|
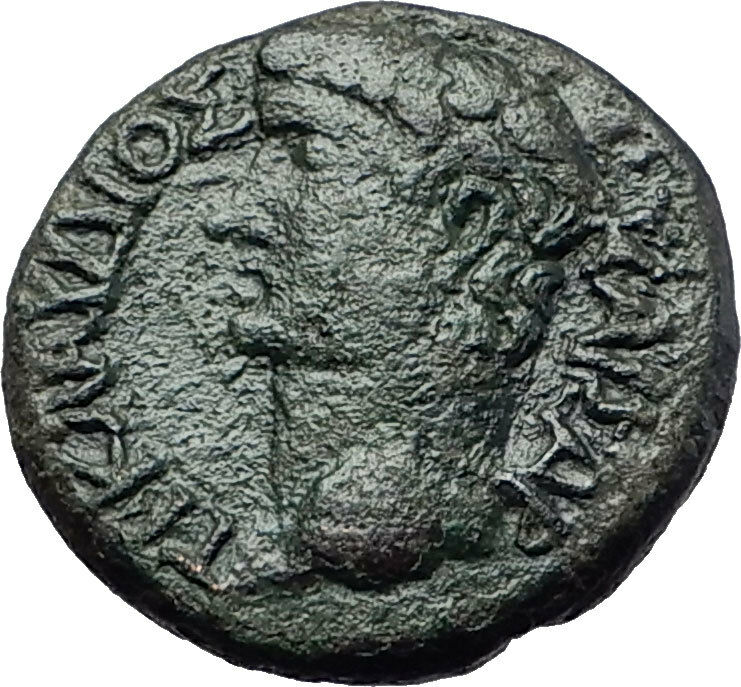
Caracalla
–
Roman Emperor
: 198-217 A.D. –
Bronze 19mm (3.77
grams) of
Coela
in
Thrace
Laureate bust right.
Prow of galley left.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured,
provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of
Authenticity.

A
galley is a type of
ship propelled by
rowers
that originated in the eastern
Mediterranean Sea
and was used for
warfare
,
trade
and
piracy
from the first millennium BC. Galleys
dominated
naval warfare
in the Mediterranean from the 8th
century BC until development of advanced sailing warships in the 17th century.
Galleys fought in the wars of
Assyria
, ancient
Phoenicia
,
Greece
,
Carthage
and
Rome
until the 4th century AD. After the fall
of the
Western Roman Empire
galleys formed the
mainstay of the
Byzantine navy
and other navies of successors
of the Roman Empire, as well as new
Muslim
navies. Medieval Mediterranean states,
notably the Italian maritime republics, including
Venice
,
Pisa
,
Genoa
and the
Ottoman Empire
relied on them as the primary
warships of their fleets until the 17th century, when they were gradually
replaced by sailing warships. Galleys continued to be applied in minor roles in
the Mediterranean and the
Baltic Sea
even after the introduction of
steam propelled
ships in the early 19th
century.
The galley engagements at
Actium
and
Lepanto
are among the greatest
naval battles
in history.
 Coela Coela
was located on the eastern part of the Thracian Chersonese, known in modern
times as the Gallipoli Peninsula. It struck coins during times of Alexander the
Great and later issued coins under the ancient Romans (known as Roman Provincial
or Greek Imperial coins.

The Gallipoli
peninsula
(Turkish:
Gelibolu
Yarımadası;
Greek
: Καλλίπολη)
is located in Turkish Thrace (or
East Thrace
), the European part of
Turkey
, with the
Aegean Sea
to the west and the
Dardanelles
strait to the east.
Gallipoli derives its name from the
Greek
“Καλλίπολις” (Kallipolis), meaning
“Beautiful City”. In
antiquity
, it was known as the Thracian
Chersonese, from
Greek
: Θρακική
Χερσόνησος (Latin:
Chersonesus Thracica).
The peninsula runs in a south-westerly direction into the
Aegean Sea
, between the Hellespont (now known
as the Dardanelles
) and the bay of Melas (today
Saros bay
). Near
Agora
it was protected by a wall running across
its full breadth. The isthmus traversed by the wall was only 36
stadia
in breadth (about 6.5 km), but the
length of the peninsula from this wall to its southern extremity, Cape Mastusia,
was 420 stadia (about 77.5 km).


Thrace
(demonym Thracian;
Bulgarian
:
Тракия, Trakiya,
Greek
: Θράκη,
Thráki,
Turkish
:
Trakya) is a historical and geographic area in southeast
Europe
. As a geographical concept, Thrace
designates a region bounded by the
Balkan Mountains
on the north,
Rhodope Mountains
and the
Aegean Sea
on the south, and by the
Black Sea
and the
Sea of Marmara
on the east. The areas it
comprises are southeastern
Bulgaria
(Northern
Thrace), northeastern
Greece
(Western
Thrace), and the European part of
Turkey
(Eastern
Thrace). The biggest part of Thrace is part of present-day Bulgaria.
In Turkey, it is also called
Rumelia
. The name comes from the
Thracians
, an ancient
Indo-European
people inhabiting Southeastern
Europe.
The historical boundaries of Thrace have varied. Noteworthy is the fact that,
at an early date, the
ancient Greeks
employed the term “Thrace” to
refer to all of the territory which lay north of
Thessaly
inhabited by the
Thracians
, a region which “had no definite
boundaries” and to which other regions (like
Macedonia
and even
Scythia
) were added. In one ancient Greek
source, the very Earth is divided into “Asia, Libya, Europa and Thracia”. As the
knowledge of world geography of the Greeks broadened, the term came to be more
restricted in its application: Thrace designated the lands bordered by the
Danube
on the north, by the Euxine Sea (Black
Sea) on the east, by northern
Macedonia
in the south and by the
Illyrian
lands (i.e.
Illyria
) to the west. This largely coincided
with the Thracian
Odrysian kingdom
, whose borders varied in time.
During this time, specifically after the Macedonian conquest, the region’s old
border with Macedonia was shifted from the
Struma River
to the
Mesta River
. This usage lasted until the Roman
conquest. Henceforth, (classical) Thrace referred only to the tract of land
largely covering the same extent of space as the modern geographical region. In
its early period, the
Roman province of Thrace
was of this extent,
but after the administrative reforms of the late 3rd century, Thracia’s much
reduced territory became the six small provinces which constituted the
Diocese of Thrace
. The medieval
Byzantine
theme
of
Thrace
contained only what today is
Eastern Thrace
.
The largest cities of Thrace are:
İstanbul
(European side),
Plovdiv
,
Burgas
,
Stara Zagora
,
Haskovo
,
Edirne
,
Çorlu
and
Tekirdag
.
Most of the Bulgarian and Greek population are Christians, while most of the
Turkish inhabitants of Thrace are Muslims.

The Roman province of Thrace
Thrace in
ancient Greek mythology
Ancient Greek mythology
provides them with a
mythical ancestor, named
Thrax
, son of the war-god
Ares, who was said to reside in Thrace. The Thracians appear in
Homer
‘s
Iliad
as
Trojan allies, led by
Acamas
and
Peiros
. Later in the Iliad,
Rhesus
, another Thracian king, makes an
appearance. Cisseus
, father-in-law to the Trojan elder
Antenor
, is also given as a Thracian king.
Homeric Thrace was vaguely defined, and stretched from the River
Axios
in the west to the
Hellespont
and
Black Sea
in the east. The
Catalogue of Ships
mentions three separate
contingents from Thrace: Thracians led by Acamas and Peiros, from
Aenus
;
Cicones
led by
Euphemus
, from southern Thrace, near
Ismaros
; and from the city of
Sestus
, on the Thracian (northern) side of the
Hellespont, which formed part of the contingent led by
Asius
. Greek mythology is replete with Thracian
kings, including
Diomedes
,
Tereus
,
Lycurgus
,
Phineus
,
Tegyrius
,
Eumolpus
,
Polymnestor
,
Poltys
, and
Oeagrus
(father of
Orpheus
). In addition to the tribe that Homer
calls Thracians, ancient Thrace was home to numerous other tribes, such as the
Edones
,
Bisaltae
,
Cicones
, and
Bistones
.
Thrace is also mentioned in Ovid’s Metamorphoses in the episode of
Philomela
, Procne, and
Tereus
. Tereus, the King of Thrace, lusts after
his sister-in-law, Philomela. He kidnaps her, holds her captive, rapes her, and
cuts out her tongue. Philomela manages to get free, however. She and her sister,
Procne, plot to get revenge, by killing Itys (son of Tereus and Procne) and
serving him to his father for dinner. At the end of the myth, all three turn
into birds—Procne, a swallow; Philomela, a nightingale; and Tereus, a
hoopoe
.
History
Ancient history
The indigenous population of Thrace was a people called the
Thracians
, divided into numerous tribal groups.
Thracian troops were known to accompany neighboring ruler
Alexander the Great
when he crossed the
Hellespont
which abuts Thrace, and took on the
Persian Empire
of the day.
The Thracians did not describe themselves as such and Thrace and
Thracians are simply the names given them by the Greeks.
Divided into separate tribes, the Thracians did not manage to form a lasting
political organization until the
Odrysian state
was founded in the 4th century
BC. Like Illyrians
, Thracian tribes of the mountainous
regions fostered a locally ruled warrior tradition, while the tribes based in
the plains were purportedly more peaceable. Recently discovered funeral mounds
in Bulgaria suggest that Thracian kings did rule regions of Thrace with distinct
Thracian national identity.
During this period, a subculture of
celibate
ascetics
called the
Ctistae
lived in Thrace, where they served as
philosophers, priests and prophets.
Medieval history
By the mid 5th century, as the Roman Empire began to crumble, Thracia fell
from the authority of Rome and into the hands of Germanic tribal rulers. With
the fall of Rome, Thracia turned into a battleground territory for the better
part of the next 1,000 years. The eastern successor of the
Roman Empire
in the Balkans, the
Byzantine Empire
, retained control over Thrace
until the 8th century when the northern half of the entire region was
incorporated into the
First Bulgarian Empire
. Byzantium regained
Thrace in the late 10th century and administered it as a
theme
, until the Bulgarians regained
control of the northern half at the end of the 12th century. Throughout the 13th
century and the first half of the 14th century, the region was changing in the
hands of the Bulgarian and the Byzantine Empire(excl. Constantinopole). In 1265
the area suffered a Mongol raid from the
Golden Horde
, led by
Nogai Khan
. In 1352, the
Ottoman
Turks
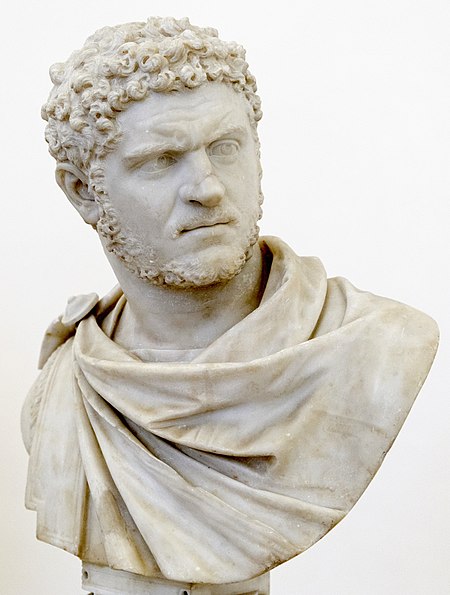
Caracalla 198-217 A.D.

Caesar:
195-198 A.D. (under
Septimius Severus
)
Augustus: 198-217 A.D. (198-209 A.D. with
Septimius Severus
) (209-211 A.D. with
Septimius Severus
and
Geta
) (211 A.D. with
Geta
) (211-217 A.D. Sole Reign)
Son of
Septimius Severus
and
Julia Domna
| Brother of
Geta
| Husband of
Plautilla
| Nephew of
Julia Maesa
| Cousin of
Julia Soaemias
and
Julia Mamaea
|
Caracalla (Latin:
Marcus Aurelius Severus Antoninus Augustus;4
April 188 – 8 April 217) was
Roman emperor
from 198 to 217 The eldest son of
Septimius Severus
, for a short time he ruled
jointly with his younger brother
Geta
until he had him murdered in 211.
Caracalla is remembered as one of the most notorious and unpleasant of emperors
because of the massacres and persecutions he authorized and instigated
throughout the Empire.
Caracalla’s reign was also notable for the
Constitutio Antoniniana
(also called the
Edict of Caracalla), granting
Roman citizenship
to all freemen throughout the
Roman Empire
, which according to historian
Cassius Dio
, was done for the purposes of
raising tax revenue. He is also one of the emperors who commissioned a large
public bath-house (thermae)
in Rome. The remains of the
Baths of Caracalla
are still one of the major
tourist attractions of the Italian capital.
Early life
Caracalla, of mixed
Punic
–Roman
and Syrian
descent, was born Lucius Septimius
Bassianus in Lugdunum
,
Gaul (now Lyon
,
France
), the son of the later Emperor Septimius
Severus and
Julia Domna
. At the age of seven, his name was
changed to Marcus Aurelius Septimius Bassianus Antoninus to create a connection
to the family of the philosopher emperor
Marcus Aurelius
. He was later given the
Caracallanickname
,
which referred to the Gallic hooded tunic he habitually wore and which he made
fashionable.
Reign (211)
Murder of brother
(211)
His father died in 211 at
Eboracum
(now
York) while on campaign in northern Britain. Caracalla was present
and was then proclaimed emperor by the troops along with his brother
Publius Septimius Antoninus Geta
. Caracalla
suspended the
campaign in Caledonia
and soon ended all
military activity, as both brothers wanted to be sole ruler thus making
relations between them increasingly hostile. When they tried to rule the Empire
jointly they actually considered dividing it in halves, but were persuaded not
to do so by their mother.
Then in December 211 at a reconciliation meeting arranged by their mother
Julia, Caracalla had Geta assassinated by members of the Praetorian Guard loyal
to himself, Geta dying in his mother’s arms. Caracalla then persecuted and
executed most of Geta’s supporters and ordered a
damnatio memoriae
pronounced by the Senate
against his brother’s memory.
Geta’s image was simply removed from all coinage, paintings and statues,
leaving a blank space next to Caracalla’s. Among those executed were his former
cousin-wife
Fulvia Plautilla
, his unnamed daughter with
Plautilla along with her brother and other members of the family of his former
father-in-law
Gaius Fulvius Plautianus
. Plautianus had
already been executed for alleged treachery against emperor Severus in 205.
About the time of his accession he ordered the
Roman currency
devalued, the silver purity of
the denarius
was decreased from 56.5% to 51.5%, the
actual silver weight dropping from 1.81 grams to 1.66 grams – though the overall
weight slightly increased. In 215 he introduced the
antoninianus
, a “double denarius” weighing
5.1 grams and containing 2.6 grams of silver – a purity of 52%.
In the Roman provinces
In 213, Caracalla went north to the German frontier to deal with the
Alamanni
tribesmen who were raiding in the
Agri Decumates
. The Romans did defeat the
Alamanni in battle near the river
Main
, but failed to win a decisive victory over
them. After a peace agreement was brokered and a large bribe payment given to
the invaders, the Senate conferred upon him the empty title of Germanicus
Maximus. He also acquired the surname Alemannicus at this time. The
following year the tyrant traveled to the East, to Syria and Egypt never to
return to Rome.
Gibbon
in his work describes Caracalla as “the
common enemy of mankind”. He left the capital in 213, about a year after the
murder of Geta, and spent the rest of his reign in the provinces, particularly
those of the East. He kept the Senate and other wealthy families in check by
forcing them to construct, at their own expense, palaces, theaters, and places
of entertainment throughout the periphery. New and heavy taxes were levied
against the bulk of the population, with additional fees and confiscations
targeted at the wealthiest families.
When the inhabitants of
Alexandria
heard Caracalla’s claims that he had
killed Geta in self-defense, they produced a satire mocking this as well as
Caracalla’s other pretensions. In 215, Caracalla savagely responded to this
insult by slaughtering the deputation of leading citizens who had unsuspectingly
assembled before the city to greet his arrival, and then unleashed his troops
for several days of looting and plunder in Alexandria. According to historian
Cassius Dio, over 20,000 people were killed.[citation
needed]
Domestic Roman policy
Affiliation with
the army
During his reign as emperor, Caracalla raised the annual pay of an average
legionary to 675
denarii
and lavished many benefits on the
army which he both feared and admired, as instructed by his father Septimius
Severus who had told him on his deathbed to always mind the soldiers and ignore
everyone else. Caracalla did manage to win the trust of the military with
generous pay rises and popular gestures, like marching on foot among the
ordinary soldiers, eating the same food, and even grinding his own flour with
them.
With the soldiers, “He forgot even the proper dignity of his rank,
encouraging their insolent familiarity,” according to Gibbon. “The vigour of the
army, instead of being confirmed by the severe discipline of the camps, melted
away in the luxury of the cities.”
His official portraiture marks a break with the detached images of the
philosopher–emperors who preceded him: his close-cropped haircut is that of a
soldier, his pugnacious scowl a realistic and threatening presence. This rugged
soldier–emperor iconic archetype was adopted by most of the following emperors
who depended on the support of the troops to rule, like his eventual successor
Maximinus Thrax
.
Seeking to secure his own legacy, Caracalla also commissioned one of Rome’s
last major architectural achievements, the
Baths of Caracalla
, the 2nd largest public
baths ever built in ancient Rome. The main room of the baths was larger than
St. Peter’s Basilica
, and could easily
accommodate over 2,000 Roman citizens at one time. The bath house opened in 216,
complete with libraries, private rooms and outdoor tracks. Internally it was
lavishly decorated with gold-trimmed marble floors, columns, mosaics and
colossal statuary.
Edict of
Caracalla (212)
The
Constitutio Antoniniana
(Latin: “Constitution
[or Edict] of Antoninus”) (also called Edict of Caracalla) was an edict
issued in 212 by Caracalla which declared that all free men in the Roman Empire
were to be given full Roman citizenship and all free women in the Empire were
given the same rights as Roman women.
Before 212, for the most part only inhabitants of Italia held full Roman
citizenship. Colonies of Romans established in other provinces, Romans (or their
descendants) living in provinces, the inhabitants of various cities throughout
the Empire, and small numbers of local nobles (such as kings of client
countries) held full citizenship also. Provincials, on the other hand, were
usually non-citizens, although many held the
Latin Right
.
The Roman Historian
Cassius Dio
contended that the sole motivation
for the edict was a desire to increase state revenue.At the time aliens did not
have to pay most taxes that were required of citizens, so although nominally
Caracalla was elevating their legal status, he was more importantly expanding
the Roman tax base. The effect of this was to remove the distinction that
citizenship had held since the foundation of Rome and as such the act had a
profound effect upon the fabric of Roman society.
War with Parthia
According to the historian Herodian, in 216, Caracalla tricked the Parthians
into believing that he accepted a marriage and peace proposal, but then had the
bride and guests slaughtered after the wedding celebrations. The thereafter
ongoing conflict and skirmishes became known as the
Parthian war of Caracalla
.
Assassination (217)
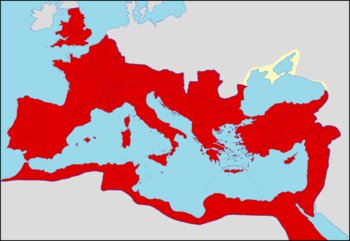
The Roman Empire during the reign of Caracalla.
While travelling from
Edessa
to continue the war with
Parthia
, he was assassinated while urinating at
a roadside near
Carrhae
on 8 April 217 (4 days after his 29th
birthday), by Julius Martialis, an officer of his personal bodyguard.
Herodian
says that Martialis’ brother had been
executed a few days earlier by Caracalla on an unproven charge; Cassius Dio, on
the other hand, says that Martialis was resentful at not being promoted to the
rank of centurion. The escort of the emperor gave him privacy to relieve
himself, and Martialis then ran forward and killed Caracalla with a single sword
stroke. While attempting to flee, the bold assassin was then quickly dispatched
by a Scythian archer of the Imperial Guard.
Caracalla was succeeded by his
Praetorian Guard Prefect
,
Macrinus
, who (according to Herodian) was most
probably responsible for having the emperor assassinated.
His nickname
According to
Aurelius Victor
in his Epitome de Caesaribus,
the agnomen
“Caracalla” refers to a Gallic
cloak
that Caracalla adopted as a personal
fashion, which spread to his army and his court. Cassius Dio and the
Historia Augusta
agree that his nickname
was derived from his cloak, but do not mention its country of origin.
Legendary king of
Britain
Geoffrey of Monmouth
‘s legendary
History of the Kings of Britain
makes
Caracalla a king of Britain, referring to him by his actual name “Bassianus”,
rather than the nickname Caracalla. In the story, after Severus’s death the
Romans wanted to make Geta king of Britain, but the Britons preferred Bassianus
because he had a British mother. The two brothers fought a battle in which Geta
was killed and Bassianus succeeded to the throne. He ruled until he was betrayed
by his Pictish
allies and overthrown by
Carausius
, who, according to Geoffrey, was a
Briton, rather than the historically much later
Menapian
Gaul that he actually was.
|






 Coela
Coela








