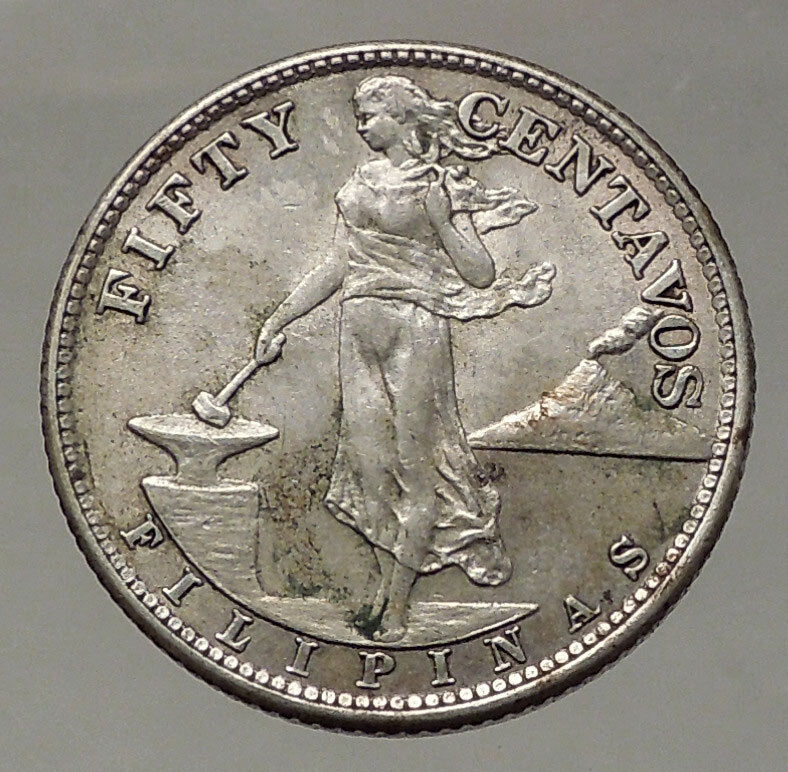
|
Philippines – 100th Birth Anniversary of Andres Bonifacio (1863-1963)
1963 Silver One Peso 38mm (26.73 grams) 0.900 Silver (0.7523 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 193
CENTRAL BANK OF THE PHILIPPINES REPUBLIC OF THE PHILIPPINES ONE PESO, Shield of arms.
* ANDRES BONIFACIO CENTENARY * 1863 1963 NATIONAL HERO, Head 1/4 left divides dates.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 Andrés Bonifacio y de Castro (November 30, 1863 – May 10, 1897) was a Filipino revolutionary leader and the president of the Tagalog Republic. He is often called “The Father of the Philippine Revolution”. He was one of the founders and later Supremo (Supreme Leader) of the Kataas-taasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan ng mga Anak ng Bayan or more commonly known as “Katipunan“, a movement which sought the independence of the Philippines from Spanish colonial rule and started the Philippine Revolution. He is considered a national hero of the Philippines. Andrés Bonifacio y de Castro (November 30, 1863 – May 10, 1897) was a Filipino revolutionary leader and the president of the Tagalog Republic. He is often called “The Father of the Philippine Revolution”. He was one of the founders and later Supremo (Supreme Leader) of the Kataas-taasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan ng mga Anak ng Bayan or more commonly known as “Katipunan“, a movement which sought the independence of the Philippines from Spanish colonial rule and started the Philippine Revolution. He is considered a national hero of the Philippines.
Philippine Revolution
Start of the uprising
The Spanish authorities confirmed the existence of the Katipunan on August 19, 1896. Hundreds of Filipino suspects, both innocent and guilty, were arrested and imprisoned for treason. José Rizal (José Protasio Rizal Mercado y Realonda) was then on his way to Cuba to serve as a doctor in the Spanish colonial army in exchange for his release from Dapitan. When the news broke, Bonifacio first tried to convince Rizal, quarantined aboard a ship in Manila Bay, to escape and join the imminent revolt. Bonifacio, Emilio Jacinto and Guillermo Masangkay disguised themselves as sailors and went to the pier where Rizal’s ship was anchored. Jacinto personally met with Rizal, who rejected their rescue offer. Rizal himself was later arrested, tried and executed.
Eluding an intensive manhunt, Bonifacio called thousands of Katipunan members to a mass gathering in Caloocan, where they decided to start their uprising. The event, marked by the tearing of cedulas (personal identity documents) was later called the “Cry of Balintawak” or “Cry of Pugad Lawin”; the exact location and date of the Cry are disputed. The Supreme Council of the Katipunan declared a nationwide armed revolution against Spain and called for a simultaneous coordinated attack on the capital Manila on August 29. Bonifacio appointed generals to lead rebel forces to Manila. Other Katipunan councils were also informed of their plans. Before hostilities erupted, Bonifacio reorganized the Katipunan into an open de facto revolutionary government and they named the nation and its government Haring Bayang Katagalugan (loosely translates to Tagalog Republic), with him as President and commander-in-chief (or generalissimo) of the rebel army and the Supreme Council as his cabinet. On August 28, Bonifacio issued the following general proclamation:
This manifesto is for all of you. It is absolutely necessary for us to stop at the earliest possible time the nameless oppositions being perpetrated on the sons of the country who are now suffering the brutal punishment and tortures in jails, and because of this please let all the brethren know that on Saturday, the 29th of the current month, the revolution shall commence according to our agreement. For this purpose, it is necessary for all towns to rise simultaneously and attack Manila at the same time. Anybody who obstructs this sacred ideal of the people will be considered a traitor and an enemy, except if he is ill; or is not physically fit, in which case he shall be tried according to the regulations we have put in force.is Mount of Liberty, 28 August 1896 – ANDRÉS BONIFACIO
On August 30, 1896, Bonifacio personally led an attack on San Juan del Monte to capture the town’s powder magazine and water station (which supplied Manila). The defending Spaniards, outnumbered, fought a delaying battle until reinforcements arrived. Once reinforced, the Spaniards drove Bonifacio’s forces back with heavy casualties. Bonifacio and his troops regrouped near Marikina, San Mateo and Montalban. Elsewhere, fighting between rebels and Spanish forces occurred in Mandaluyong, Sampaloc, Santa Ana, Pandacan, Pateros, Marikina, Caloocan, Makati and Taguig. The conventional view among Filipino historians is that the planned general Katipunan offensive on Manila was aborted in favor of Bonifacio’s attack on San Juan del Monte, which sparked a general state of rebellion in the area. However, more recent studies have advanced the view that the planned offensive did push through and the rebel attacks were integrated; according to this view, Bonifacio’s San Juan del Monte battle was only a part of a bigger whole – an unrecognized “Battle for Manila”. Despite his reverses, Bonifacio was not completely defeated and was still considered a threat. Further, the revolt had spread to the surrounding provinces by the end of August.
Campaigns around Manila
By December 1896, the Spanish government recognized three major centers of rebellion: Cavite (under Mariano Alvarez, Emilio Aguinaldo and others), Bulacan (under Mariano Llanera) and Morong (under Bonifacio). The revolt was most successful in Cavite, which mostly fell under rebel control by September-October 1896.
While Manila is traditionally regarded as the “Heartland of the Philippine Revolution”, Cavite and its surrounding municipalities bore the brunt of the Spanish military campaign, becoming a no man’s land. Rebels in the area were generally engaged in hit-and-run guerrilla warfare against Spanish positions in Manila, Morong, Nueva Ecija and Pampanga. From Morong, Bonifacio served as tactician for rebel guerrillas and issued commands to areas other than his personal sector, though his reputation suffered when he lost battles he personally led.
From September to October 1896, Bonifacio supervised the establishment of Katipunan mountain and hill bases like Balara in Marikina, Pantayanin in Antipolo, Ugong in Pasig and Tungko in Bulacan. Bonifacio appointing generals for these areas, or approving selections the troops themselves made.
On November 7, 1896 Bonifacio led an assault on San Mateo, Marikina and Montalban. The Spanish were forced to retreat, leaving these areas to the rebels, except for the municipal hall of San Mateo where some Spanish troops had barricaded. While Bonifacio’s troops laid siege to the hall, other Katipunan forces set up defensive lines along the nearby Langka (or Nangka) river against Spanish reinforcements coming from the direction of Marikina. After three days, Spanish counterattacks broke through the Nangka river lines. The Spanish troops thus recaptured the rebel positions and surprised Bonifacio in San Mateo, who ordered a general retreat to Balara. They were pursued, and Bonifacio was nearly killed shielding Emilio Jacinto from a Spanish bullet which grazed his collar.
In Balara, Bonifacio commissioned Julio Nakpil to compose a national anthem. Nakpil produced a hymn called Marangal na Dalit ng Katagalugan (“Honorable Hymn of the Tagalogs”) and became the official national anthem during the entire period of the revolution until it was replaced years later by another national anthem commissioned by the new Republica Filipina government that replaced the Haring Bayang Katagalugan.
Bonifacio in Cavite
After Bonifacio’s disastrous defeat in Manila, Bonifacio sought refuge in Cavite where the revolutionaries were victorious. There were two Katipunan provincial chapters in Cavite that became rival factions: the Magdalo, headed by Emilio Aguinaldo’s cousin Baldomero Aguinaldo, and the Magdiwang, headed by Mariano Álvarez, uncle of Bonifacio’s wife. Leaders of both factions came from the upper class, in contrast to Bonifacio, who came from the lower middle class. After initial successes, Emilio Aguinaldo issued a manifesto in the name of the Magdalo ruling council which proclaimed a provisional and revolutionary government – despite the existence of the Katipunan government. Emilio Aguinaldo in particular had won fame for victories in the province. The Magdalo and Magdiwang clashed over authority and jurisdiction and did not help each other in battle. Bonifacio, as the recognized overall leader of the revolution, was invited by the Cavite leaders to mediate between them and unify their efforts. After multiple letters were sent to Bonifacio urging him to come, in December 1896 he traveled to Cavite accompanied by his wife, his brothers Procopio and Ciriaco, and some troops, including Emilio Jacinto, Bonifacio’s secretary and right-hand man. Jacinto was said to be against Bonifacio’s expedition to Cavite.
In Cavite, friction grew between Bonifacio and the Magdalo leaders. Apolinario Mabini, who later served as Emilio Aguinaldo’s adviser, writes that at this point the Magdalo leaders “already paid little heed to his authority and orders.” Bonifacio was partial to the Magdiwang, perhaps due to his kinship ties with Mariano Álvarez, or more importantly, due to their stronger recognition of his authority. When Aguinaldo and Edilberto Evangelista went to receive Bonifacio at Zapote, they were irritated with what they regarded as his attitude of superiority. In his memoirs Aguinaldo wrote that Bonifacio acted “as if he were a king”. Another time, Bonifacio ordered the arrest of one Katipunan general from Laguna surnamed Fernandez, who was accompanying the Magdalo leaders in paying their respect to Bonifacio, for failing to support his attack in Manila, but the other Magdalo leaders refused to surrender him. Townspeople in Noveleta (a Magdiwang town) acclaimed Bonifacio as the ruler of the Philippines, to the chagrin of the Magdalo leaders, (Bonifacio replied: “long live Philippine Liberty!”). Aguinaldo disputed with Bonifacio over strategic troop placements and blamed him for the capture of the town of Silang. The Spanish, through Jesuit Superior Pio Pi, wrote to Aguinaldo about the possibility of peace negotiations. When Bonifacio found out, he and the Magdiwang council rejected the proposed peace talks. Bonifacio was also angered that the Spanish considered Aguinaldo the “chief of the rebellion” instead of him. However, Aguinaldo continued to arrange negotiations which never took place. Bonifacio believed Aguinaldo was willing to surrender the revolution.
Bonifacio was also subject to rumors that he had stolen Katipunan funds, his sister was the mistress of a priest, and he was an agent provocateur paid by friars to foment unrest. Also circulated were anonymous letters which told the people of Cavite not to idolize Bonifacio because he was a Mason, a mere Manila employee, allegedly an atheist, and uneducated. According to these letters, Bonifacio did not deserve the title of Supremo since only God was supreme. This last allegation was made despite the fact that Supremo was meant to be used in conjunction with Presidente, i.e. Presidente Supremo (Supreme President) to distinguish the president of the Katipunan Supreme Council from council presidents of subordinate Katipunan chapters like the Magdalo and Magdiwang. Bonifacio suspected the rumor-mongering to be the work of the Magdalo leader Daniel Tirona. He confronted Tirona, whose airy reply provoked Bonifacio to such anger that he drew a gun and would have shot Tirona if others had not intervened.
On December 31, Bonifacio and the Magdalo and Magdiwang leaders held a meeting in Imus, ostensibly to determine the leadership of Cavite in order to end the rivalry between the two factions. The issue of whether the Katipunan should be replaced by a revolutionary government was brought up by the Magdalo, and this eclipsed the rivalry issue. The Magdalo argued that the Katipunan, as a secret society, should have ceased to exist once the Revolution was underway. They also held that Cavite should not be divided. Bonifacio and the Magdiwang contended that the Katipunan served as their revolutionary government since it had its own constitution, laws, and provincial and municipal governments. Edilberto Evangelista presented a draft constitution for the proposed government to Bonifacio but he rejected it as it was too similar to the Spanish Maura Law. Upon the event of restructuring, Bonifacio was given carte blanche to appoint a committee tasked with setting up a new government; he would also be in charge of this committee. He tasked Emilio Aguinaldo to record the minutes of the meeting and requested for it to establish this authority, but these were never done and never provided.
After Tejeros convention
On March 23, 1897, the day after the Tejeros convention, Bonifacio with his men and remaining supporters in the province (mostly of the Magdiwang faction) met again in the Tejeros estate house and drafted a document called Acta de Tejeros which called for the rejection of the previous days election. This document was signed by Bonifacio and 44 others, including Artemio Ricarte, Mariano Alvarez and Pascual Alvarez. Then, in a later meeting on April 19 in Naic, another document, the Naic Military Agreement, was drawn up which declared that its 41 signatories, “… having discovered the treason committed by certain officers who have been sowing discord and conniving with the Spaniards [and other offensive acts]”, had “agreed to deliver the people from this grave danger” by raising an army corps “by persuasion or force” under the command of General Pio del Pilar. The document’s 41 signatories included Bonifacio, Ricarte and del Pilar. The meeting was interrupted by Aguinaldo and del Pilar. Mariano Noriel and others present then promptly returned to Aguinaldo’s fold. Aguinaldo attempted to persuade Bonifacio to cooperate with his government, but Bonifacio refused and proceeded to Indang, Cavite planning to get out of Cavite and proceed back to Morong.
In late April, Aguinaldo fully assumed the presidential office after consolidating his position among the Cavite elite – most of Bonifacio’s Magdiwang supporters shifting allegiance to Aguinaldo. Aguinaldo’s government then ordered the arrest of Bonifacio, who was then moving out of Cavite.
Trial and death
In April 1897, Aguinaldo ordered the arrest of Bonifacio after he received a letter alleging that Bonifacio had burned down a village and ordered the burning of the church of Indang after townspeople refused to give him provisions. Many of the principal men of Indang, among them Severino de las Alas, presented Emilio Aguinaldo with several complaints against Bonifacio that the Supremo’s men stole carabaos (water buffalo) and other work animals by force and butchered them for food. On April 25, a party of Aguinaldo’s men led by Colonel Agapito Bonzón and Major José Ignacio “Intsik” Paua caught up with Bonifacio at his camp in barrio Limbon, Indang. The unsuspecting Bonifacio received them cordially. Early the next day, Bonzón and Paua attacked Bonifacio’s camp. Bonifacio was surprised and refused to fight against “fellow Tagalogs”, ordering his men to hold their fire, but shots were nevertheless exchanged. Bonifacio was shot in the arm by Bonzón, and Paua stabbed him in the neck but was prevented from striking further by one of Bonifacio’s men, who offered to die in Bonifacio’s place. Andrés’s brother Ciriaco was shot dead, while his other brother Procopio was beaten, and his wife Gregoria may have been raped by Bonzón. From Indang, a half-starved and wounded Bonifacio was carried by hammock to Naic, which had become President Aguinaldo’s headquarters.
Bonifacio’s party was brought to Naic, where he and Procopio stood trial on charges of sedition and treason against Aguinaldo’s government and conspiracy to murder Aguinaldo. The jury was composed entirely of Aguinaldo’s men and even Bonifacio’s defence lawyer himself declared his client’s guilt. Bonifacio was barred from confronting the state witness on the charge of conspiracy to murder on the grounds that the latter had been killed in battle. However, after the trial the witness was seen alive with the prosecutors.
The Bonifacio brothers were found guilty despite insufficient evidence and recommended to be executed. Aguinaldo commuted the sentence to deportation on May 8, 1897 but Pío del Pilar and Mariano Noriel persuaded him to withdraw the order for the sake of preserving unity. In this they were seconded by Mamerto Natividád and other bona fide supporters of Aguinaldo. The Bonifacio brothers were executed on May 10, 1897 in the mountains of Maragondon. Apolinario Mabini wrote that Bonifacio’s death demoralized many rebels from Manila, Laguna and Batangas who had come to help those in Cavite, and caused them to quit. In other areas, Bonifacio’s close associates like Emilio Jacinto and Macario Sakay continued the Katipunan and never recognized Aguinaldo’s authority.
The historical assessment of Bonifacio involves several controversial points. His death is alternately viewed as a justified execution for treason and a “legal murder” fueled by politics. Some historians consider him to be the rightful first President of the Philippines instead of Aguinaldo. Some historians have also opined that Bonifacio share or even take the place of José Rizal as the (foremost) Philippine national hero. The purported discovery of Bonifacio’s remains has also been questioned.
Trial and execution
Historians have condemned the trial of the Bonifacio brothers as unjust. The jury was entirely composed of Aguinaldo’s men; Bonifacio’s defense lawyer acted more like a prosecutor as he himself declared Bonifacio’s guilt and instead appealed for less punishment; and Bonifacio was not allowed to confront the state witness for the charge of conspiracy on the grounds that the latter had been killed in battle, but later the witness was seen with the prosecutors.
Teodoro Agoncillo writes that Bonifacio’s declaration of authority in opposition to Aguinaldo posed a danger to the revolution, because a split in the rebel forces would result in almost certain defeat to their united and well-armed Spanish foe. In contrast, Renato Constantino contends that Bonifacio was neither a danger to the revolution in general for he still planned to fight the Spanish, nor to the revolution in Cavite since he was leaving; but Bonifacio was definitely a threat to the Cavite leaders who wanted control of the Revolution, so he was eliminated. Constantino contrasts Bonifacio who had no record of compromise with the Spanish with the Cavite leaders who did compromise, resulting in the Pact of Biak-na-Bato whereas the revolution was officially halted and its leaders exiled, though many Filipinos continued to fight especially Katipunan leaders used to be close to Bonifacio (Aguinaldo eventually, unofficially allied with the United States, did return to take charge of the revolution during the
  The Philippines, officially known as the Republic of the Philippines (Filipino: Republika ng Pilipinas), is a sovereign island country in Southeast Asia situated in the western Pacific Ocean. It consists of about 7,641 islands that are categorized broadly under three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon , Visayas , and Mindanao . The capital city of the Philippines is Manila and the most populous city is Quezon City , both part of Metro Manila . The Philippines, officially known as the Republic of the Philippines (Filipino: Republika ng Pilipinas), is a sovereign island country in Southeast Asia situated in the western Pacific Ocean. It consists of about 7,641 islands that are categorized broadly under three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon , Visayas , and Mindanao . The capital city of the Philippines is Manila and the most populous city is Quezon City , both part of Metro Manila .
 The Philippines’ location on the Pacific Ring of Fire and close to the equator makes the Philippines prone to earthquakes and typhoons, but also endows it with abundant natural resources and some of the world’s greatest biodiversity . The Philippines has an area of approximately 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi), and a population of more than 100 million with faster growth than any other east Asian country. It is the seventh-most populated country in Asia and the 12th most populated country in the world. An additional 12 million Filipinos live overseas , comprising one of the world’s largest diasporas . Multiple ethnicities and cultures are found throughout the islands. In prehistoric times, Negritos were some of the archipelago’s earliest inhabitants. They were followed by successive waves of Austronesian peoples . Exchanges with Chinese, Malay , Indian , and Islamic states occurred. Then, various nations were established under the rule of Datus , Rajahs , Sultans Lakans.. The Philippines’ location on the Pacific Ring of Fire and close to the equator makes the Philippines prone to earthquakes and typhoons, but also endows it with abundant natural resources and some of the world’s greatest biodiversity . The Philippines has an area of approximately 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi), and a population of more than 100 million with faster growth than any other east Asian country. It is the seventh-most populated country in Asia and the 12th most populated country in the world. An additional 12 million Filipinos live overseas , comprising one of the world’s largest diasporas . Multiple ethnicities and cultures are found throughout the islands. In prehistoric times, Negritos were some of the archipelago’s earliest inhabitants. They were followed by successive waves of Austronesian peoples . Exchanges with Chinese, Malay , Indian , and Islamic states occurred. Then, various nations were established under the rule of Datus , Rajahs , Sultans Lakans..
The arrival of Ferdinand Magellan Homonhon, Eastern Samar in 1521 marked the beginning of Hispanic colonization. In 1543, Spanish explorer Ruy López de Villalobos named the archipelago Las Islas Filipinas in honor of Philip II of Spain . With the arrival of Miguel López de Legazpi from Mexico City, in 1565, the first Hispanic settlement in the archipelago was established. The Philippines became part of the Spanish Empire for more than 300 years. This resulted in Roman Catholicism becoming the dominant religion. During this time, Manila became the western hub of the trans-Pacific trade connecting Asia with Acapulco in the Americas using Manila galleons .
As the 19th century gave way to the 20th, there followed in quick succession the Philippine Revolution , which spawned the short-lived First Philippine Republic , followed by the bloody Philippine–American War of conquest by US military force. Aside from the period of Japanese occupation , the United States retained sovereignty over the islands until after World War II , when the Philippines was recognized as an independent nation. Since then, the Philippines has often had a tumultuous experience with democracy, which included the overthrow of a dictatorship by a non-violent revolution .
The nation’s large population and economic potential have led it to be classified as a middle power . It is a founding member of the United Nations , World Trade Organization , Association of Southeast Asian Nations , the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum, and the East Asia Summit . It also hosts the headquarters of the Asian Development Bank . The Philippines is considered to be an emerging market and a newly industrialized country , which has an economy transitioning from being one based on agriculture to one based more on services and manufacturing.
|





 Andrés Bonifacio y de Castro (November 30, 1863 – May 10, 1897) was a Filipino revolutionary leader and the president of the Tagalog Republic. He is often called “The Father of the Philippine Revolution”. He was one of the founders and later Supremo (Supreme Leader) of the Kataas-taasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan ng mga Anak ng Bayan or more commonly known as “Katipunan“, a movement which sought the independence of the Philippines from Spanish colonial rule and started the Philippine Revolution. He is considered a national hero of the Philippines.
Andrés Bonifacio y de Castro (November 30, 1863 – May 10, 1897) was a Filipino revolutionary leader and the president of the Tagalog Republic. He is often called “The Father of the Philippine Revolution”. He was one of the founders and later Supremo (Supreme Leader) of the Kataas-taasan, Kagalanggalangang Katipunan ng mga Anak ng Bayan or more commonly known as “Katipunan“, a movement which sought the independence of the Philippines from Spanish colonial rule and started the Philippine Revolution. He is considered a national hero of the Philippines. 
 The Philippines, officially known as the Republic of the Philippines (Filipino:
The Philippines, officially known as the Republic of the Philippines (Filipino:  The Philippines’ location on the Pacific Ring of Fire and close to the equator makes the Philippines prone to earthquakes and typhoons, but also endows it with abundant natural resources and some of the world’s greatest biodiversity . The Philippines has an area of approximately 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi), and a population of more than 100 million with faster growth than any other east Asian country. It is the seventh-most populated country in Asia and the 12th most populated country in the world. An additional 12 million Filipinos live overseas , comprising one of the world’s largest diasporas . Multiple ethnicities and cultures are found throughout the islands. In prehistoric times, Negritos were some of the archipelago’s earliest inhabitants. They were followed by successive waves of Austronesian peoples . Exchanges with Chinese, Malay , Indian , and Islamic states occurred. Then, various nations were established under the rule of Datus , Rajahs , Sultans Lakans..
The Philippines’ location on the Pacific Ring of Fire and close to the equator makes the Philippines prone to earthquakes and typhoons, but also endows it with abundant natural resources and some of the world’s greatest biodiversity . The Philippines has an area of approximately 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 sq mi), and a population of more than 100 million with faster growth than any other east Asian country. It is the seventh-most populated country in Asia and the 12th most populated country in the world. An additional 12 million Filipinos live overseas , comprising one of the world’s largest diasporas . Multiple ethnicities and cultures are found throughout the islands. In prehistoric times, Negritos were some of the archipelago’s earliest inhabitants. They were followed by successive waves of Austronesian peoples . Exchanges with Chinese, Malay , Indian , and Islamic states occurred. Then, various nations were established under the rule of Datus , Rajahs , Sultans Lakans..




