|
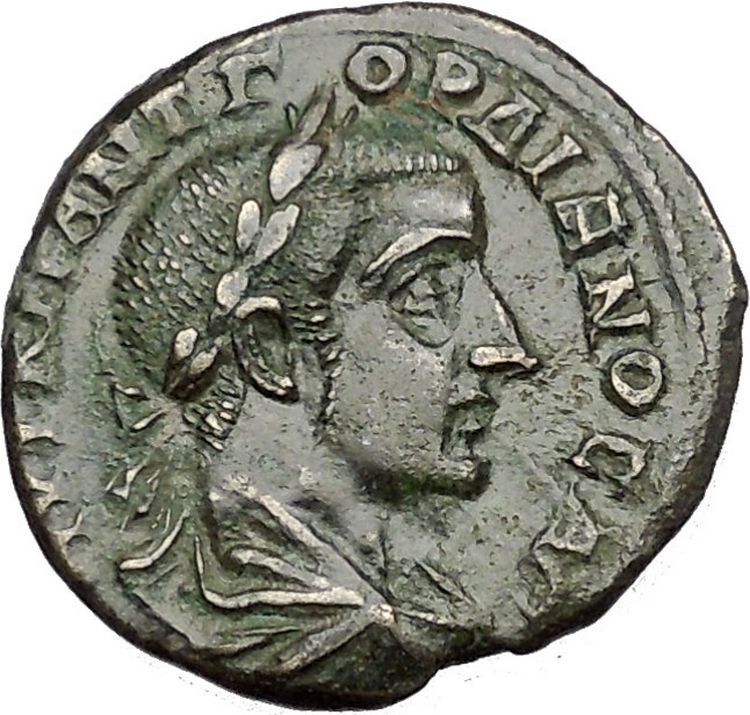
Caracalla
–
Roman Emperor
: 198-217 A.D. –
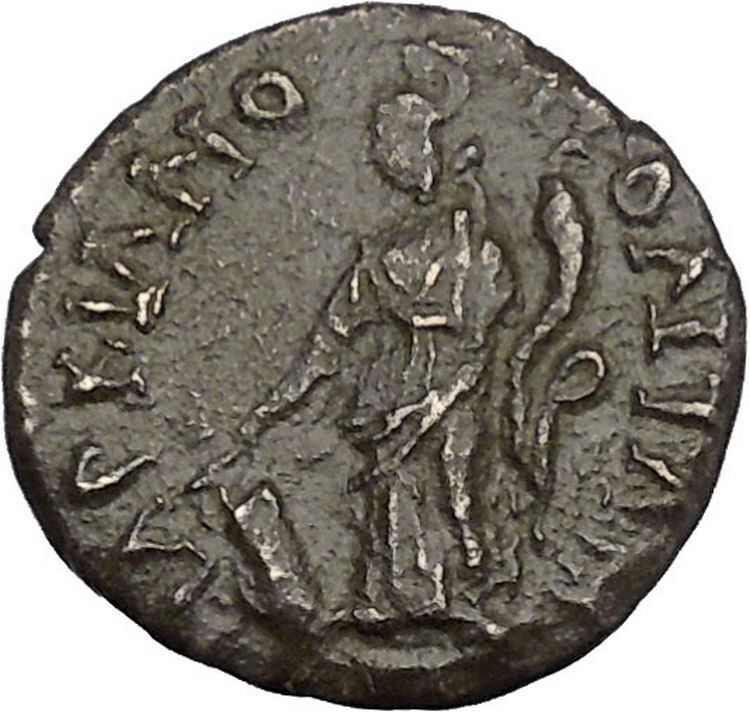
Bronze 27mm (12.37 grams) of
Anchialus
in
Thrace
AV K M AV ANTΩNINO, Laureate, draped and cuirassed bust right.
ΟVΛΠΙΑΝΩΝ AΓXIAΛEΩN,
Tyche standing left, holding patera over lit altar and cornucopia.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured,
provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of
Authenticity.
Tyche (Greek for luck; the Roman equivalent was
Fortuna
)
was the presiding
tutelary deity
that governed the fortune and
prosperity of a city, its destiny. Increasingly during the Hellenistic period, cities had their
own specific iconic version of Tyche, wearing a
mural crown
(a crown like the
walls of the city).

The
Greek historian Polybius
believed that when no cause can be
discovered to events such as floods, droughts, frosts or even in politics, then
the cause of these events may be fairly attributed to Tyche.
Stylianos Spyridakis concisely expressed Tyche’s appeal in a
Hellenistic world of arbitrary violence and unmeaning reverses: “In the
turbulent years of the
Epigoni of Alexander
, an awareness of the
instability of human affairs led people to believe that Tyche, the blind
mistress of Fortune, governed mankind with an inconstancy which explained the
vicissitudes of the time.”
In literature, she might be given various genealogies, as a daughter of
Hermes
and
Aphrodite
, or considered as one of the
Oceanids
, daughters of
Oceanus
and
Tethys
, or of
Zeus. She was connected with
Nemesis
and
Agathos Daimon
(“good spirit”).
She was uniquely venerated at
Itanos
in Crete, as Tyche Protogeneia,
linked with the Athenian
Protogeneia
(“firstborn”), daughter of
Erechtheus
, whose self-sacrifice saved the
city.
She had temples at
Caesarea Maritima
,
Antioch
,
Alexandria
and
Constantinople
. In
Alexandria
the Tychaeon, the temple of
Tyche, was described by
Libanius
as one of the most magnificent of the
entire Hellenistic world.
Tyche appears on many
coins
of the Hellenistic period in the three
centuries before the Christian era, especially from cities in the Aegean.
Unpredictable turns of fortune drive the complicated plotlines of
Hellenistic romances
, such as
Leucippe and Clitophon
or
Daphnis and Chloe
. She experienced a
resurgence in another era of uneasy change, the final days of publicly
sanctioned
Paganism
, between the late-fourth-century
emperors
Julian
and
Theodosius I
who definitively closed the
temples. The effectiveness of her capricious power even achieved respectability
in philosophical circles during that generation, though among poets it was a
commonplace to revile her for a fickle harlot.
In medieval art
, she was depicted as carrying a
cornucopia
, an
emblematic
ship’s rudder, and the
wheel of fortune
, or she may stand on the
wheel, presiding over the entire circle of fate.
The constellation of
Virgo
is sometimes identified as the heavenly
figure of Tyche, as well as other goddesses such as
Demeter
and
Astraea
.
Pomorie (Bulgarian:
Поморие; formerly known as Αγχίαλος
Anchialos in
Greek
, Anchialus in
Latin
) is a town
and seaside resort in southeastern
Bulgaria
,
located on a narrow rocky peninsula in
Burgas Bay
on the southern
Bulgarian Black Sea Coast
. It is located in
Burgas Province
20 km from
Burgas
and 18
km from Sunny Beach
. The ultrasaline lagoon
Lake
Pomorie
, the northernmost of the
Burgas
Lakes
, lies in the immediate proximity. It is the center of
Pomorie Municipality
.
Pomorie is an ancient city and today an important tourist destination. As of
September 2005 it has a population of 14,600 and the mayor is Petar Zlatanov. It
lies at
 42.55°N 42.55°N
27.65°E /
42.55; 27.65
/ 42°33′N
27°39′E.
Possibly founded in the 5th or 4th century BC as a colony of Apollonia (today
Sozopol
),
Anchialos was mentioned in
Strabo
‘s
Geographica as a small town. It was briefly captured by Messembria (Nesebar)
in the 2nd century BC, but reconquered by Apollonia and its fortified walls
destroyed. The name Anchialos is derived from
Ancient Greek
“anchi-” (“near, close to”) and “als-” (either “salt” or a
poetic and uncommon word for “sea”).
The western Black Sea coast was ultimately conquered by the
Romans
under
Marcus Licinius Crassus
in 29-28 BC after continuous campaigns in the area
since 72-71. The fortified wall was meanwhile rebuilt, as evidenced by
Ovid in 9 AD en
route to
Tomis
. In the early 1st century AD Anchialos was the centre of a
strategia of the vassal
Odrysian kingdom
, and the town had a
Thracian
population in the 6th century AD according to the early
Byzantine
historian
Procopius
.
As the Odrysian kingdom’s self-independence was abolished in 45 AD, Anchialos
became part of the
Roman province
of
Thrace
and was
formally proclaimed a city under Emperor
Trajan
. At the
time the city controlled a vast territory bordering that of Augusta Trajana (Stara
Zagora) and reaching the
Tundzha
to
the west, bordering that of Messembria to the north and the southern shore of
Lake
Burgas
to the south. Anchialos acquired the appearance of a Roman city and
thrived considerably in the 2nd and 3rd century under the
Severan Dynasty
, seving as the most important import and export station of
Thrace.
Caracalla 198-217 A.D.
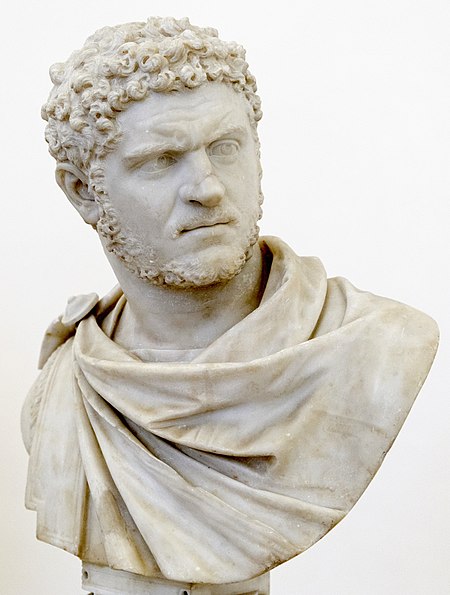

Caesar:
195-198 A.D. (under
Septimius Severus
)
Augustus: 198-217 A.D. (198-209 A.D. with
Septimius Severus
) (209-211 A.D. with
Septimius Severus
and
Geta
) (211 A.D. with
Geta
) (211-217 A.D. Sole Reign)
Son of
Septimius Severus
and
Julia Domna
| Brother of
Geta
| Husband of
Plautilla
| Nephew of
Julia Maesa
| Cousin of
Julia Soaemias
and
Julia Mamaea
|
Caracalla (Latin:
Marcus Aurelius Severus Antoninus Augustus;4
April 188 – 8 April 217) was
Roman emperor
from 198 to 217 The eldest son of
Septimius Severus
, for a short time he ruled
jointly with his younger brother
Geta
until he had him murdered in 211.
Caracalla is remembered as one of the most notorious and unpleasant of emperors
because of the massacres and persecutions he authorized and instigated
throughout the Empire.
Caracalla’s reign was also notable for the
Constitutio Antoniniana
(also called the
Edict of Caracalla), granting
Roman citizenship
to all freemen throughout the
Roman Empire
, which according to historian
Cassius Dio
, was done for the purposes of
raising tax revenue. He is also one of the emperors who commissioned a large
public bath-house (thermae)
in Rome. The remains of the
Baths of Caracalla
are still one of the major
tourist attractions of the Italian capital.
Early life
Caracalla, of mixed
Punic
–Roman
and Syrian
descent, was born Lucius Septimius
Bassianus in Lugdunum
,
Gaul (now Lyon
,
France
), the son of the later Emperor Septimius
Severus and
Julia Domna
. At the age of seven, his name was
changed to Marcus Aurelius Septimius Bassianus Antoninus to create a connection
to the family of the philosopher emperor
Marcus Aurelius
. He was later given the
Caracallanickname
,
which referred to the Gallic hooded tunic he habitually wore and which he made
fashionable.
Reign (211)
Murder of brother
(211)
His father died in 211 at
Eboracum
(now
York) while on campaign in northern Britain. Caracalla was present
and was then proclaimed emperor by the troops along with his brother
Publius Septimius Antoninus Geta
. Caracalla
suspended the
campaign in Caledonia
and soon ended all
military activity, as both brothers wanted to be sole ruler thus making
relations between them increasingly hostile. When they tried to rule the Empire
jointly they actually considered dividing it in halves, but were persuaded not
to do so by their mother.
Then in December 211 at a reconciliation meeting arranged by their mother
Julia, Caracalla had Geta assassinated by members of the Praetorian Guard loyal
to himself, Geta dying in his mother’s arms. Caracalla then persecuted and
executed most of Geta’s supporters and ordered a
damnatio memoriae
pronounced by the Senate
against his brother’s memory.
Geta’s image was simply removed from all coinage, paintings and statues,
leaving a blank space next to Caracalla’s. Among those executed were his former
cousin-wife
Fulvia Plautilla
, his unnamed daughter with
Plautilla along with her brother and other members of the family of his former
father-in-law
Gaius Fulvius Plautianus
. Plautianus had
already been executed for alleged treachery against emperor Severus in 205.
About the time of his accession he ordered the
Roman currency
devalued, the silver purity of
the denarius
was decreased from 56.5% to 51.5%, the
actual silver weight dropping from 1.81 grams to 1.66 grams – though the overall
weight slightly increased. In 215 he introduced the
antoninianus
, a “double denarius” weighing
5.1 grams and containing 2.6 grams of silver – a purity of 52%.
In the Roman provinces
In 213, Caracalla went north to the German frontier to deal with the
Alamanni
tribesmen who were raiding in the
Agri Decumates
. The Romans did defeat the
Alamanni in battle near the river
Main
, but failed to win a decisive victory over
them. After a peace agreement was brokered and a large bribe payment given to
the invaders, the Senate conferred upon him the empty title of Germanicus
Maximus. He also acquired the surname Alemannicus at this time. The
following year the tyrant traveled to the East, to Syria and Egypt never to
return to Rome.
Gibbon
in his work describes Caracalla as “the
common enemy of mankind”. He left the capital in 213, about a year after the
murder of Geta, and spent the rest of his reign in the provinces, particularly
those of the East. He kept the Senate and other wealthy families in check by
forcing them to construct, at their own expense, palaces, theaters, and places
of entertainment throughout the periphery. New and heavy taxes were levied
against the bulk of the population, with additional fees and confiscations
targeted at the wealthiest families.
When the inhabitants of
Alexandria
heard Caracalla’s claims that he had
killed Geta in self-defense, they produced a satire mocking this as well as
Caracalla’s other pretensions. In 215, Caracalla savagely responded to this
insult by slaughtering the deputation of leading citizens who had unsuspectingly
assembled before the city to greet his arrival, and then unleashed his troops
for several days of looting and plunder in Alexandria. According to historian
Cassius Dio, over 20,000 people were killed.[citation
needed]
Domestic Roman policy
Affiliation with
the army
During his reign as emperor, Caracalla raised the annual pay of an average
legionary to 675
denarii
and lavished many benefits on the
army which he both feared and admired, as instructed by his father Septimius
Severus who had told him on his deathbed to always mind the soldiers and ignore
everyone else. Caracalla did manage to win the trust of the military with
generous pay rises and popular gestures, like marching on foot among the
ordinary soldiers, eating the same food, and even grinding his own flour with
them.
With the soldiers, “He forgot even the proper dignity of his rank,
encouraging their insolent familiarity,” according to Gibbon. “The vigour of the
army, instead of being confirmed by the severe discipline of the camps, melted
away in the luxury of the cities.”
His official portraiture marks a break with the detached images of the
philosopher–emperors who preceded him: his close-cropped haircut is that of a
soldier, his pugnacious scowl a realistic and threatening presence. This rugged
soldier–emperor iconic archetype was adopted by most of the following emperors
who depended on the support of the troops to rule, like his eventual successor
Maximinus Thrax
.
Seeking to secure his own legacy, Caracalla also commissioned one of Rome’s
last major architectural achievements, the
Baths of Caracalla
, the 2nd largest public
baths ever built in ancient Rome. The main room of the baths was larger than
St. Peter’s Basilica
, and could easily
accommodate over 2,000 Roman citizens at one time. The bath house opened in 216,
complete with libraries, private rooms and outdoor tracks. Internally it was
lavishly decorated with gold-trimmed marble floors, columns, mosaics and
colossal statuary.
Edict of
Caracalla (212)
The
Constitutio Antoniniana
(Latin: “Constitution
[or Edict] of Antoninus”) (also called Edict of Caracalla) was an edict
issued in 212 by Caracalla which declared that all free men in the Roman Empire
were to be given full Roman citizenship and all free women in the Empire were
given the same rights as Roman women.
Before 212, for the most part only inhabitants of Italia held full Roman
citizenship. Colonies of Romans established in other provinces, Romans (or their
descendants) living in provinces, the inhabitants of various cities throughout
the Empire, and small numbers of local nobles (such as kings of client
countries) held full citizenship also. Provincials, on the other hand, were
usually non-citizens, although many held the
Latin Right
.
The Roman Historian
Cassius Dio
contended that the sole motivation
for the edict was a desire to increase state revenue.At the time aliens did not
have to pay most taxes that were required of citizens, so although nominally
Caracalla was elevating their legal status, he was more importantly expanding
the Roman tax base. The effect of this was to remove the distinction that
citizenship had held since the foundation of Rome and as such the act had a
profound effect upon the fabric of Roman society.
War with Parthia
According to the historian Herodian, in 216, Caracalla tricked the Parthians
into believing that he accepted a marriage and peace proposal, but then had the
bride and guests slaughtered after the wedding celebrations. The thereafter
ongoing conflict and skirmishes became known as the
Parthian war of Caracalla
.
Assassination (217)
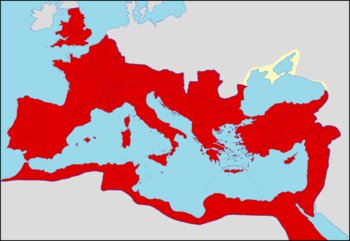
The Roman Empire during the reign of Caracalla.
While travelling from
Edessa
to continue the war with
Parthia
, he was assassinated while urinating at
a roadside near
Carrhae
on 8 April 217 (4 days after his 29th
birthday), by Julius Martialis, an officer of his personal bodyguard.
Herodian
says that Martialis’ brother had been
executed a few days earlier by Caracalla on an unproven charge; Cassius Dio, on
the other hand, says that Martialis was resentful at not being promoted to the
rank of centurion. The escort of the emperor gave him privacy to relieve
himself, and Martialis then ran forward and killed Caracalla with a single sword
stroke. While attempting to flee, the bold assassin was then quickly dispatched
by a Scythian archer of the Imperial Guard.
Caracalla was succeeded by his
Praetorian Guard Prefect
,
Macrinus
, who (according to Herodian) was most
probably responsible for having the emperor assassinated.
His nickname
According to
Aurelius Victor
in his Epitome de Caesaribus,
the agnomen
“Caracalla” refers to a Gallic
cloak
that Caracalla adopted as a personal
fashion, which spread to his army and his court. Cassius Dio and the
Historia Augusta
agree that his nickname
was derived from his cloak, but do not mention its country of origin.
Legendary king of
Britain
Geoffrey of Monmouth
‘s legendary
History of the Kings of Britain
makes
Caracalla a king of Britain, referring to him by his actual name “Bassianus”,
rather than the nickname Caracalla. In the story, after Severus’s death the
Romans wanted to make Geta king of Britain, but the Britons preferred Bassianus
because he had a British mother. The two brothers fought a battle in which Geta
was killed and Bassianus succeeded to the throne. He ruled until he was betrayed
by his Pictish
allies and overthrown by
Carausius
, who, according to Geoffrey, was a
Briton, rather than the historically much later
Menapian
Gaul that he actually was.
|












