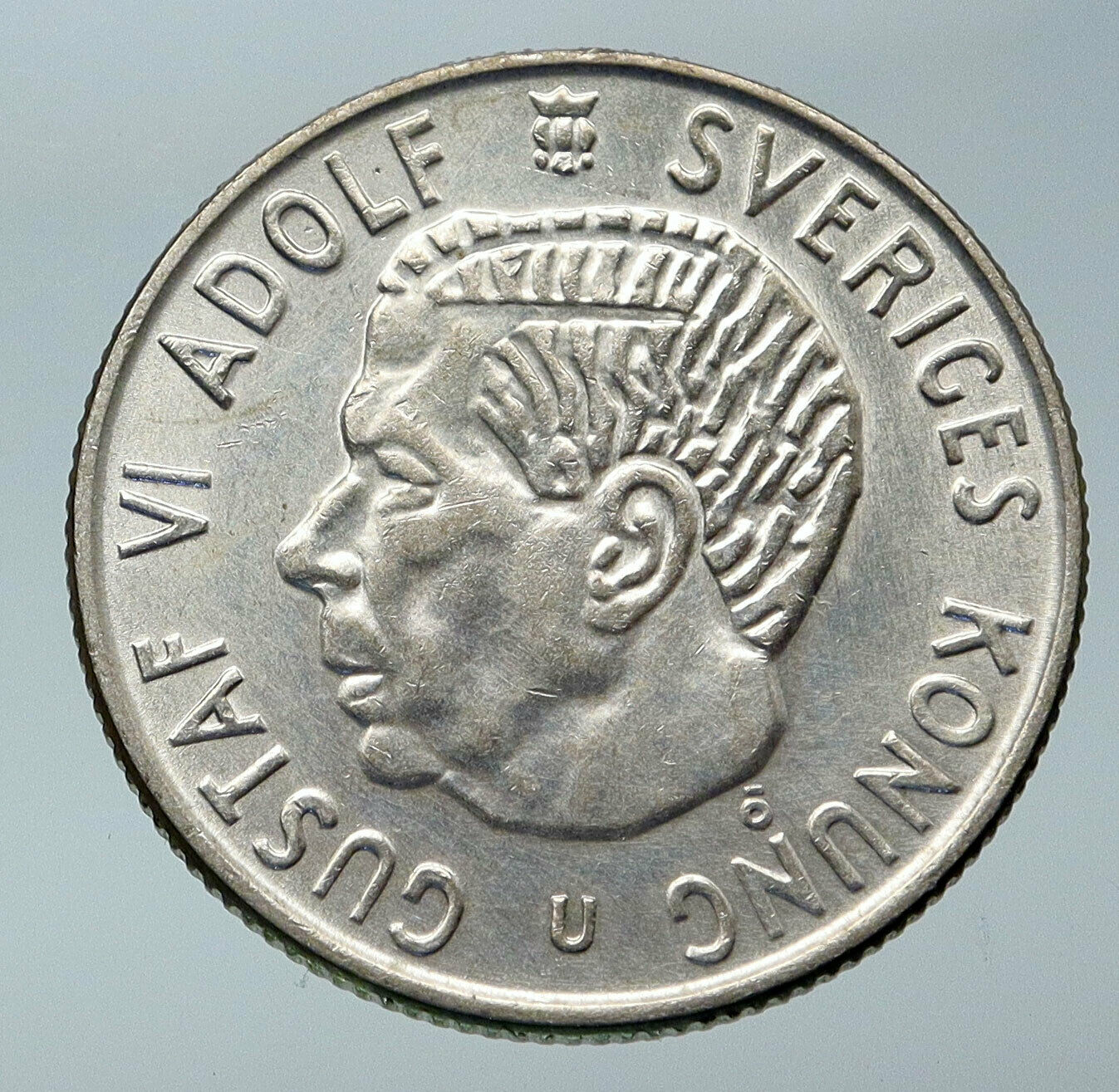
Sweden under Gustaf V – King: 8 December 1907 – 29 October 1950 – 500th Anniversary of the Riksdag
1935 Silver 5 Kronor 35mm (25.01 grams) 0.900 Silver (0.7263 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 806
GUSTAF V SVERIGES KONUNG MED FOLKET FÖR FOSTERLANDET, Portrait in left profile of Gustav V surrounded by an inscription of his royal name and title as well as his motto . At sides of the tip of neck-cut at left the mark of the city of Stockholm while at right the initial of the surname of the director of the mint (G). Above the signature of the engraver (EL).
1435 * SVERIGES * RIKSDAG * 1935
* 5 KRONOR *, Shield with the three crowns of Sweden, over a cross. Value in legend around the rim.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 The Riksdag (Swedish: riksdagen or Sveriges riksdag) is the national legislature and the supreme decision-making body of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral legislature with 349 members (Swedish: riksdagsledamöter), elected proportionally and serving, from 1994 onwards, on fixed four-year terms. The Riksdag (Swedish: riksdagen or Sveriges riksdag) is the national legislature and the supreme decision-making body of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral legislature with 349 members (Swedish: riksdagsledamöter), elected proportionally and serving, from 1994 onwards, on fixed four-year terms.
The constitutional functions of the Riksdag are enumerated in the Instrument of Government (Swedish: Regeringsformen), and its internal workings are specified in greater detail in the Riksdag Act (Swedish: Riksdagsordningen).
 The seat of the Riksdag is at Parliament House (Swedish: Riksdagshuset), on the island of Helgeandsholmen in the central parts of Stockholm. The Riksdag has its institutional roots in the feudal Riksdag of the Estates, by tradition thought to have first assembled in Arboga in 1435, and in 1866 following reforms of the 1809 Instrument of Government that body was transformed into a bicameral legislature with an upper chamber (Swedish: Första Kammaren) and a lower chamber (Swedish: Andra Kammaren). The seat of the Riksdag is at Parliament House (Swedish: Riksdagshuset), on the island of Helgeandsholmen in the central parts of Stockholm. The Riksdag has its institutional roots in the feudal Riksdag of the Estates, by tradition thought to have first assembled in Arboga in 1435, and in 1866 following reforms of the 1809 Instrument of Government that body was transformed into a bicameral legislature with an upper chamber (Swedish: Första Kammaren) and a lower chamber (Swedish: Andra Kammaren).
The most recent general election was held on 9 September 2018.
The Swedish word riksdag, in definite form riksdagen, is a general term for “parliament” or “assembly”, but it is typically only used for Sweden’s legislature and certain related institutions. In addition to Sweden’s parliament, it is also used for the Parliament of Finland and the Estonian Riigikogu, as well as the historical German Reichstag and the Danish Rigsdagen. In Swedish use, riksdagen is usually uncapitalized. Riksdag derives from the genitive of rike, referring to royal power, and dag, meaning diet or conference; the German word Reichstag and the Danish Rigsdag are cognate. The Oxford English Dictionary traces English use of the term “Riksdag” in reference to the Swedish assembly back to 1855.
 Gustaf V (Oscar Gustaf Adolf 16 June 1858 – 29 October 1950) was King of Sweden from 1907. He was the eldest son of King Oscar II of Sweden and Sophia of Nassau, a half-sister of Adolphe, Grand Duke of Luxembourg. Reigning from the death of his father Oscar II in 1907 until his own death 43 years later, he holds the record of being the oldest monarch of Sweden and the second-longest reigning after Magnus IV (the longest as an adult). He was also the last Swedish monarch to exercise his royal prerogatives, which largely died with him, although formally abolished only with the remaking of the Swedish constitution in 1974. He was the first Swedish king since the High Middle Ages not to have a coronation and hence never wore a crown, a tradition continuing to date. Gustaf V (Oscar Gustaf Adolf 16 June 1858 – 29 October 1950) was King of Sweden from 1907. He was the eldest son of King Oscar II of Sweden and Sophia of Nassau, a half-sister of Adolphe, Grand Duke of Luxembourg. Reigning from the death of his father Oscar II in 1907 until his own death 43 years later, he holds the record of being the oldest monarch of Sweden and the second-longest reigning after Magnus IV (the longest as an adult). He was also the last Swedish monarch to exercise his royal prerogatives, which largely died with him, although formally abolished only with the remaking of the Swedish constitution in 1974. He was the first Swedish king since the High Middle Ages not to have a coronation and hence never wore a crown, a tradition continuing to date.
Gustaf ascended the throne in 1907, and his early reign saw the rise of parliamentary rule in Sweden, although the leadup to World War I pre-empted his overthrow of Liberal Prime Minister Karl Staaff in 1914, replacing him with his own figurehead Hjalmar Hammarskjöld (father of Dag Hammarskjöld) for most of the war. However, after the Liberals and Social Democrats secured a parliamentary majority under Staaff’s successor, Nils Edén, he allowed Edén to form a new government which de facto stripped the monarchy of all virtual powers and enacted universal and equal suffrage, including for women, by 1919. Bowing fully to the principles of parliamentary democracy, he remained a popular figurehead for the remaining 31 years of his rule, although not completely without influence – during World War II he allegedly urged Per Albin Hansson’s coalition government to accept requests from Nazi Germany for logistics support, refusing which might have provoked an invasion. This remains controversial to date, although he is not known to have shown much support for fascism or radical nationalism; his pro-German and anti-Communist stance was well known also in World War I.
Following his death at age 92, he was implicated as a homosexual in the Haijby affair. His supposed lover – career criminal and accused pedophile Kurt Haijby – was imprisoned in 1952 for blackmail of the court in the 1930s. (Homosexuality was a criminal offense in Sweden until 1944, though Gustaf’s position would have granted automatic immunity.) An avid hunter and sportsman, he presided over the 1912 Olympic Games and chaired the Swedish Association of Sports from 1897 to 1907. Most notably, he represented Sweden (under the alias of Mr G.) as a competitive tennis player, keeping up competitive tennis until his 80s, when his eyesight deteriorated rapidly.
 Sweden, officially the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. It borders Norway and Finland, and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund. At 450,295 square kilometres (173,860 sq mi), Sweden is the third-largest country in the European Union by area, with a total population of over 9.8 million. Sweden consequently has a low population density of 21 inhabitants per square kilometre (54/sq mi), with the highest concentration in the southern half of the country. Approximately 85% of the population lives in urban areas. Southern Sweden is predominantly agricultural, while the north is heavily forested. Sweden is part of the geographical area of Fennoscandia. Sweden, officially the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. It borders Norway and Finland, and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund. At 450,295 square kilometres (173,860 sq mi), Sweden is the third-largest country in the European Union by area, with a total population of over 9.8 million. Sweden consequently has a low population density of 21 inhabitants per square kilometre (54/sq mi), with the highest concentration in the southern half of the country. Approximately 85% of the population lives in urban areas. Southern Sweden is predominantly agricultural, while the north is heavily forested. Sweden is part of the geographical area of Fennoscandia.
 Germanic peoples have inhabited Sweden since prehistoric times, emerging into history as the Geats/Götar and Swedes/Svear and constituting the sea peoples known as the Norsemen. Sweden emerged as an independent and unified country during the Middle Ages. In the 17th century, it expanded its territories to form the Swedish Empire, which became one of the great powers of Europe until the early 18th century. Swedish territories outside the Scandinavian Peninsula were gradually lost during the 18th and 19th centuries, beginning with the annexation of present-day Finland by Russia in 1809. The last war in which Sweden was directly involved was in 1814, when Norway was militarily forced into personal union. Germanic peoples have inhabited Sweden since prehistoric times, emerging into history as the Geats/Götar and Swedes/Svear and constituting the sea peoples known as the Norsemen. Sweden emerged as an independent and unified country during the Middle Ages. In the 17th century, it expanded its territories to form the Swedish Empire, which became one of the great powers of Europe until the early 18th century. Swedish territories outside the Scandinavian Peninsula were gradually lost during the 18th and 19th centuries, beginning with the annexation of present-day Finland by Russia in 1809. The last war in which Sweden was directly involved was in 1814, when Norway was militarily forced into personal union.
Since then, Sweden has been at peace, maintaining an official policy of neutrality in foreign affairs. The union with Norway was peacefully dissolved in 1905, leading to Sweden’s current borders. Though it was formally neutral through both world wars, Sweden engaged in humanitarian efforts, such as taking in refugees from German-occupied Europe. After the end of the Cold War, Sweden joined the European Union on 1 January 1995, but declined NATO membership.
Today, Sweden is a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary democracy, with the Monarch as the head of state. The capital city is Stockholm, which is also the most populous city in the country. Legislative power is vested in the 349-member unicameral Riksdag. Executive power is exercised by the Government, chaired by the Prime Minister. Sweden is a unitary state, currently divided into 21 counties and 290 municipalities.
Sweden maintains a Nordic social welfare system that provides universal health care and tertiary education for its citizens. It has the world’s eighth-highest per capita income and ranks highly in numerous metrics of national performance, including quality of life, health, education, protection of civil liberties, economic competitiveness, equality, prosperity and human development. Sweden has been a member of the European Union since 1 January 1995, but declined Eurozone membership following a referendum. It is also a member of the United Nations, the Nordic Council, Council of Europe, the World Trade Organization and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
|





 The Riksdag (Swedish: riksdagen or Sveriges riksdag) is the national legislature and the supreme decision-making body of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral legislature with 349 members (Swedish: riksdagsledamöter), elected proportionally and serving, from 1994 onwards, on fixed four-year terms.
The Riksdag (Swedish: riksdagen or Sveriges riksdag) is the national legislature and the supreme decision-making body of Sweden. Since 1971, the Riksdag has been a unicameral legislature with 349 members (Swedish: riksdagsledamöter), elected proportionally and serving, from 1994 onwards, on fixed four-year terms.  The seat of the Riksdag is at Parliament House (Swedish: Riksdagshuset), on the island of Helgeandsholmen in the central parts of Stockholm. The Riksdag has its institutional roots in the feudal Riksdag of the Estates, by tradition thought to have first assembled in Arboga in 1435, and in 1866 following reforms of the 1809 Instrument of Government that body was transformed into a bicameral legislature with an upper chamber (Swedish: Första Kammaren) and a lower chamber (Swedish: Andra Kammaren).
The seat of the Riksdag is at Parliament House (Swedish: Riksdagshuset), on the island of Helgeandsholmen in the central parts of Stockholm. The Riksdag has its institutional roots in the feudal Riksdag of the Estates, by tradition thought to have first assembled in Arboga in 1435, and in 1866 following reforms of the 1809 Instrument of Government that body was transformed into a bicameral legislature with an upper chamber (Swedish: Första Kammaren) and a lower chamber (Swedish: Andra Kammaren).  Gustaf V (Oscar Gustaf Adolf 16 June 1858 – 29 October 1950) was King of Sweden from 1907. He was the eldest son of King Oscar II of Sweden and Sophia of Nassau, a half-sister of Adolphe, Grand Duke of Luxembourg. Reigning from the death of his father Oscar II in 1907 until his own death 43 years later, he holds the record of being the oldest monarch of Sweden and the second-longest reigning after Magnus IV (the longest as an adult). He was also the last Swedish monarch to exercise his royal prerogatives, which largely died with him, although formally abolished only with the remaking of the Swedish constitution in 1974. He was the first Swedish king since the High Middle Ages not to have a coronation and hence never wore a crown, a tradition continuing to date.
Gustaf V (Oscar Gustaf Adolf 16 June 1858 – 29 October 1950) was King of Sweden from 1907. He was the eldest son of King Oscar II of Sweden and Sophia of Nassau, a half-sister of Adolphe, Grand Duke of Luxembourg. Reigning from the death of his father Oscar II in 1907 until his own death 43 years later, he holds the record of being the oldest monarch of Sweden and the second-longest reigning after Magnus IV (the longest as an adult). He was also the last Swedish monarch to exercise his royal prerogatives, which largely died with him, although formally abolished only with the remaking of the Swedish constitution in 1974. He was the first Swedish king since the High Middle Ages not to have a coronation and hence never wore a crown, a tradition continuing to date. Sweden, officially the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. It borders Norway and Finland, and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund. At 450,295 square kilometres (173,860 sq mi), Sweden is the third-largest country in the European Union by area, with a total population of over 9.8 million. Sweden consequently has a low population density of 21 inhabitants per square kilometre (54/sq mi), with the highest concentration in the southern half of the country. Approximately 85% of the population lives in urban areas. Southern Sweden is predominantly agricultural, while the north is heavily forested. Sweden is part of the geographical area of Fennoscandia.
Sweden, officially the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. It borders Norway and Finland, and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund. At 450,295 square kilometres (173,860 sq mi), Sweden is the third-largest country in the European Union by area, with a total population of over 9.8 million. Sweden consequently has a low population density of 21 inhabitants per square kilometre (54/sq mi), with the highest concentration in the southern half of the country. Approximately 85% of the population lives in urban areas. Southern Sweden is predominantly agricultural, while the north is heavily forested. Sweden is part of the geographical area of Fennoscandia.
 Germanic peoples have inhabited Sweden since prehistoric times, emerging into history as the Geats/Götar and Swedes/Svear and constituting the sea peoples known as the Norsemen. Sweden emerged as an independent and unified country during the Middle Ages. In the 17th century, it expanded its territories to form the Swedish Empire, which became one of the great powers of Europe until the early 18th century. Swedish territories outside the Scandinavian Peninsula were gradually lost during the 18th and 19th centuries, beginning with the annexation of present-day Finland by Russia in 1809. The last war in which Sweden was directly involved was in 1814, when Norway was militarily forced into personal union.
Germanic peoples have inhabited Sweden since prehistoric times, emerging into history as the Geats/Götar and Swedes/Svear and constituting the sea peoples known as the Norsemen. Sweden emerged as an independent and unified country during the Middle Ages. In the 17th century, it expanded its territories to form the Swedish Empire, which became one of the great powers of Europe until the early 18th century. Swedish territories outside the Scandinavian Peninsula were gradually lost during the 18th and 19th centuries, beginning with the annexation of present-day Finland by Russia in 1809. The last war in which Sweden was directly involved was in 1814, when Norway was militarily forced into personal union.




