|
Seleukid Empire
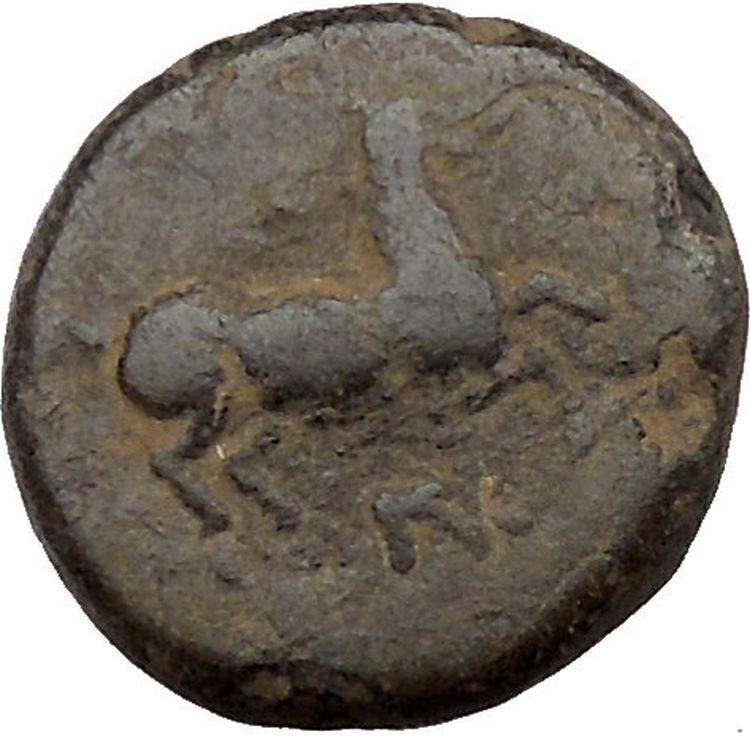
Antiochos III, Megas – King: 222-187 B.C.
Bronze 16mm (3.30 grams) Uncertain Mint 67 in Seleukia or Mesopotamia
Reference: HGC 9, 527
Rare R3
Diademed head of Antiochos III right.
ΒΑΣΙΛΕΩΣ ANTIOXOY, Apollo seated left on
omphalos, holding arrow and grounded bow; monogram in field to left.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured,
provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of
Authenticity.

In
Greek
and
Roman mythology
,
Apollo, is one of the most
important and diverse of the
Olympian deities
. The ideal of the
kouros
(a beardless youth), Apollo has been
variously recognized as a god of light and the sun; truth and prophecy;
archery
; medicine and healing; music, poetry,
and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son of
Zeus and Leto
, and has a
twin
sister, the chaste huntress
Artemis
. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced
Etruscan mythology
as Apulu. Apollo was
worshiped in both
ancient Greek
and
Roman religion
, as well as in the modern
Greco
–Roman
Neopaganism
.
As the patron of Delphi
(Pythian Apollo), Apollo was an
oracular
god — the prophetic deity of the
Delphic Oracle
. Medicine and healing were
associated with Apollo, whether through the god himself or mediated through his
son Asclepius
, yet Apollo was also seen as a god
who could bring ill-health and deadly
plague
as well as one who had the ability to
cure. Amongst the god’s custodial charges, Apollo became associated with
dominion over
colonists
, and as the patron defender of herds
and flocks. As the leader of the
Muses (Apollon Musagetes) and director of their choir, Apollo
functioned as the patron god of music and
poetry
.
Hermes
created the
lyre for him, and the instrument became a common
attribute
of Apollo. Hymns sung to Apollo were
called paeans
.
In Hellenistic times, especially during the third century BCE, as Apollo
Helios he became identified among Greeks with
Helios
,
god of the sun
, and his sister Artemis
similarly equated with
Selene
,
goddess of the moon
. In Latin texts, on the
other hand, Joseph Fontenrose declared himself unable to find any conflation of
Apollo with
Sol
among the
Augustan poets
of the first century, not even
in the conjurations of
Aeneas
and
Latinus
in
Aeneid
XII (161–215). Apollo and Helios/Sol
remained separate beings in literary and mythological texts until the third
century CE.
Antiochus III the Great, (Greek
Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας; ca. 241–187 BC,
ruled 222–187 BC), younger son of
Seleucus II Callinicus
, became the 6th ruler of the
Seleucid Empire
as a youth of about eighteen in 223 BC. Ascending the throne
at young age, Antiochus was an ambitious ruler. Although his early attempts in
war against the
Ptolemaic Kingdom
were unsuccessful, in the following years of conquest
Antiochus proved himself as the most successful Seleucid King after
Seleucus I
himself. His traditional designation, the Great, reflects
an epithet he briefly assumed after his Eastern Campaign (it appears in regnal
formulas at Amyzon in 203 and 202 BC, but not later). Antiochos also assumed the
title “Basileus Megas” (which is
Greek
for Great King), the
traditional title of
the Persian kings, which he adopted after his conquest of Koile Seleukia.
//
Early years
Antiochus III inherited a disorganized state. Not only had
Asia Minor
become detached, but the farther eastern provinces had broken away,
Bactria
under
the Greek
Diodotus of Bactria
, and
Parthia
under
the nomad chieftain
Arsaces
. Soon after Antiochus’s accession,
Media
and
Persis
revolted under their governors, the brothers
Molon
and
Alexander
.
The young king, under the baneful influence of the minister
Hermeias
,
authorised an attack on
Judea
instead of
going in person to face the rebels. The attack on Judea proved a fiasco, and the
generals sent against Molon and Alexander met with disaster. Only in Asia Minor,
where the king’s cousin, the able
Achaeus
represented the Seleucid cause, did its prestige recover, driving
the Pergamene power back to its earlier limits.
In 221 BC Antiochus at last went east, and the rebellion of Molon and
Alexander collapsed. The submission of Lesser Media, which had asserted its
independence under
Artabazanes
, followed. Antiochus rid himself of Hermeias by assassination
and returned to Seleukia
(220 BC). Meanwhile Achaeus himself had revolted and assumed the title of king
in Asia Minor. Since, however, his power was not well enough grounded to allow
of his attacking Seleukia, Antiochus considered that he might leave Achaeus for the
present and renew his attempt on Judea.
The campaigns of 219 BC and 218 BC carried the Seleucid armies almost to the
confines of
Ptolemaic Egypt
, but in 217 BC
Ptolemy IV
confronted Antiochus at the
battle of Raphia
and inflicted a defeat upon him which nullified all
Antiochus’s successes and compelled him to withdraw north of the
Lebanon
. In
216 BC Antiochus went north to deal with Achaeus, and had by 214 BC driven him
from the field into Sardis
. Antiochus contrived to get possession of the person of
Achaeus
(see
Polybius
),
but the citadel held out until 213 BC under Achaeus’ widow
Laodice
and then surrendered.
Having thus recovered the central part of Asia Minor – for the Seleucid
government had perforce to tolerate the dynasties in
Pergamon
,
Bithynia
and Cappadocia
– Antiochus turned to recover the outlying provinces of the north
and east. He obliged
Xerxes of Armenia
to acknowledge his supremacy in 212 BC. In 209 BC
Antiochus invaded Parthia
, occupied the capital
Hecatompylus
and pushed forward into
Hyrcania
.
The Parthian king
Arsaces II
apparently successfully sued for peace.
Bactrian
campaign and Indian expedition
Year 209 BC saw Antiochus in
Bactria
,
where the
Greco-Bactrian
king
Euthydemus I
had supplanted the original rebel. Antiochus again met with
success.
After sustaining a famous siege in his capital
Bactra
(Balkh), Euthydemus obtained an honourable peace by which
Antiochus promised Euthydemus’ son
Demetrius
the hand of one of his daughters.
Antiochus next, following in the steps of Alexander, crossed into the
Kabul
valley,
renewed his friendship with the
Indian
king
Sophagasenus
and returned west by way of
Seistan
and Kerman (206/5). According to
Polybius
:
-
“He crossed the Caucasus (Hindu
Kush) and descended into India; renewed his friendship with
Sophagasenus
(Subhashsena in Prakrit) the king of the Indians; received
more elephants, until he had a hundred and fifty altogether; and having once
more provisioned his troops, set out again personally with his army: leaving
Androsthenes of Cyzicus the duty of taking home the treasure which this king
had agreed to hand over to him.”
Polybius 11.39
Persia and Koile
Seleukia campaigns
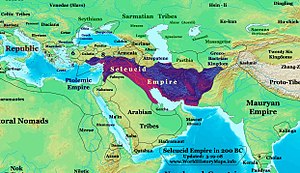
The Seleucid Empire in 200BC, (before Antiochus was defeated by the
Romans)..
From
Seleucia on the Tigris
he led a short expedition down the
Persian
Gulf
against the
Gerrhaeans
of
the Arabian coast (205 BC/204 BC). Antiochus seemed to have restored the
Seleucid empire in the east, and the achievement brought him the title of “the
Great.” (Antiochos Megas). In 205 BC/204 BC the infant
Ptolemy V Epiphanes
succeeded to the Egyptian throne, and Antiochus is said
(notably by Polybios) to have concluded a secret pact with
Philip V of Macedon
for the partition of the Ptolemaic possessions. Under
the terms of this pact,
Macedon
were to receive Egypt’s around the Aegean Sea and
Cyrene
while Antiochus would take
Cyprus
and
Egypt.
Once more Antiochus attacked the Ptolemaic province of Koile Seleukia and
Phoenicia, and by 199 BC he seems to have had possession of it before the
Aetolian,
Scopas
, recovered it for Ptolemy. But that recovery proved brief, for in 198
BC Antiochus defeated Scopas at the
Battle of Panium
, near the sources of the
Jordan
,
a battle which marks the end of Ptolemaic rule in Judea.
War against Rome
|
[show]
|
| |
Thermopylae
–
Eurymedon
–
Myonessus
–
Magnesia
|
|
Antiochus then moved to Asia Minor to secure the coast towns which had
belonged to the Ptolemaic overseas dominions and the independent Greek cities.
This enterprise brought him into antagonism with
Rome
, since Smyrna
and
Lampsacus
appealed to the republic of the west, and the tension became greater after
Antiochus had in 196 BC established a footing in
Thrace
. The
evacuation of Greece by the Romans gave Antiochus his opportunity, and he now
had the fugitive
Hannibal
at
his court to urge him on.
Aetolians. In
191 BC, however, the Romans under
Manius Acilius Glabrio
routed him at
Thermopylae
and obliged him to withdraw to Asia. The Romans followed up
their success by attacking Antiochus in
Anatolia
,
and the decisive victory of
Scipio Asiaticus
at
Magnesia ad Sipylum
(190 BC), following the defeat of Hannibal at sea off
Side, delivered
Asia Minor into their hands.
By the
Treaty of Apamea
(188 BC) the Seleucid king abandoned all the country north
of the
Taurus
, which Rome distributed amongst its friends. As a consequence of this
blow to the Seleucid power, the outlying provinces of the empire, recovered by
Antiochus, reasserted their independence.
Antiochus mounted a fresh expedition to the east in
Luristan
, where he died in an attempt to rob a temple at Elymaïs, Persia, in
187 BC. The Seleucid kingdom as Antiochus left it fell to his son,
Seleucus IV Philopator
, by his wife
Laodice
.
|
Born:
241 BC
Died: |
|
Regnal titles |
| Preceded by
Seleucus III Ceraunus
|
Seleucid King
223–187 BC |
Succeeded by
Seleucus IV Philopator
|
Seleucid
Empire
Σελεύκεια
Seleúkeia |

|
312 BC–63 BC |
↓
|
|
|
The Seleucid Empire in 301 BC.
|
The Seleucid Empire
was a
Hellenistic
state ruled by the Seleucid dynasty
founded by
Seleucus I Nicator
following the division of
the empire created by
Alexander the Great
. Seleucus received
Babylonia
and, from there, expanded his
dominions to include much of Alexander’s
near eastern
territories. At the height of its
power, it included central
Anatolia
, the
Levant
,
Mesopotamia
,
Kuwait
,
Persia
,
Afghanistan
,
Turkmenistan
, and northwest parts of
India
.
The Seleucid Empire was a major center of
Hellenistic
culture that maintained the
preeminence of
Greek
customs where a Greek-Macedonian
political elite dominated, mostly in the urban areas. The Greek population of
the cities who formed the dominant elite were reinforced by emigration from
Greece
. Seleucid expansion into
Anatolia
and Greece was abruptly halted after
decisive defeats
at the hands of the
Roman army
. Their attempts to defeat their old
enemy
Ptolemaic Egypt
were frustrated by Roman
demands. Much of the eastern part of the empire was conquered by the
Parthians
under
Mithridates I of Parthia
in the mid-2nd century
BC, yet the Seleucid kings continued to rule a
rump state
from
the Seleukid Kingdom
until the invasion by
Armenian
king
Tigranes the Great
and their ultimate overthrow
by the Roman
general
Pompey
.
|











