|
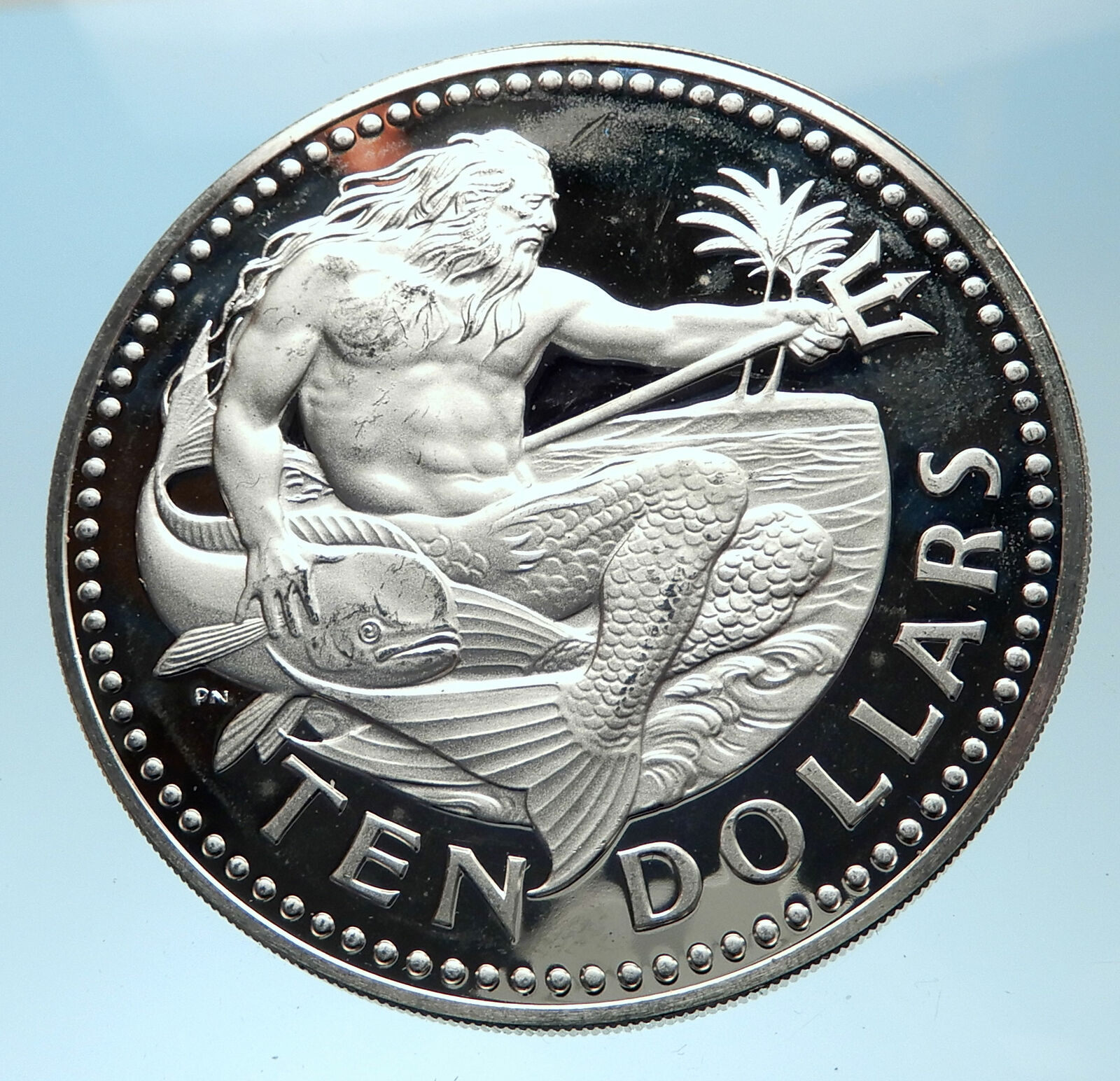
Barbados – 10th Anniversary of Caribbean Development Bank
1980 FM Proof Silver 25 Dollars 38mm (30.32 grams) 0.500 Silver (0.4546 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 30
BARBADOS PRIDE AND INDUSTRY, National Coat-of-arms.
·1970·TENTH·ANNIVERSARY·1980· CARIBBEAN DEVELOPMENT BANK 25 DOLLARS, Globe above flag.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
The Caribbean Development Bank (CDB) is a financial institution that helps Caribbean nations finance social and economic programs in its member countries. CDB was established by an Agreement signed on October 18, 1969, in Kingston, Jamaica, and entered into force on January 26, 1970.[1] The permanent headquarters of the bank is located at Wildey, St. Michael, Barbados; adjacent to the campus of the Samuel Jackman Prescod Polytechnic. There are no other offices of the bank. The headquarters serves all of the regional borrowing member countries with staff recruited from its members.
CDB’s membership of 27 countries consists of 19 regional borrowing members, three regional non-borrowing members and five members from outside the Region.
As of December 31, 2014, CDB recorded total assets of US$2.61 billion (this includes US$1.38 billion of ordinary Capital resources and US$1.23 billion of Special Funds Resources). CDB has an “Aa1” with stable outlook rating with Moody’s Rating Agency, and an “AA/A-1+” with stable outlook rating with Standard and Poor’s Rating Agency. In 2014, the Bank approved loans and grants of US$269.5 million.
At the end of 2014, the bank had total equity of US$822 million.
 Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of North America. It is 34 kilometres (21 miles) in length and up to 23 km (14 mi) in width, covering an area of 432 km2 (167 sq mi). It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 km (62 mi) east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, Barbados is east of the Windwards, part of the Lesser Antilles, roughly at 13°N of the equator. It is about 168 km (104 mi) east of both the countries of Saint Lucia and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and 400 km (250 mi) north-east of Trinidad and Tobago. Barbados is outside the principal Atlantic hurricane belt. Its capital and largest city is Bridgetown. Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of North America. It is 34 kilometres (21 miles) in length and up to 23 km (14 mi) in width, covering an area of 432 km2 (167 sq mi). It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 km (62 mi) east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, Barbados is east of the Windwards, part of the Lesser Antilles, roughly at 13°N of the equator. It is about 168 km (104 mi) east of both the countries of Saint Lucia and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and 400 km (250 mi) north-east of Trinidad and Tobago. Barbados is outside the principal Atlantic hurricane belt. Its capital and largest city is Bridgetown.
.svg/85px-Coat_of_arms_of_Barbados_(2).svg.png) Inhabited by Kalinago people since the 13th century, and prior to that by other Amerindians, Barbados was visited by Spanish navigators in the late 15th century and claimed for the Spanish Crown. It first appeared in a Spanish map in 1511. The Portuguese visited the island in 1536, but they left it unclaimed, with their only remnants being an introduction of wild hogs for a good supply of meat whenever the island was visited. An English ship, the Olive Blossom, arrived in Barbados in 1625; its men took possession of it in the name of King James I. In 1627, the first permanent settlers arrived from England, and it became an English and later British colony. As a wealthy sugar colony, it became an English centre of the African slave trade until that trade was outlawed in 1807, with final emancipation of slaves in Barbados occurring over a period of years from 1833. Inhabited by Kalinago people since the 13th century, and prior to that by other Amerindians, Barbados was visited by Spanish navigators in the late 15th century and claimed for the Spanish Crown. It first appeared in a Spanish map in 1511. The Portuguese visited the island in 1536, but they left it unclaimed, with their only remnants being an introduction of wild hogs for a good supply of meat whenever the island was visited. An English ship, the Olive Blossom, arrived in Barbados in 1625; its men took possession of it in the name of King James I. In 1627, the first permanent settlers arrived from England, and it became an English and later British colony. As a wealthy sugar colony, it became an English centre of the African slave trade until that trade was outlawed in 1807, with final emancipation of slaves in Barbados occurring over a period of years from 1833.
 On 30 November 1966, Barbados became an independent state and Commonwealth realm with the British monarch (currently Queen Elizabeth II) as hereditary head of state. It has a population of 284,996 people, predominantly of African descent. Despite being classified as an Atlantic island, Barbados is considered to be a part of the Caribbean, where it is ranked as a leading tourist destination. Forty percent of the tourists come from the UK, with the US and Canada making up the next large groups of visitors to the island. On 30 November 1966, Barbados became an independent state and Commonwealth realm with the British monarch (currently Queen Elizabeth II) as hereditary head of state. It has a population of 284,996 people, predominantly of African descent. Despite being classified as an Atlantic island, Barbados is considered to be a part of the Caribbean, where it is ranked as a leading tourist destination. Forty percent of the tourists come from the UK, with the US and Canada making up the next large groups of visitors to the island.
|





 Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of North America. It is 34 kilometres (21 miles) in length and up to 23 km (14 mi) in width, covering an area of 432 km2 (167 sq mi). It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 km (62 mi) east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, Barbados is east of the Windwards, part of the Lesser Antilles, roughly at 13°N of the equator. It is about 168 km (104 mi) east of both the countries of Saint Lucia and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and 400 km (250 mi) north-east of Trinidad and Tobago. Barbados is outside the principal Atlantic hurricane belt. Its capital and largest city is Bridgetown.
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of North America. It is 34 kilometres (21 miles) in length and up to 23 km (14 mi) in width, covering an area of 432 km2 (167 sq mi). It is situated in the western area of the North Atlantic and 100 km (62 mi) east of the Windward Islands and the Caribbean Sea; therein, Barbados is east of the Windwards, part of the Lesser Antilles, roughly at 13°N of the equator. It is about 168 km (104 mi) east of both the countries of Saint Lucia and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines and 400 km (250 mi) north-east of Trinidad and Tobago. Barbados is outside the principal Atlantic hurricane belt. Its capital and largest city is Bridgetown. .svg/85px-Coat_of_arms_of_Barbados_(2).svg.png) Inhabited by Kalinago people since the 13th century, and prior to that by other Amerindians, Barbados was visited by Spanish navigators in the late 15th century and claimed for the Spanish Crown. It first appeared in a Spanish map in 1511. The Portuguese visited the island in 1536, but they left it unclaimed, with their only remnants being an introduction of wild hogs for a good supply of meat whenever the island was visited. An English ship, the Olive Blossom, arrived in Barbados in 1625; its men took possession of it in the name of King James I. In 1627, the first permanent settlers arrived from England, and it became an English and later British colony. As a wealthy sugar colony, it became an English centre of the African slave trade until that trade was outlawed in 1807, with final emancipation of slaves in Barbados occurring over a period of years from 1833.
Inhabited by Kalinago people since the 13th century, and prior to that by other Amerindians, Barbados was visited by Spanish navigators in the late 15th century and claimed for the Spanish Crown. It first appeared in a Spanish map in 1511. The Portuguese visited the island in 1536, but they left it unclaimed, with their only remnants being an introduction of wild hogs for a good supply of meat whenever the island was visited. An English ship, the Olive Blossom, arrived in Barbados in 1625; its men took possession of it in the name of King James I. In 1627, the first permanent settlers arrived from England, and it became an English and later British colony. As a wealthy sugar colony, it became an English centre of the African slave trade until that trade was outlawed in 1807, with final emancipation of slaves in Barbados occurring over a period of years from 1833.  On 30 November 1966, Barbados became an independent state and Commonwealth realm with the British monarch (currently Queen Elizabeth II) as hereditary head of state. It has a population of 284,996 people, predominantly of African descent. Despite being classified as an Atlantic island, Barbados is considered to be a part of the Caribbean, where it is ranked as a leading tourist destination. Forty percent of the tourists come from the UK, with the US and Canada making up the next large groups of visitors to the island.
On 30 November 1966, Barbados became an independent state and Commonwealth realm with the British monarch (currently Queen Elizabeth II) as hereditary head of state. It has a population of 284,996 people, predominantly of African descent. Despite being classified as an Atlantic island, Barbados is considered to be a part of the Caribbean, where it is ranked as a leading tourist destination. Forty percent of the tourists come from the UK, with the US and Canada making up the next large groups of visitors to the island. 




