|
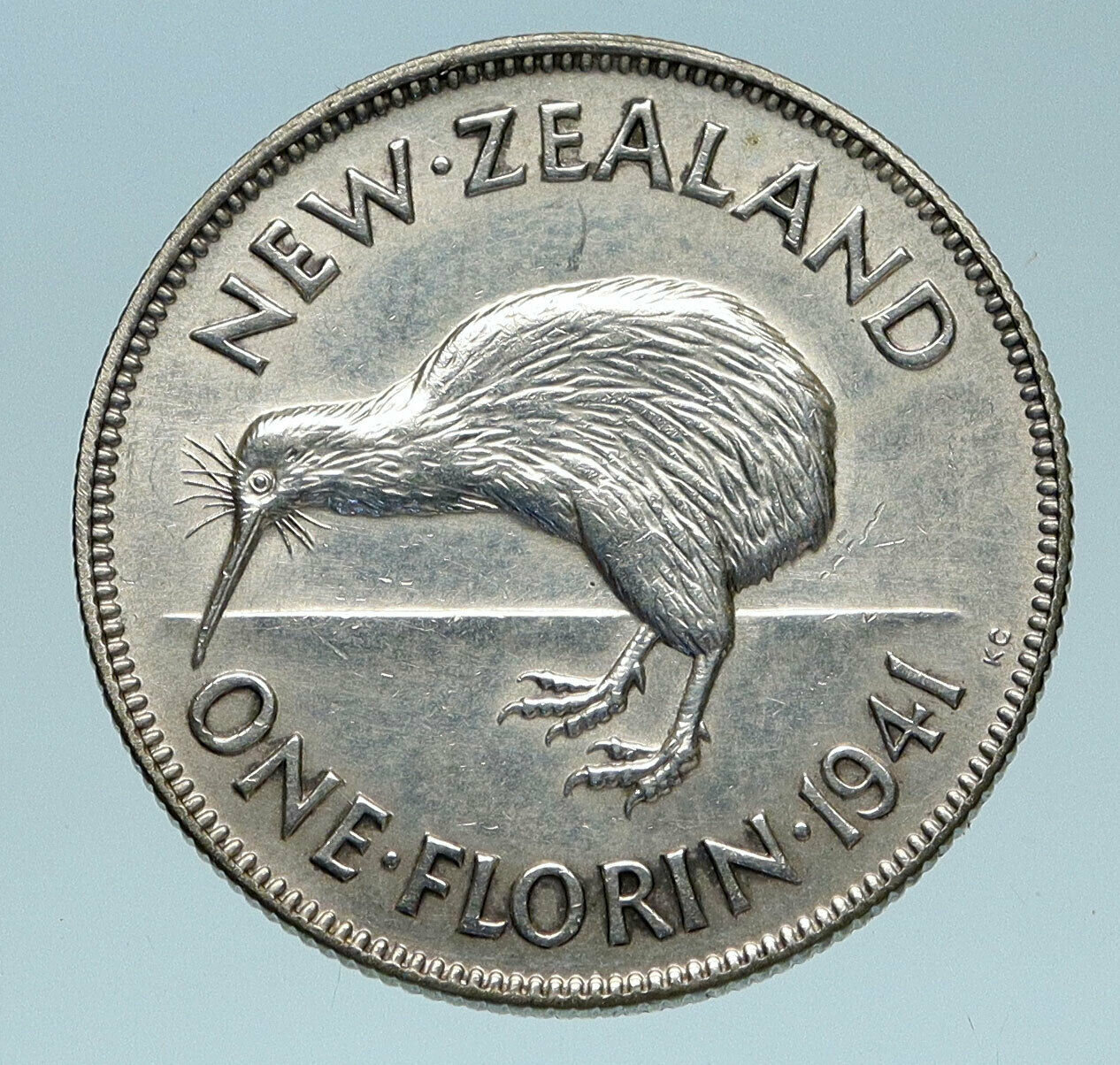
New Zeland under George V – King: 6 May 1910 – 20 January 1936
1937 Silver Florin 15mm (1.40 grams) 0.500 Silver (0.0227 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 1 (1933-36) | Engraver: Percy Metcalfe, George Kruger Gray
GEORGE V KING EMPEROR, Crowned bust of King George V left, legend around.
NEW·ZEALAND 3d ·1934·, Two carved patu (Māori short-handled clubs).
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 A patu is a club or pounder used by the Māori. The word patu in the Māori language means to strike, hit, beat, kill or subdue. A patu is a club or pounder used by the Māori. The word patu in the Māori language means to strike, hit, beat, kill or subdue.
These types of short-handled clubs were mainly used as a striking weapon. The blow administered with this weapon was a horizontal thrust straight from the shoulder at the enemy’s temple. If the foe could be grasped by the hair then the patu would be driven up under the ribs or jaw. Patu were made from hardwood, whale bone, or stone. The most prestigious material for the patu was pounamu (greenstone). Patu made from pounamu were generally called “mere”. Maori decorated the patu by carving into the wood, bone or stone.
Types of patu include:
- patu pounamu or mere: made from pounamu (greenstone).
- patu onewa: made of stone. These resemble the mere in outline but thicker, because the stone used was more easily broken than the resilient pounamu.
- patu paraoa: made of whale bone
- patu tawaka and patuki: made from wood. Other styles of short handled wooden clubs include the kotiate and wahaika.
Less traditional is the rare patu pora, made from iron and the hatchet (patiti).
The patu normally has “a round or rectangular hole in the handle for the tau, or wrist cord”. The wrist cord is generally a short or medium piece of rope that is tied together to form a complete loop. The wielder places his hand inside the loop up to his wrist, and quickly spins the patu in order to wind up the cord (around the wrist and hand) thus securing the weapon on the hand. A feathered tassel may also be added at the end of the cord as a form of distraction to the adversary as the patu is wielded against him.
Types of nonweapon patu include:
- patu muka: a pounder used to soften flax fibre (muka) in preparation for weaving.
- patu aruhe: a pounder used to break up edible fern roots for food.
 George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936. George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
He was the second son of Albert Edward, Prince of Wales (later King Edward VII), and the grandson of the reigning British monarch, Queen Victoria. From the time of his birth, he was third in the line of succession behind his father and his elder brother, Prince Albert Victor, Duke of Clarence and Avondale. From 1877 to 1891, George served in the Royal Navy, until the unexpected death of his elder brother in early 1892 put him directly in line for the throne. On the death of his grandmother in 1901, George’s father became King-Emperor of the British Empire, and George was created Prince of Wales. He succeeded his father in 1910. He was the only Emperor of India to be present at his own Delhi Durbar.
His reign saw the rise of socialism, communism, fascism, Irish republicanism, and the Indian independence movement, all of which radically changed the political landscape. The Parliament Act 1911 established the supremacy of the elected British House of Commons over the unelected House of Lords. As a result of the First World War (1914-18) the empires of his first cousins Tsar Nicholas II of Russia and Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany fell while the British Empire expanded to its greatest effective extent. In 1917, George became the first monarch of the House of Windsor, which he renamed from the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha as a result of anti-German public sentiment. In 1924 he appointed the first Labour ministry and in 1931 the Statute of Westminster recognised the dominions of the Empire as separate, independent states within the Commonwealth of Nations. He was plagued by illness throughout much of his later reign and at his death was succeeded by his eldest son, Edward VIII.
 New Zealand is an island nation in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The country geographically comprises two main landmasses-the North Island (or Te Ika-a-Māui), and the South Island (or Te Waipounamu)-and around 600 smaller islands. New Zealand is situated some 1,500 kilometres (900 mi) east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and roughly 1,000 kilometres (600 mi) south of the Pacific island areas of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. Because of its remoteness, it was one of the last lands to be settled by humans. During its long period of isolation, New Zealand developed a distinct biodiversity of animal, fungal and plant life. The country’s varied topography and its sharp mountain peaks, such as the Southern Alps, owe much to the tectonic uplift of land and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand’s capital city is Wellington, while its most populous city is Auckland. New Zealand is an island nation in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The country geographically comprises two main landmasses-the North Island (or Te Ika-a-Māui), and the South Island (or Te Waipounamu)-and around 600 smaller islands. New Zealand is situated some 1,500 kilometres (900 mi) east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and roughly 1,000 kilometres (600 mi) south of the Pacific island areas of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. Because of its remoteness, it was one of the last lands to be settled by humans. During its long period of isolation, New Zealand developed a distinct biodiversity of animal, fungal and plant life. The country’s varied topography and its sharp mountain peaks, such as the Southern Alps, owe much to the tectonic uplift of land and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand’s capital city is Wellington, while its most populous city is Auckland.
 Sometime between 1250 and 1300 CE, Polynesians settled in the islands that later were named New Zealand and developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of Britain and Māori chiefs signed the Treaty of Waitangi, which declared British sovereignty over the islands. In 1841, New Zealand became a colony within the British Empire and in 1907 it became a Dominion. Today, the majority of New Zealand’s population of 4.7 million is of European descent; the indigenous Māori are the largest minority, followed by Asians and Pacific Islanders. Reflecting this, New Zealand’s culture is mainly derived from Māori and early British settlers, with recent broadening arising from increased immigration. The official languages are English, Māori and New Zealand Sign Language, with English predominant. Sometime between 1250 and 1300 CE, Polynesians settled in the islands that later were named New Zealand and developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of Britain and Māori chiefs signed the Treaty of Waitangi, which declared British sovereignty over the islands. In 1841, New Zealand became a colony within the British Empire and in 1907 it became a Dominion. Today, the majority of New Zealand’s population of 4.7 million is of European descent; the indigenous Māori are the largest minority, followed by Asians and Pacific Islanders. Reflecting this, New Zealand’s culture is mainly derived from Māori and early British settlers, with recent broadening arising from increased immigration. The official languages are English, Māori and New Zealand Sign Language, with English predominant.
New Zealand is a developed country and ranks highly in international comparisons of national performance, such as health, education, economic freedom and quality of life. Since the 1980s, New Zealand has transformed from an agrarian, regulated economy to a market economy. Nationally, legislative authority is vested in an elected, unicameral Parliament, while executive political power is exercised by the Cabinet, led by the Prime Minister, who is currently Bill English. Queen Elizabeth II is the country’s head of state and is represented by a governor-general, currently Dame Patsy Reddy. In addition, New Zealand is organised into 11 regional councils and 67 territorial authorities for local government purposes. The Realm of New Zealand also includes Tokelau (a dependent territory); the Cook Islands and Niue (self-governing states in free association with New Zealand); and the Ross Dependency, which is New Zealand’s territorial claim in Antarctica. New Zealand is a member of the United Nations, Commonwealth of Nations, ANZUS, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Pacific Islands Forum, and Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation.
|





 A patu is a club or pounder used by the Māori. The word patu in the Māori language means to strike, hit, beat, kill or subdue.
A patu is a club or pounder used by the Māori. The word patu in the Māori language means to strike, hit, beat, kill or subdue.  George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936.
George V (George Frederick Ernest Albert; 3 June 1865 – 20 January 1936) was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions, and Emperor of India, from 6 May 1910 until his death in 1936. New Zealand is an island nation in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The country geographically comprises two main landmasses-the North Island (or Te Ika-a-Māui), and the South Island (or Te Waipounamu)-and around 600 smaller islands. New Zealand is situated some 1,500 kilometres (900 mi) east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and roughly 1,000 kilometres (600 mi) south of the Pacific island areas of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. Because of its remoteness, it was one of the last lands to be settled by humans. During its long period of isolation, New Zealand developed a distinct biodiversity of animal, fungal and plant life. The country’s varied topography and its sharp mountain peaks, such as the Southern Alps, owe much to the tectonic uplift of land and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand’s capital city is Wellington, while its most populous city is Auckland.
New Zealand is an island nation in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The country geographically comprises two main landmasses-the North Island (or Te Ika-a-Māui), and the South Island (or Te Waipounamu)-and around 600 smaller islands. New Zealand is situated some 1,500 kilometres (900 mi) east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and roughly 1,000 kilometres (600 mi) south of the Pacific island areas of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. Because of its remoteness, it was one of the last lands to be settled by humans. During its long period of isolation, New Zealand developed a distinct biodiversity of animal, fungal and plant life. The country’s varied topography and its sharp mountain peaks, such as the Southern Alps, owe much to the tectonic uplift of land and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand’s capital city is Wellington, while its most populous city is Auckland. Sometime between 1250 and 1300 CE, Polynesians settled in the islands that later were named New Zealand and developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of Britain and Māori chiefs signed the Treaty of Waitangi, which declared British sovereignty over the islands. In 1841, New Zealand became a colony within the British Empire and in 1907 it became a Dominion. Today, the majority of New Zealand’s population of 4.7 million is of European descent; the indigenous Māori are the largest minority, followed by Asians and Pacific Islanders. Reflecting this, New Zealand’s culture is mainly derived from Māori and early British settlers, with recent broadening arising from increased immigration. The official languages are English, Māori and New Zealand Sign Language, with English predominant.
Sometime between 1250 and 1300 CE, Polynesians settled in the islands that later were named New Zealand and developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of Britain and Māori chiefs signed the Treaty of Waitangi, which declared British sovereignty over the islands. In 1841, New Zealand became a colony within the British Empire and in 1907 it became a Dominion. Today, the majority of New Zealand’s population of 4.7 million is of European descent; the indigenous Māori are the largest minority, followed by Asians and Pacific Islanders. Reflecting this, New Zealand’s culture is mainly derived from Māori and early British settlers, with recent broadening arising from increased immigration. The official languages are English, Māori and New Zealand Sign Language, with English predominant.





