|
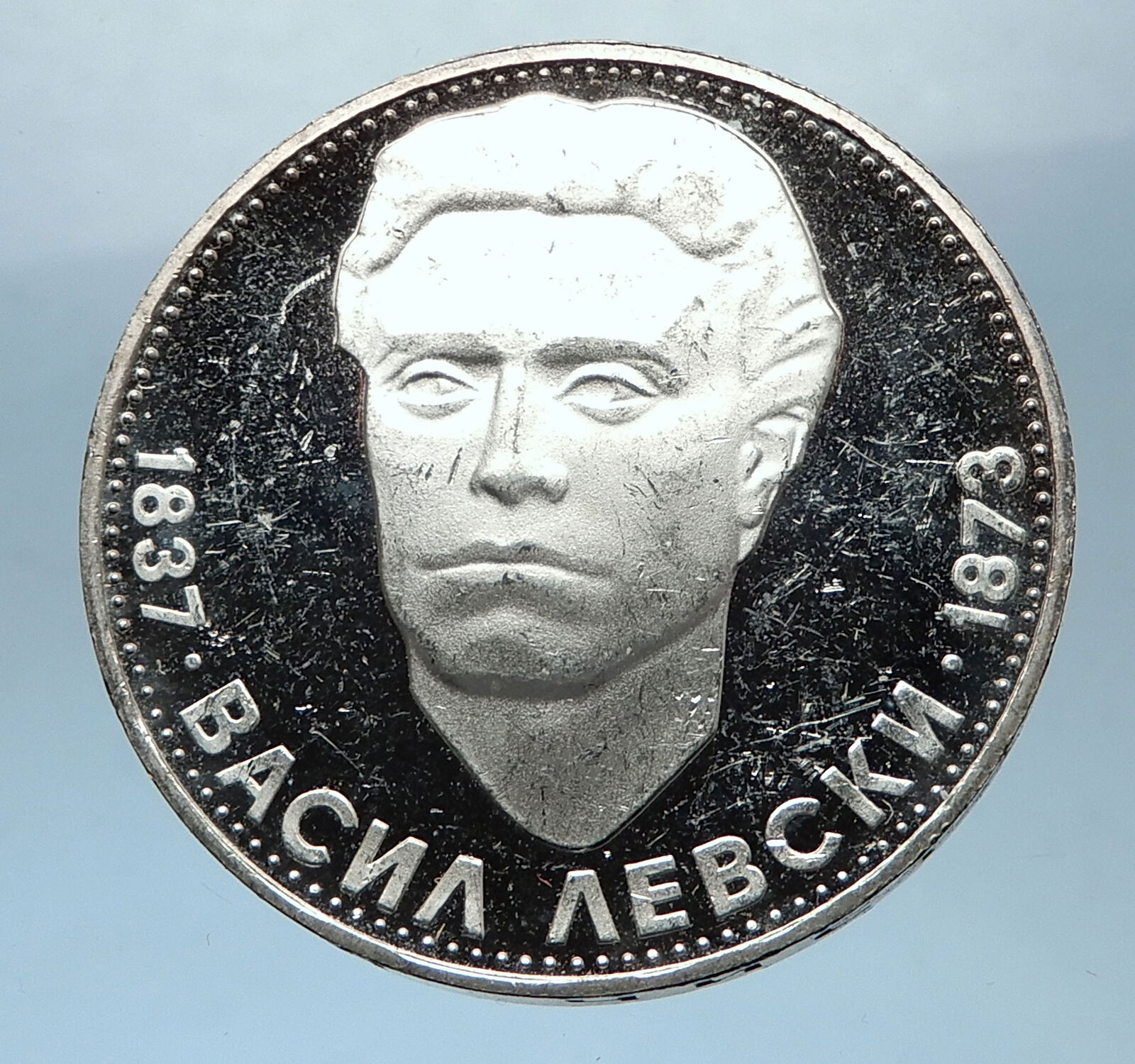
Bulgaria – 150 Years Since the Birth of Vasil Levski
1987 Silver 20 Leva 30mm (11.23 grams) 0.500 Silver (0.1804 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 164
НАРОДНА РЕПУБЛИКА БЪЛГАРИЯ 1987. 20 ЛЕВА, Coat of arms of People’s Republic of Bulgaria. Denomination and date.
150 Г. ОТ РОЖДЕНИЕТО НА ВАСИЛ ЛЕВСКИ, Bust of Vasil Levsky 1/4 right.
Edge Lettering: Ако спечеля, печеля за цял народ…
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 Vasil Levski (Bulgarian: Васил Левски, originally spelled Василъ Лѣвскій, pronounced [vɐˈsiɫ ˈlɛfski]), born Vasil Ivanov Kunchev (Васил Иванов Кунчев; 18 July 1837 – 18 February 1873), was a Bulgarian revolutionary and is a national hero of Bulgaria today. Dubbed the Apostle of Freedom, Levski ideologised and strategised a revolutionary movement to liberate Bulgaria from Ottoman rule. Levski founded the Internal Revolutionary Organisation, and sought to foment a nationwide uprising through a network of secret regional committees. Vasil Levski (Bulgarian: Васил Левски, originally spelled Василъ Лѣвскій, pronounced [vɐˈsiɫ ˈlɛfski]), born Vasil Ivanov Kunchev (Васил Иванов Кунчев; 18 July 1837 – 18 February 1873), was a Bulgarian revolutionary and is a national hero of Bulgaria today. Dubbed the Apostle of Freedom, Levski ideologised and strategised a revolutionary movement to liberate Bulgaria from Ottoman rule. Levski founded the Internal Revolutionary Organisation, and sought to foment a nationwide uprising through a network of secret regional committees.
Born in the Sub-Balkan town of Karlovo to middle class parents, Levski became an Orthodox monk before emigrating to join the two Bulgarian Legions in Serbia and other Bulgarian revolutionary groups. Abroad, he acquired the nickname Levski, “Lionlike”. After working as a teacher in Bulgarian lands, he propagated his views and developed the concept of his Bulgaria-based revolutionary organisation, an innovative idea that superseded the foreign-based detachment strategy of the past. In Romania, Levski helped institute the Bulgarian Revolutionary Central Committee, composed of Bulgarian expatriates. During his tours of Bulgaria, Levski established a wide network of insurrectionary committees. Ottoman authorities, however, captured him at an inn near Lovech and executed him by hanging in Sofia.
Levski looked beyond the act of liberation: he envisioned a “pure and sacred” Bulgarian republic of ethnic and religious equality. His concepts have been described as a struggle for human rights, inspired by the progressive liberalism of the French Revolution and 19th century Western European society. Levski is commemorated with monuments in Bulgaria and Serbia, and numerous national institutions bear his name. In 2007, he topped a nationwide television poll as the all-time greatest Bulgarian.

Bulgaria (Bulgarian: България, tr. Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria (Bulgarian: Република България, tr. Republika Bǎlgariya, IPA: [rɛˈpublikɐ bɐɫˈɡarijɐ]), is a country in southeastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. With a territory of 110,994 square kilometres (42,855 sq mi), Bulgaria is Europe’s 16th-largest country.
 Organised prehistoric cultures began developing on current Bulgarian lands during the Neolithic period. Its ancient history saw the presence of the Thracians, Ancient Greeks, Persians, Celts, Romans, Goths, Alans and Huns. The emergence of a unified Bulgarian state dates back to the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681 AD, which dominated most of the Balkans and functioned as a cultural hub for Slavs during the Middle Ages. With the downfall of the Second Bulgarian Empire in 1396, its territories came under Ottoman rule for nearly five centuries. The Russo-Turkish War of 1877-78 led to the formation of the Third Bulgarian State. The following years saw several conflicts with its neighbours, which prompted Bulgaria to align with Germany in both world wars. In 1946 it became a one-party socialist state as part of the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc. In December 1989 the ruling Communist Party allowed multi-party elections, which subsequently led to Bulgaria’s transition into a democracy and a market-based economy. Organised prehistoric cultures began developing on current Bulgarian lands during the Neolithic period. Its ancient history saw the presence of the Thracians, Ancient Greeks, Persians, Celts, Romans, Goths, Alans and Huns. The emergence of a unified Bulgarian state dates back to the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681 AD, which dominated most of the Balkans and functioned as a cultural hub for Slavs during the Middle Ages. With the downfall of the Second Bulgarian Empire in 1396, its territories came under Ottoman rule for nearly five centuries. The Russo-Turkish War of 1877-78 led to the formation of the Third Bulgarian State. The following years saw several conflicts with its neighbours, which prompted Bulgaria to align with Germany in both world wars. In 1946 it became a one-party socialist state as part of the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc. In December 1989 the ruling Communist Party allowed multi-party elections, which subsequently led to Bulgaria’s transition into a democracy and a market-based economy.

Bulgaria’s population of 7.2 million people is predominantly urbanised and mainly concentrated in the administrative centres of its 28 provinces. Most commercial and cultural activities are centred on the capital and largest city, Sofia. The strongest sectors of the economy are heavy industry, power engineering, and agriculture, all of which rely on local natural resources.
The country’s current political structure dates to the adoption of a democratic constitution in 1991. Bulgaria is a unitary parliamentary republic with a high degree of political, administrative, and economic centralisation. It is a member of the European Union, NATO, and the Council of Europe; a founding state of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE); and has taken a seat at the UN Security Council three times.
|





 Vasil Levski (Bulgarian: Васил Левски, originally spelled Василъ Лѣвскій, pronounced [vɐˈsiɫ ˈlɛfski]), born Vasil Ivanov Kunchev (Васил Иванов Кунчев; 18 July 1837 – 18 February 1873), was a Bulgarian revolutionary and is a national hero of Bulgaria today. Dubbed the Apostle of Freedom, Levski ideologised and strategised a revolutionary movement to liberate Bulgaria from Ottoman rule. Levski founded the Internal Revolutionary Organisation, and sought to foment a nationwide uprising through a network of secret regional committees.
Vasil Levski (Bulgarian: Васил Левски, originally spelled Василъ Лѣвскій, pronounced [vɐˈsiɫ ˈlɛfski]), born Vasil Ivanov Kunchev (Васил Иванов Кунчев; 18 July 1837 – 18 February 1873), was a Bulgarian revolutionary and is a national hero of Bulgaria today. Dubbed the Apostle of Freedom, Levski ideologised and strategised a revolutionary movement to liberate Bulgaria from Ottoman rule. Levski founded the Internal Revolutionary Organisation, and sought to foment a nationwide uprising through a network of secret regional committees. 
 Organised prehistoric cultures began developing on current Bulgarian lands during the Neolithic period. Its ancient history saw the presence of the Thracians, Ancient Greeks, Persians, Celts, Romans, Goths, Alans and Huns. The emergence of a unified Bulgarian state dates back to the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681 AD, which dominated most of the Balkans and functioned as a cultural hub for Slavs during the Middle Ages. With the downfall of the Second Bulgarian Empire in 1396, its territories came under Ottoman rule for nearly five centuries. The Russo-Turkish War of 1877-78 led to the formation of the Third Bulgarian State. The following years saw several conflicts with its neighbours, which prompted Bulgaria to align with Germany in both world wars. In 1946 it became a one-party socialist state as part of the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc. In December 1989 the ruling Communist Party allowed multi-party elections, which subsequently led to Bulgaria’s transition into a democracy and a market-based economy.
Organised prehistoric cultures began developing on current Bulgarian lands during the Neolithic period. Its ancient history saw the presence of the Thracians, Ancient Greeks, Persians, Celts, Romans, Goths, Alans and Huns. The emergence of a unified Bulgarian state dates back to the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681 AD, which dominated most of the Balkans and functioned as a cultural hub for Slavs during the Middle Ages. With the downfall of the Second Bulgarian Empire in 1396, its territories came under Ottoman rule for nearly five centuries. The Russo-Turkish War of 1877-78 led to the formation of the Third Bulgarian State. The following years saw several conflicts with its neighbours, which prompted Bulgaria to align with Germany in both world wars. In 1946 it became a one-party socialist state as part of the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc. In December 1989 the ruling Communist Party allowed multi-party elections, which subsequently led to Bulgaria’s transition into a democracy and a market-based economy.





