|
Philippines – US Administration
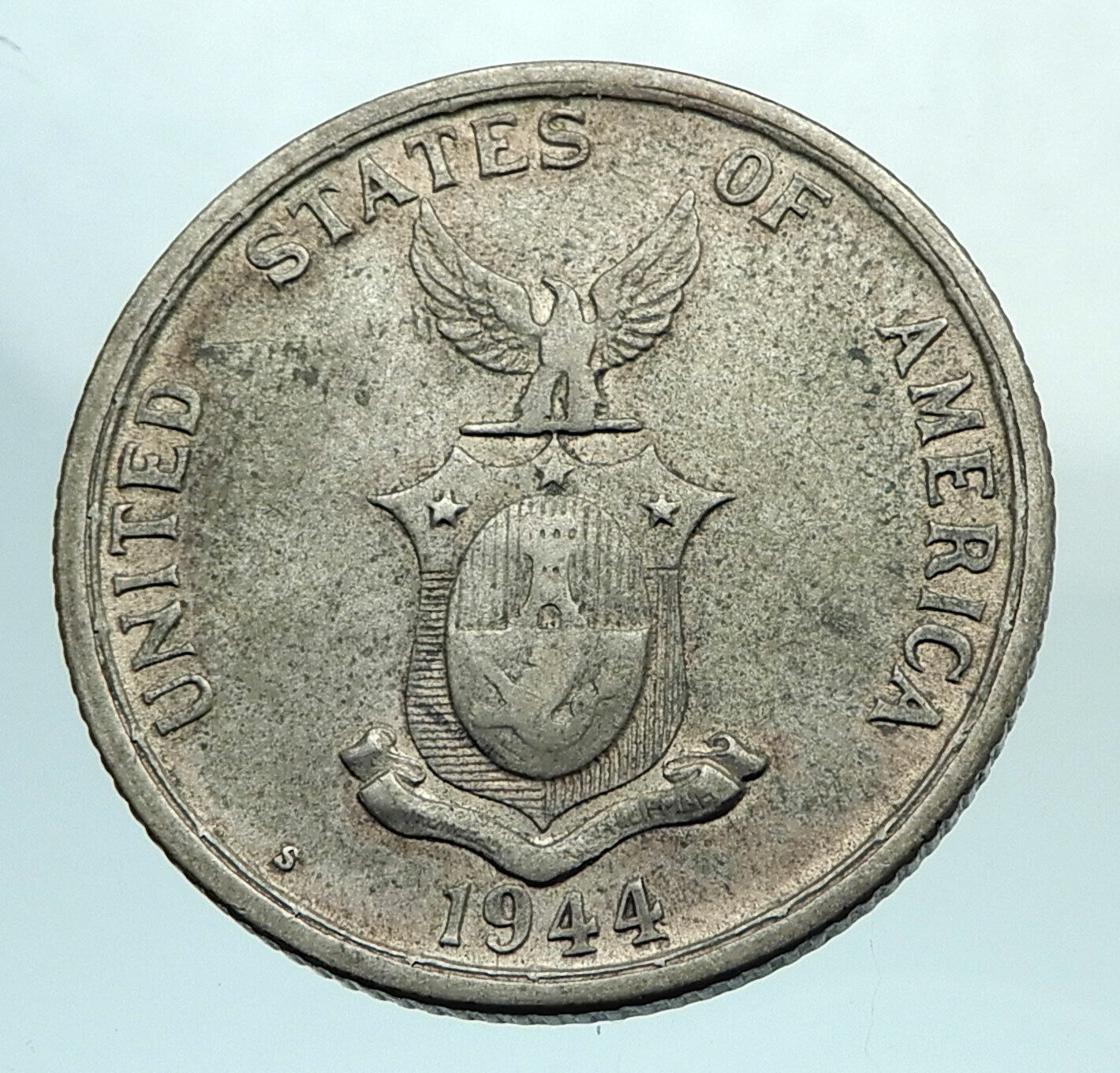
1944 S Silver 50 Centavos 27mm (10.13 grams) 0.750 Silver (0.2396 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 183
50 CENTAVOS FILIPINAS, Figure of Liberty, (considered by many to be the daughter of the designer ‘Blanca’) striking anvil with hammer. Shows work being done by Americans in building a better Philippines. Volcano, Mt. Mayon, topped with smoke rings.
UNITED STATES OF AMERICA· S, Eagle above shield with 3 stars and stripes, oval within.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
American colonization of the Philippines: The history of the Philippines from 1898 to 1946 describes the period of the American colonization of the Philippines. It began with the outbreak of the Spanish-American War in April 1898, when the Philippines was still a colony of the Spanish East Indies, and concluded when the United States formally recognized the independence of the Republic of the Philippines on July 4, 1946.
 With the signing of the Treaty of Paris on December 10, 1898, Spain ceded the Philippines to the United States, thereby beginning the era of American colonization. The interim U.S. military government of the Philippine Islands experienced a period of great political turbulence, characterised by the Philippine-American War. With the signing of the Treaty of Paris on December 10, 1898, Spain ceded the Philippines to the United States, thereby beginning the era of American colonization. The interim U.S. military government of the Philippine Islands experienced a period of great political turbulence, characterised by the Philippine-American War.
In the U.S., there was a movement for Philippine independence; some said that the U.S. had no right to a land where many of the people wanted self-government. In 1898 Andrew Carnegie, an industrialist and steel magnate, offered to pay the U.S. government $20 million to give the Philippines its independence.
On November 7, 1900, Spain and the U.S. signed the Treaty of Washington, clarifying that the territories relinquished by Spain to the United States included any and all islands belonging to the Philippine Archipelago, but lying outside the lines described in the Treaty of Paris. That treaty explicitly named the islands of Cagayan Sulu and Sibutu and their dependencies as among the relinquished territories.
Beginning in 1901, the military government was replaced by a civilian government-the Insular Government of the Philippine Islands-with William Howard Taft serving as its first Governor-General. Also, a series of insurgent governments that lacked significant international and diplomatic recognition existed between 1898 and 1904.
 Following the passage of the Philippine Independence Act in 1934, a Philippine presidential election was held in 1935. Manuel L. Quezon was elected and inaugurated second President of the Philippines on November 15, 1935. The Insular Government was dissolved and the Commonwealth of the Philippines, intended to be a transitional government in preparation for the country’s full achievement of independence in 1946, was brought into existence. Following the passage of the Philippine Independence Act in 1934, a Philippine presidential election was held in 1935. Manuel L. Quezon was elected and inaugurated second President of the Philippines on November 15, 1935. The Insular Government was dissolved and the Commonwealth of the Philippines, intended to be a transitional government in preparation for the country’s full achievement of independence in 1946, was brought into existence.
After the World War II Japanese invasion in 1941 and subsequent occupation of the Philippines, the United States and Philippine Commonwealth military recaptured the Philippines in 1945. The United States formally recognised the independence of the Republic of the Philippines on July 4, 1946, according to the terms of the Philippine Independence Act.
Military agreements
A 1947 Military Bases Agreement gave the United States a 99-year lease on a number of Philippine military and naval bases in which U.S. authorities had virtual territorial rights. In August 1951, a mutual defense treaty (MDT) was signed between representatives of the Philippines and the United States. The overall accord contained eight articles and dictated that both nations would support each other if either the Philippines or the United States were to be attacked by an external party. An amendment to the bases agreement in 1966 reduced its 99-year term to 25 years. In 1979, after two years of negotiation, the bases agreement was renewed with some amendments.
 Pursuant to the bases agreement, the United States maintained and operated major facilities at Clark Air Base until November 1991, and at Subic Bay Naval Complex and several small subsidiary installations in the Philippines until November 1992. In July 1991, negotiators from the two countries reached agreement on a draft treaty providing for the clean-up and turn over of Clark to the Philippine government in 1992, and for the lease of Subic Bay Naval Base by the U.S. for ten years. By 1991, operations at Clark had already been scaled back because of the end of the Cold War, with the last combat aircraft leaving in 1990, before the base was heavily damaged by the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo. Pursuant to the bases agreement, the United States maintained and operated major facilities at Clark Air Base until November 1991, and at Subic Bay Naval Complex and several small subsidiary installations in the Philippines until November 1992. In July 1991, negotiators from the two countries reached agreement on a draft treaty providing for the clean-up and turn over of Clark to the Philippine government in 1992, and for the lease of Subic Bay Naval Base by the U.S. for ten years. By 1991, operations at Clark had already been scaled back because of the end of the Cold War, with the last combat aircraft leaving in 1990, before the base was heavily damaged by the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo.
On September 16, 1991, the Philippine Senate rejected renewal of the bases agreement by a slim margin, and despite further efforts to salvage the situation, the two sides could not reach an agreement. As a result, the Philippine Government informed the U.S. on December 6, 1991, that it would have one year to complete withdrawal. That withdrawal went smoothly and was completed ahead of schedule, with the last U.S. forces departing on November 24, 1992. On departure, the U.S. Government turned over assets worth more than $1.3 billion to the Philippines, including an airport and ship-repair facility. Agencies formed by the Philippine Government have converted the former military bases for civilian commercial use, with Subic Bay serving as a flagship for that effort. The Philippine government on July 16, 2015 announced that it will revive a US-built deep-water naval base in Subic Bay
 The Philippines, officially known as the Republic of the Philippines (Filipino: Republika ng Pilipinas), is a sovereign island country in Southeast Asia situated in the western Pacific Ocean. It consists of about 7,641 islands that are categorized broadly under three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. The capital city of the Philippines is Manila and the most populous city is Quezon City, both part of Metro Manila. The Philippines, officially known as the Republic of the Philippines (Filipino: Republika ng Pilipinas), is a sovereign island country in Southeast Asia situated in the western Pacific Ocean. It consists of about 7,641 islands that are categorized broadly under three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. The capital city of the Philippines is Manila and the most populous city is Quezon City, both part of Metro Manila.
 The Philippines’ location on the Pacific Ring of Fire and close to the equator makes the Philippines prone to earthquakes and typhoons, but also endows it with abundant natural resources and some of the world’s greatest biodiversity. The Philippines has an area of approximately 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi), and a population of more than 100 million with faster growth than any other east Asian country. It is the seventh-most populated country in Asia and the 12th most populated country in the world. An additional 12 million Filipinos live overseas, comprising one of the world’s largest diasporas. Multiple ethnicities and cultures are found throughout the islands. In prehistoric times, Negritos were some of the archipelago’s earliest inhabitants. They were followed by successive waves of Austronesian peoples. Exchanges with Chinese, Malay, Indian, and Islamic states occurred. Then, various nations were established under the rule of Datus, Rajahs, Sultans or Lakans. The Philippines’ location on the Pacific Ring of Fire and close to the equator makes the Philippines prone to earthquakes and typhoons, but also endows it with abundant natural resources and some of the world’s greatest biodiversity. The Philippines has an area of approximately 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi), and a population of more than 100 million with faster growth than any other east Asian country. It is the seventh-most populated country in Asia and the 12th most populated country in the world. An additional 12 million Filipinos live overseas, comprising one of the world’s largest diasporas. Multiple ethnicities and cultures are found throughout the islands. In prehistoric times, Negritos were some of the archipelago’s earliest inhabitants. They were followed by successive waves of Austronesian peoples. Exchanges with Chinese, Malay, Indian, and Islamic states occurred. Then, various nations were established under the rule of Datus, Rajahs, Sultans or Lakans.
 The arrival of Ferdinand Magellan in Homonhon, Eastern Samar in 1521 marked the beginning of Hispanic colonization. In 1543, Spanish explorer Ruy López de Villalobos named the archipelago Las Islas Filipinas in honor of Philip II of Spain. With the arrival of Miguel López de Legazpi from Mexico City, in 1565, the first Hispanic settlement in the archipelago was established. The Philippines became part of the Spanish Empire for more than 300 years. This resulted in Roman Catholicism becoming the dominant religion. During this time, Manila became the western hub of the trans-Pacific trade connecting Asia with Acapulco in the Americas using Manila galleons. The arrival of Ferdinand Magellan in Homonhon, Eastern Samar in 1521 marked the beginning of Hispanic colonization. In 1543, Spanish explorer Ruy López de Villalobos named the archipelago Las Islas Filipinas in honor of Philip II of Spain. With the arrival of Miguel López de Legazpi from Mexico City, in 1565, the first Hispanic settlement in the archipelago was established. The Philippines became part of the Spanish Empire for more than 300 years. This resulted in Roman Catholicism becoming the dominant religion. During this time, Manila became the western hub of the trans-Pacific trade connecting Asia with Acapulco in the Americas using Manila galleons.
As the 19th century gave way to the 20th, there followed in quick succession the Philippine Revolution, which spawned the short-lived First Philippine Republic, followed by the bloody Philippne-American War of conquest by US military force. Aside from the period of Japanese occupation, the United States retained sovereignty over the islands until after World War II, when the Philippines was recognized as an independent nation. Since then, the Philippines has often had a tumultuous experience with democracy, which included the overthrow of a dictatorship by a non-violent revolution.
The nation’s large population and economic potential have led it to be classified as a middle power. It is a founding member of the United Nations, World Trade Organization, Association of Southeast Asian Nations, the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum, and the East Asia Summit. It also hosts the headquarters of the Asian Development Bank. The Philippines is considered to be an emerging market and a newly industrialized country, which has an economy transitioning from being one based on agriculture to one based more on services and manufacturing.
|





 With the signing of the Treaty of Paris on December 10, 1898, Spain ceded the Philippines to the United States, thereby beginning the era of American colonization. The interim U.S. military government of the Philippine Islands experienced a period of great political turbulence, characterised by the Philippine-American War.
With the signing of the Treaty of Paris on December 10, 1898, Spain ceded the Philippines to the United States, thereby beginning the era of American colonization. The interim U.S. military government of the Philippine Islands experienced a period of great political turbulence, characterised by the Philippine-American War.  Following the passage of the Philippine Independence Act in 1934, a Philippine presidential election was held in 1935. Manuel L. Quezon was elected and inaugurated second President of the Philippines on November 15, 1935. The Insular Government was dissolved and the Commonwealth of the Philippines, intended to be a transitional government in preparation for the country’s full achievement of independence in 1946, was brought into existence.
Following the passage of the Philippine Independence Act in 1934, a Philippine presidential election was held in 1935. Manuel L. Quezon was elected and inaugurated second President of the Philippines on November 15, 1935. The Insular Government was dissolved and the Commonwealth of the Philippines, intended to be a transitional government in preparation for the country’s full achievement of independence in 1946, was brought into existence.  Pursuant to the bases agreement, the United States maintained and operated major facilities at Clark Air Base until November 1991, and at Subic Bay Naval Complex and several small subsidiary installations in the Philippines until November 1992. In July 1991, negotiators from the two countries reached agreement on a draft treaty providing for the clean-up and turn over of Clark to the Philippine government in 1992, and for the lease of Subic Bay Naval Base by the U.S. for ten years. By 1991, operations at Clark had already been scaled back because of the end of the Cold War, with the last combat aircraft leaving in 1990, before the base was heavily damaged by the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo.
Pursuant to the bases agreement, the United States maintained and operated major facilities at Clark Air Base until November 1991, and at Subic Bay Naval Complex and several small subsidiary installations in the Philippines until November 1992. In July 1991, negotiators from the two countries reached agreement on a draft treaty providing for the clean-up and turn over of Clark to the Philippine government in 1992, and for the lease of Subic Bay Naval Base by the U.S. for ten years. By 1991, operations at Clark had already been scaled back because of the end of the Cold War, with the last combat aircraft leaving in 1990, before the base was heavily damaged by the 1991 eruption of Mount Pinatubo.  The Philippines, officially known as the Republic of the Philippines (Filipino: Republika ng Pilipinas), is a sovereign island country in Southeast Asia situated in the western Pacific Ocean. It consists of about 7,641 islands that are categorized broadly under three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. The capital city of the Philippines is Manila and the most populous city is Quezon City, both part of Metro Manila.
The Philippines, officially known as the Republic of the Philippines (Filipino: Republika ng Pilipinas), is a sovereign island country in Southeast Asia situated in the western Pacific Ocean. It consists of about 7,641 islands that are categorized broadly under three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. The capital city of the Philippines is Manila and the most populous city is Quezon City, both part of Metro Manila. The Philippines’ location on the Pacific Ring of Fire and close to the equator makes the Philippines prone to earthquakes and typhoons, but also endows it with abundant natural resources and some of the world’s greatest biodiversity. The Philippines has an area of approximately 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi), and a population of more than 100 million with faster growth than any other east Asian country. It is the seventh-most populated country in Asia and the 12th most populated country in the world. An additional 12 million Filipinos live overseas, comprising one of the world’s largest diasporas. Multiple ethnicities and cultures are found throughout the islands. In prehistoric times, Negritos were some of the archipelago’s earliest inhabitants. They were followed by successive waves of Austronesian peoples. Exchanges with Chinese, Malay, Indian, and Islamic states occurred. Then, various nations were established under the rule of Datus, Rajahs, Sultans or Lakans.
The Philippines’ location on the Pacific Ring of Fire and close to the equator makes the Philippines prone to earthquakes and typhoons, but also endows it with abundant natural resources and some of the world’s greatest biodiversity. The Philippines has an area of approximately 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi), and a population of more than 100 million with faster growth than any other east Asian country. It is the seventh-most populated country in Asia and the 12th most populated country in the world. An additional 12 million Filipinos live overseas, comprising one of the world’s largest diasporas. Multiple ethnicities and cultures are found throughout the islands. In prehistoric times, Negritos were some of the archipelago’s earliest inhabitants. They were followed by successive waves of Austronesian peoples. Exchanges with Chinese, Malay, Indian, and Islamic states occurred. Then, various nations were established under the rule of Datus, Rajahs, Sultans or Lakans. The arrival of Ferdinand Magellan in Homonhon, Eastern Samar in 1521 marked the beginning of Hispanic colonization. In 1543, Spanish explorer Ruy López de Villalobos named the archipelago Las Islas Filipinas in honor of Philip II of Spain. With the arrival of Miguel López de Legazpi from Mexico City, in 1565, the first Hispanic settlement in the archipelago was established. The Philippines became part of the Spanish Empire for more than 300 years. This resulted in Roman Catholicism becoming the dominant religion. During this time, Manila became the western hub of the trans-Pacific trade connecting Asia with Acapulco in the Americas using Manila galleons.
The arrival of Ferdinand Magellan in Homonhon, Eastern Samar in 1521 marked the beginning of Hispanic colonization. In 1543, Spanish explorer Ruy López de Villalobos named the archipelago Las Islas Filipinas in honor of Philip II of Spain. With the arrival of Miguel López de Legazpi from Mexico City, in 1565, the first Hispanic settlement in the archipelago was established. The Philippines became part of the Spanish Empire for more than 300 years. This resulted in Roman Catholicism becoming the dominant religion. During this time, Manila became the western hub of the trans-Pacific trade connecting Asia with Acapulco in the Americas using Manila galleons.




