|
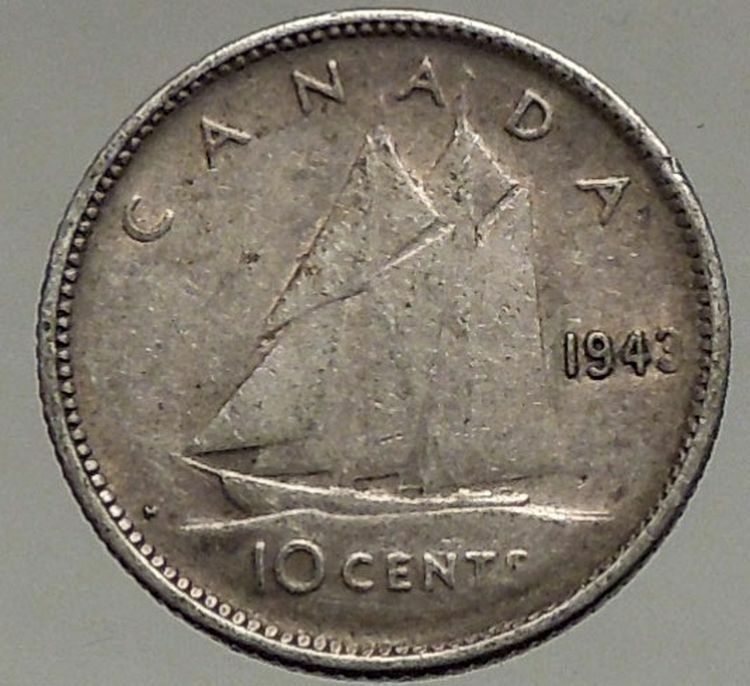
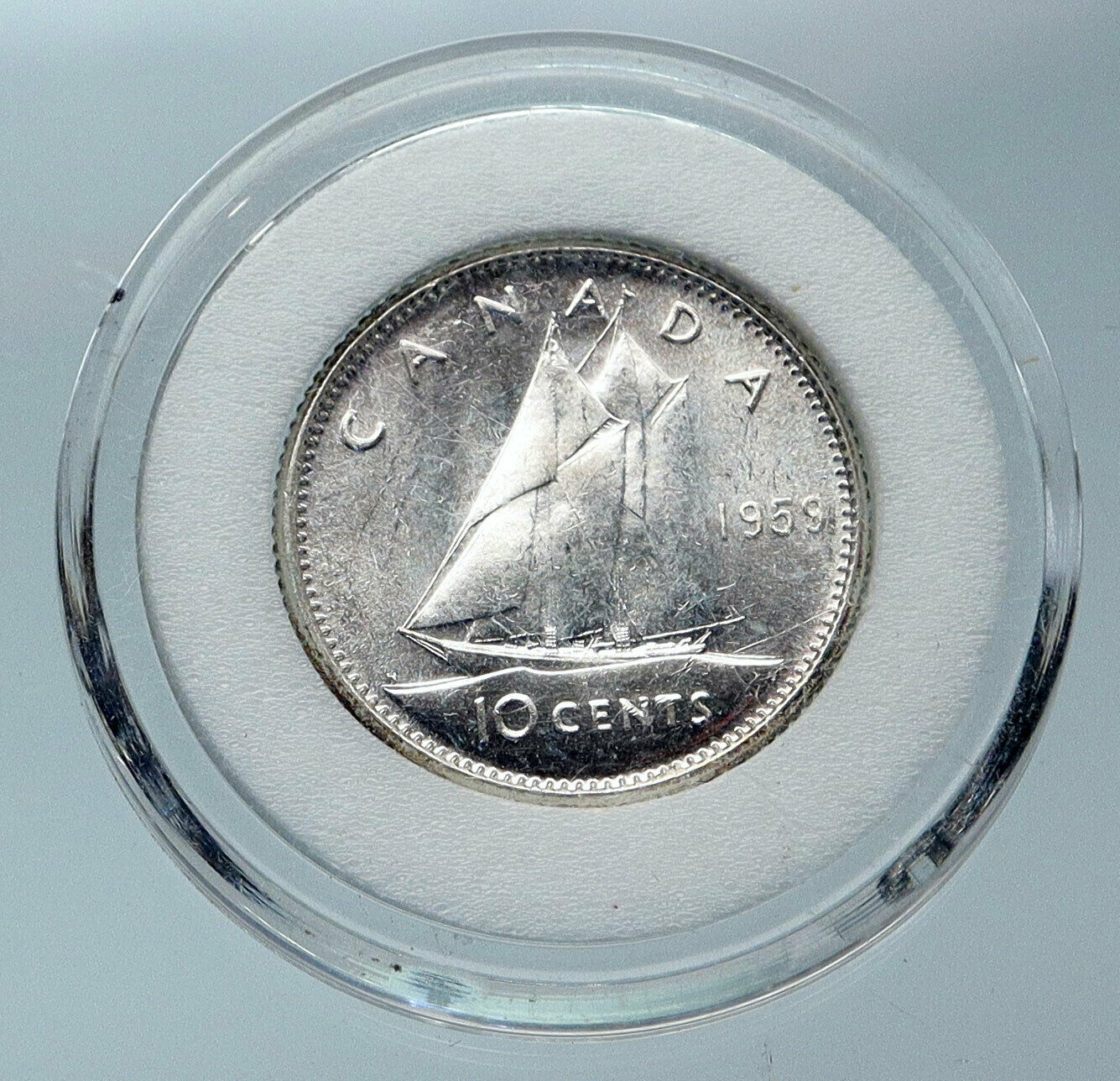
Canada under Elizabeth II – Queen: 6 February 1952–present
1867-1967 Canadian Confederation Centennial
1967 Silver 10 Cents 18.03mm (2.27 grams) 0.800 Silver (0.0596 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM #67 | Designer: Alex Colville
ELIZABETH II D◦G◦REGINA, crowned draped bust of young Elizabeth II right.
10 CENTS CANADA 1867-1967, Atlantic mackerel left.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured,
provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of
Authenticity.
available for sale in my storeall coins of CanadaClick here to see

The
Atlantic mackerel
(Scomber
scombrus) is a
pelagic
schooling species of
mackerel
found on both sides of the
North Atlantic
Ocean. The species is also called Boston mackerel, or just mackerel.
The Atlantic mackerel is by far the most common of the 10 species of the
family caught in British waters. It is extremely common in huge shoals migrating
towards the coast to feed on small fish and prawns during the summer.
Abundant in cold and temperate shelf areas, it forms large schools near the
surface. They overwinter in deeper waters but move closer to shore in spring
when water temperatures range between 11 and 14 °C (52 and 57 °F).
It is found in the north-east Atlantic: North Sea (east) and British Isles
(west). The North Sea stock decreased dramatically in the 1960s because of
direct overfishing.
Male and female Atlantic mackerel grow at about the same rate, reaching a
maximum age of about 20 years and a maximum
fork length
around 47 cm (19 in). Most Atlantic mackerel are sexually mature by the age of
three years.
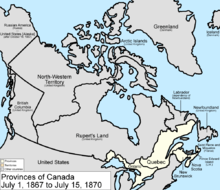
Canadian
Confederation (French:
Confédération canadienne) was the
process by which the
federal
Dominion
of
Canada
was formed on July 1, 1867. On that day,
three
British colonies
became four
provinces
of the new dominion. The existing
United Province of Canada
was divided into the
new provinces of
Ontario
and
Quebec
, and two other colonies,
New Brunswick
and
Nova Scotia
, also became provinces of the new
Dominion of Canada
.

Terminology
Canada is a
federal state
and not a confederate association
of sovereign states, the usual meaning of
confederation
; but is often considered to be
among the world’s more
decentralized
federations.
In this Canadian context, confederation generally describes the
political process that united the colonies in the 1860s and related events, and
the subsequent incorporation of other colonies and territories. The term
confederation is now often used to describe Canada in an abstract way, “the
Fathers of Confederation
” itself being one such
usage. Provinces and territories that became part of Canada after 1867 are also
said to have
joined, or entered into, confederation
(but not
the Confederation). Confederation is, loosely translated, a confederation
of colonies. The term is also used to divide
Canadian history
into pre-Confederation (i.e.
pre-1867) and post-Confederation (i.e. post-1867) periods.
History
Further information:
Constitutional history of Canada
Colonial organization
Map of
North America
before the
French and Indian War
, that is part
of the greater world-wide conflict known as the
Seven Years’ War
(1756 to 1763).
Possessions of Britain (pink), France (sky blue), and Spain (green)
All the
former colonies and territories
that became
involved in the Canadian Confederation on July 1, 1867, were initially part of
New France
, and were once ruled by
France
.
Nova Scotia
was granted in 1621 to
Sir William Alexander
under
charter
by
James VI
. This claim overlapped the French
claims to
Acadia
, and although the
Scottish colony
of Nova Scotia was short-lived,
for political reasons, the conflicting imperial interests of France and the 18th
century
Great Britain
led to a long and bitter struggle
for control. Present-day mainland Nova Scotia was finally acquired by the
British by the
Treaty of Utrecht
of 1713 and the Acadian
population was eventually
expelled
by the British in 1755. They called
Acadia
Nova Scotia
, which included present-day
New Brunswick
. The rest of New France was
acquired by the British by the
Treaty of Paris (1763)
, which ended the
Seven Years’ War
. From 1763 to 1791, most of
New France became the
Province of Quebec
. However, in 1769 the
present-day
Prince Edward Island
, which had been part of
Acadia, was renamed “St John’s Island” and organized as a separate colony. It
was renamed “Prince Edward Island” in 1798 in honour of
Prince Edward, Duke of Kent and Strathearn
.
The first
English
attempt at settlement had been in
Newfoundland
, which would not join the
Confederation until 1949. The
Society of Merchant Venturers
of
Bristol
began to settle
Newfoundland and Labrador
at
Cuper’s Cove
as far back as 1610, and
Newfoundland had also been the subject of a
French colonial enterprise
.
In the wake of the
American Revolution
, an estimated 50,000
United Empire Loyalists
fled to
British North America
. The British created the
separate colony of New Brunswick in 1784 for the Loyalists who settled in the
western part of Nova Scotia. While Nova Scotia (including New Brunswick)
received slightly more than half of this influx, many Loyalists also settled in
the Province of Quebec, which by the
Constitutional Act of 1791
was separated into a
predominantly English
Upper Canada
and a predominantly French
Lower Canada
. The
War of 1812
and subsequent
Treaty of 1818
established the
49th parallel
as the border with the United
States from the
Great Lakes
to the
Rocky Mountains
in Western Canada.
Canadian Territory at Confederation.
Following the
Rebellions of 1837
,
Lord Durham
in his
Durham Report
, recommended that Upper Canada
and Lower Canada should be joined to form the
Province of Canada
and that the new province
should have a
responsible government
. As a result of Durham’s
report, the
British Parliament
passed the
Act of Union 1840
, and the Province of Canada
was formed in 1841. The new province was divided into two parts:
Canada West
(the former Upper Canada) and
Canada East
(the former Lower Canada).
Ministerial responsibility
was granted by
Governor General
Lord Elgin
in 1848, first to Nova Scotia and
then to Canada. In the following years, the British would extend responsible
government to Prince Edward Island (1851), New Brunswick (1854), and
Newfoundland
(1855).
The area which constitutes modern-day
British Columbia
is the remnants of the
Hudson’s Bay Company’s
Columbia District
and
New Caledonia District
following the
Oregon Treaty
. Prior to joining Canada in 1871,
British Columbia consisted of the separate
Colony of British Columbia
(formed in 1858, in
an area where the Crown had previously granted a monopoly to the Hudson’s Bay
Company), and the
Colony of Vancouver Island
(formed in 1849)
constituting a separate
crown colony
until it was united with the
Colony of British Columbia in 1866.
The remainder of modern-day Canada was made up of
Rupert’s Land
and the
North-Western Territory
(both of which were
controlled by the
Hudson’s Bay Company
and sold to Canada in
1870) and the
Arctic Islands
, which were under direct British
control and became a part of Canada in 1880.

Elizabeth
II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; born 21 April 1926)
is, and has been since her accession in 1952, Queen of the United Kingdom,
Canada, Australia, and New Zealand, and
Head of the Commonwealth
. She is also Queen of
12 countries that have become independent since her accession: Jamaica,
Barbados, the Bahamas, Grenada, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands, Tuvalu, Saint
Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Belize, Antigua and Barbuda, and Saint
Kitts and Nevis.
Elizabeth was born in London to the Duke and Duchess of York, later King
George VI
and
Queen Elizabeth
, and was the elder of their two
daughters. She was educated privately at home. Her father acceded to the throne
on the
abdication
of his brother
Edward VIII
in 1936, from which time she was
the
heir presumptive
. She began to undertake public
duties during
World War II
, serving in the
Auxiliary Territorial Service
. In 1947, she
married
Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh
, with whom she
has four children:
Charles
,
Anne
,
Andrew
, and
Edward
.
Elizabeth’s many historic visits and meetings include a
state visit to the Republic of Ireland
and
reciprocal visits to and from the Pope. She has seen major constitutional
changes, such as
devolution
in the United Kingdom, Canadian
patriation
, and the
decolonisation of Africa
. She has also reigned
through various wars and conflicts involving many of
her realms
. She is the world’s oldest reigning
monarch as well as Britain’s
longest-lived
. In 2015, she surpassed the reign
of her great-great-grandmother,
Queen Victoria
, to become the
longest-reigning British monarch
and the
longest-reigning queen regnant
in world
history.
Times of personal significance have included the births and marriages of her
children, grandchildren and great grandchildren, her
coronation in 1953
, and the celebration of
milestones such as her
Silver
,
Golden
and
Diamond
Jubilees in 1977, 2002, and 2012,
respectively. Moments of sadness for her include the death of her father, aged
56; the assassination of Prince Philip’s uncle,
Lord Mountbatten
; the breakdown of her
children’s marriages in 1992 (her
annus horribilis
); the death in 1997 of her
son’s former wife,
Diana, Princess of Wales
; and the deaths of her
mother and
sister
in 2002. Elizabeth has occasionally
faced
republican
sentiments and severe press
criticism of the
royal family
, but support for the monarchy and
her personal popularity remain high.
.svg/220px-Canada_(orthographic_projection).svg.png)
Canada
is a country, consisting of
ten provinces and t
 hree hree
territories, in the northern part of the continent of North America.
It extends from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean,
covering 9.98 million square kilometres (3.85 million square miles) in total,
making it the world’s
second-largest country by total area
and the
fourth-largest country by land area
. Canada’s
common border with the United States
forms the
world’s longest land border. Canada is sparsely populated overall, the majority
of its land territory being dominated by
forest
and
tundra
as well as the mountain range of the
Rocky Mountains
; about four-fifths of the
population live near to the southern border. The majority of Canada has a cold
or severely cold winter climate, but southerly areas are warm in summer.
The land now called Canada has been inhabited for millennia by various
Aboriginal peoples
. Beginning in the late 15th
century,
British
and
French colonies
were established on the
region’s Atlantic coast. As a consequence of
various conflicts
, the United Kingdom gained
and lost North American territories until left, in the late 18th century, with
what mostly comprises Canada today. Pursuant to the
British North America Act
, on July 1, 1867,
three colonies
joined
to form the autonomous
federal Dominion
of Canada. This began an
accretion
of provinces and territories to the
new self-governing
Dominion
. In 1931, Britain granted Canada near
total independence with the
Statute of Westminster 1931
and full
sovereignty was attained when the
Canada Act 1982
severed the vestiges of legal
dependence on the
British parliament
.
Canada is a
federal
parliamentary democracy
and a
constitutional monarchy
, Queen
Elizabeth II
being the current head of state.
The country is
officially bilingual
at the federal level. It
is one of the world’s most ethnically diverse and
multicultural
nations, the product of
large-scale immigration from many countries, with a population of approximately
35 million as of 2015. Its advanced economy is
the eleventh largest in the world
, relying
chiefly upon its abundant natural resources and well-developed international
trade networks. Canada’s
long and complex relationship
with the United
States has had a significant impact on its economy and culture.
Canada is a
developed country
and one of the wealthiest in
the world, with the
tenth highest
nominal per capita income
globally, and the
eighth highest
ranking in the
Human Development Index
. It
ranks among the highest
in international
measurements of government transparency, civil liberties, quality of life,
economic freedom, and education. Canada is a
Commonwealth Realm
member of the
Commonwealth of Nations
, a member of the
Francophonie
, and part of several major
international and intergovernmental institutions or groupings including the
North Atlantic Treaty Organization, the
G8
, the
Group of Ten
, the
G20
, the
North American Free Trade Agreement
and the
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
forum.
|









.svg/220px-Canada_(orthographic_projection).svg.png)
 hree
hree 




