|
Gaius – Caesar: 1 B.C. – 4 A.D.
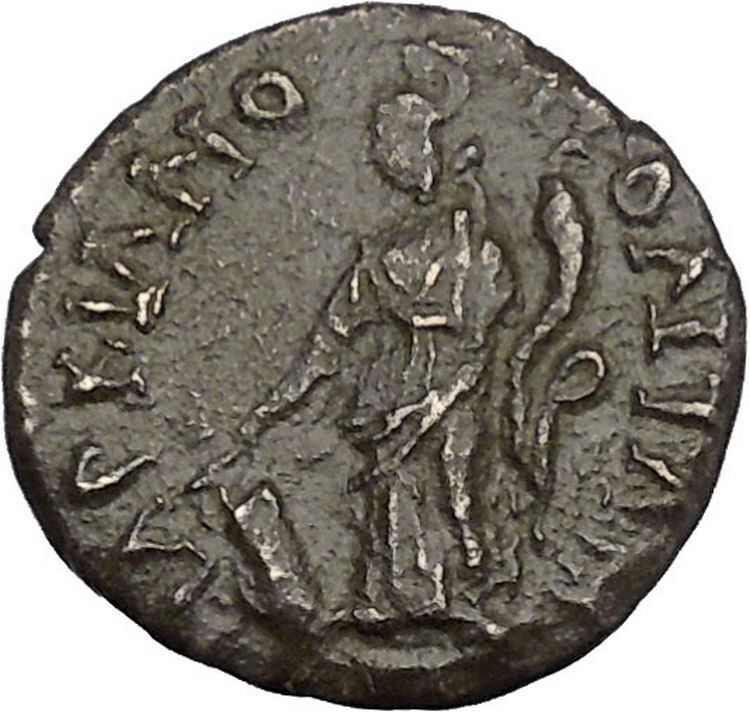
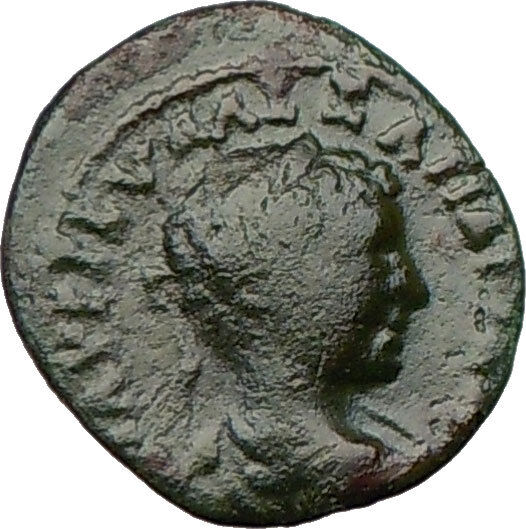
Bronze Hemiassarion 16mm (3.79 grams) of PHRYGIA. Laodicea ad Lycum. Struck circa 5 B.C.
under the magistrate Antonius Polemon Philopatris,
Reference: RPC I 2900; SNG Copenhagen 557.
Certification: NGC Ancients XF Strike: 4/5 Surface: 4/5 5771969-008
ΓAIOΣ KAIΣAΡ, bare head right.
/ ΛAOΔIKEΩN, eagle standing facing, turned slightly to right and with head to left, monogram of ΠΟΛΕ to left and monogram of ΦΙΛΟΠΑΤ to right.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 Gaius Caesar (Latin: Gaius Julius Caesar; 20 BC – 21 February AD 4) was consul in AD 1 and the grandson of Augustus, the first emperor of the Roman Empire. Although he was born to Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa and Julia the Elder, Augustus’ only daughter, Gaius and his younger brother, Lucius Caesar were raised by their grandfather as his adopted sons and joint-heirs to the empire. He would experience an accelerated political career befitting a member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, with the Roman Senate allowing him to advance his career without first holding a questorship or praetorship, offices that ordinary senators were required to hold as part of the cursus honorum. Gaius Caesar (Latin: Gaius Julius Caesar; 20 BC – 21 February AD 4) was consul in AD 1 and the grandson of Augustus, the first emperor of the Roman Empire. Although he was born to Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa and Julia the Elder, Augustus’ only daughter, Gaius and his younger brother, Lucius Caesar were raised by their grandfather as his adopted sons and joint-heirs to the empire. He would experience an accelerated political career befitting a member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, with the Roman Senate allowing him to advance his career without first holding a questorship or praetorship, offices that ordinary senators were required to hold as part of the cursus honorum.
In 1 BC Gaius was given command of the eastern provinces, after which he concluded a peace treaty with King Phraates V of Parthia on an island in the Euphrates. Shortly afterward, he was appointed to the office of consul the following year in AD 1. The year after Gaius’ consulship, Lucius died at Massilia in the month of August. Approximately eighteen months later, Gaius died of an illness in Lycia. Although he married his second cousin, Livilla prior to his death, they did not have children. Following the deaths of Gaius and Lucius, Augustus adopted his stepson as well as his sole-surviving grandson, Tiberius and Agrippa Postumus, respectively in AD 4.
Early life and family
Gaius was born in Rome in 20 BC to Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa and Julia the Elder. He was a part of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, and was related to all the Julio-Claudian emperors. On his mother’s side, he was the oldest grandson of emperor Augustus. He was the brother-in-law of Tiberius by his half-sister Vipsania Agrippina, and Claudius by his sister Agrippina the Elder’s marriage to Germanicus. The last emperor of the dynasty was Nero, who was Gaius’ great-nephew and the grandson of Germanicus. An annual sacrifice on his birthday was granted in a decree.
In 17 BC, his brother Lucius was born. Immediately after, emperor Augustus adopted him and Lucius from their father by a symbolic sale, and named both Gaius and Lucius his heirs. Their adoptive father initiated them into administrative life when they were still young, and sent them to the provinces as consul elects. Augustus taught Gaius and Lucius how to read, swim, and the other elements of education, taking special pains to train them to imitate his own handwriting, mostly by himself. Shortly after their adoption in the summer, Augustus held the fifth ever Ludi Saeculares (“Secular Games”). The adoption of the boys coupled with the games served to introduce a new era of peace – the Pax Augusta.
That year his family left for the province of Syria, because his father was given command of the eastern provinces with proconsular imperium maius. Four years later, in 13 BC, Gaius took part with his brothers Lucius and Postumus in the Trojan games with the other patrician youths at the dedication of the Theatre of Marcellus.
Also in 13 BC, his father returned to Rome and was promptly sent to Pannonia to suppress a rebellion. Agrippa arrived there that winter (in 12 BC), but the Pannonians gave up their plans. Agrippa returned to Campania in Italy, where he fell ill and died soon after. The death of Gaius’ father made succession a pressing issue. The aurei and denarii issued in 13-12 BC made clear the Emperor’s dynastic plans for Gaius and Lucius. Their father was no longer available to assume the reigns of power if the Emperor were to die, and Augustus had to make it clear who his intended heirs were in case anything should happen.
To learn about military affairs, he accompanied Tiberius in his campaign against the Sicambri in 8 BC. The year before, Tiberius’ brother Drusus the Elder died on his way back from a campaign across the Rhine. Tiberius was given command of Germania, and waged two campaigns across the Rhine in 8 BC and 7 BC. He marched his army between the Elbe and the Rhine, and met little resistance, except from the Sicambri. Tiberius came close to exterminating the Sicambri, and had those who survived transported to the Roman side of the Rhine, where they could be watched more closely.
Career
Gaius was elected consul designatus by the Comitia Centuriata in 6 BC with the intention that he should assume the consulship in his twentieth year. The next year, Augustus made him a pontifex, and granted him the right to attend senate meetings, behold spectacles, and to be present at banquets with senators. Roman support for the young prince soon spread through Italy; statues and inscriptions were set up in every district to commemorate the fact that he had been nominated as a consul at an unprecedented age of fourteen.
The following year (5 BC), when he attained military age, he assumed the toga virilis, and was introduced by Augustus to the senate, who declared him as princeps iuventutis (“leader of the youth”) and sevir turmae (commander of a cavalry division). Having been designated consul, he was allowed to give his opinion to the senate. Lucius, three years his junior, was granted the same honors after the appropriate interval had elapsed.
The Herodian succession
Following the death of King Herod of Judaea in December 5 BC, his sons Antipas and Archelaus both came to Rome with their own copy of Herod’s will to plead their case as to why they each deserved to inherit their father’s kingdom. Augustus, as usual, declined the sole responsibility of decision. He convened a council of senators, among whom he included Gaius. The council decided to ratify the will brought by Archelaus, which included a large bequest to Augustus and his wife Livia.
The cities of Judaea rose in revolt after the procurator, Sabinus, garrisoned Syria Palaestina to guard the tens of millions of sesterces promised to the Emperor. The governor of Syria, Varus, was forced to bring in the legions from Syria to restore order.
At the same time, King Phraates V of Parthia had seized Armenia with the help of Armenian nationalists, and expelled Tigranes IV, the king installed by Rome. Historian Ferrero speculates that Phraates may have been hoping to use Armenia as a bargaining chip to secure the release of his sons who were held captive by the Romans. Roman supremacy in Asia depended on its possession of Armenia as a protectorate. Before Rome could deal with the Parthians in Armenia, it would first need to make its Syrian legions available, which were still tied down in Palestine.
In order to free up the legions there, the Kingdom of Judaea was divided among the sons of Herod the Great. One half remained under Archelaus, while the other half was subdivided between his brothers, Antipas and Philip. This served to restore stability to the region, whilst keeping Judaea from becoming powerful. Having settled matters in Judaea, the Emperor decided to deploy an army to Armenia to re-establish its status as a Roman protectorate and to show the eastern world that Rome held dominion over all land as far as the Euphrates.
Command in Asia
Departure
Due to his advanced age, Augustus was unable to travel to the east himself. There were few the Emperor trusted to settle matters in the east, but he was confident Gaius could. Gaius made a good choice, because his presence represented that of the imperial family – all orders, promises, or threats coming from him were as valid as if they came from the Emperor himself. Nonetheless, he was only eighteen, and therefore too young for the conduct of important business.
Before leaving for the east, he and his brother Lucius were given the authority to consecrate buildings, and they did, with their management of the games held to celebrate the dedication of the Temple of Mars Ultor (1 August 2 BC). His youngest brother, Postumus, participated in the Trojan game with the rest of the equestrian youth. 260 lions were slaughtered in the Circus Maximus, there was gladiatorial combat, a naval battle between the “Persians” and the “Athenians”, and 36 crocodiles were slaughtered in the Circus Flaminius.
Friends of Augustus had hoped that he would abandon his plan of sending Gaius to the east but, faced with the troubles in the east, he persisted with the plan and dispatched Gaius to Syria at the beginning of 1 BC. The Emperor entrusted Gaius with proconsular authority and had his second cousin, Livilla, marry him. Livilla was the daughter of Drusus the Elder and Antonia Minor.
Due to his youth and inexperience, the Emperor had others go with him as advisors. Among his entourage to the east were: Marcus Lollius as adiutor (“helper”), Publius Sulpicius Quirinus as rector (“guide”), the future historian Velleius Paterculus, Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus (grandfather of Nero), Juba II of Numidia, and future praetorian prefect Sejanus.
On his way to Syria, Gaius paid a visit to Tiberius who had abandoned politics and retired to Rhodes. According to Suetonius, he had met Tiberius with a cold reception on the isle of Samos. Tiberius was alienated at the meeting, both by the behavior of Lollius and his centurions. Suetonius continued, saying Tiberius wrote to the Emperor that Lollius be replaced. Lollius’ rivalry with Tiberius continued even after Gaius’ entourage arrived in the east. Lollius strove to turn Gaius against him: Gaius, in any case, had no affection for the man who had contributed, directly or indirectly, to the ruin of his mother. On one occasion, Lollius offered to decapitate Tiberius if Gaius gave the word. Suetonius says that it is Lollius’ growing influence that compelled Tiberius to plea with Augustus for his return to Rome.
Consulship
The next year, on 1 January, he entered the consulship in absentia with his brother-in-law, Lucius Aemilius Paullus, in accordance with the decision of 6 BC which named him consul designate. Gaius, who was twenty, had reached Asia, and was probably at Antioch at the time his consulship commenced, where he was organizing an army for the invasion of Armenia and opening negotiations with Phraates in the hopes of securing an agreement. The Emperor did not desire an open war, and the king of Parthia seemed open to peace. Negotiations were probably hastened by the presence of Gaius’ army in Syria, which threatened Parthia. From every corner the young consul was visited by envoys offering requests and paying homage. This year, monuments were raised to him and to his brother as the son of Ares or as Ares himself.
His inexperience meant he was forced to rely on his companions, namely the unruly Lollius, who had taken advantage of the powers he held, and was reportedly holding towns, individuals, and even sovereign princes for ransom. After Gaius opened negotiations with Phraates, Lollius offered the Parthian king certain concessions in return for money.
Preparations for the war continued into the spring and summer of 1 AD, at which point there had been a successful breakthrough in negotiations. As Phraates was not willing to go to war, he agreed to evacuate Armenia and abandon his brothers who were still in Roman captivity. In the second half of the year, Gaius had advanced with his army to the Pharthian frontier to an unknown spot and brought Phraates to a final agreement on the proposals, in which he renounced all claims to Armenia and all power over his half-brothers.
It was about this time that Augustus passed through Judea and commended Gaius for not offering prayers at Jerusalem, as it would have been provocative to the Jews living there.
Expedition in Arabia
Sometime in the course of his time in the east, Gaius led an expedition into Arabia. Exactly where and for what purpose remains uncertain, though Pliny mentioned it in connection with Aelius Gallus’ exploits in South Arabia. The term “Arabia” is never defined, and the term was used loosely by Roman sources. Various reasons, such as an attempt by Rome to control the incense trade, have been suggested but never proven. Juba II, former king of Mauretania, accompanied Gaius to the east. In order to prepare Gaius for his encounter with the Arabs, Juba wrote him a treatise. According to Pliny, the young prince made it as far as the Gulf of Aqaba. It is certain that this expedition happened before his time in Armenia, and, referencing Gaius’ cenotaph in Pisa, it is almost certain to have taken place during his consulship.
Author and historian John Grainger places Gaius at the Gulf of Aqaba, or in Nabataea. It is known that the Nabataean Kingdom later became the province of Arabia, and so, it might be that Gaius conducted his “Arabian expedition” to either support or to discipline the King of Nabataea, Aretas IV. This is probably evidenced by the continuation of coinage in the king’s name after Gaius’ consulship.
Cassius Dio, in a fragmentary notice, mentions trouble in Egypt which was suppressed by a tribune of the Praetorian Guard. It is very likely this man was part of Gaius’ entourage, but other than that nothing is known of him.
Supremacy in Armenia 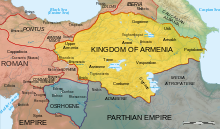 Map of Armenia and the Roman client states in eastern Asia Minor. Map of Armenia and the Roman client states in eastern Asia Minor.
In the year following his consulship, in spring, he had held a meeting with Phraates on the bank of the Euphrates, in which a banquet was held to celebrate a peace treaty. It was here that Phraates, offended by Lollius, disclosed the guardian’s secret negotiations to Gaius. It was for the crime of extorting presents from kings (regnum muneribus) that Lollius lost the friendship of Gaius and drank poison. Pliny says he amassed a fortune from his crimes and that, as a result, his granddaughter could afford to wear jewelry worth 40,000,000 sesterces, a considerable amount of money. The death of Lollius was fortunate to Tiberius, after which Gaius consented to his return to Rome and consequent return to Roman politics.
At the same time, the throne of Armenia had become vacant and, with permission from the Emperor, Gaius placed Ariobarzanes of Media on the throne. The Romans weren’t the only ones interested in Armenia: the Parthians stirred up a revolt among nationalists in the nation. A large force of rebels had occupied the fortress in the city of Artagira. Gaius was drawn into the conflict, and invaded Armenia in late August of 3. He enountered no serious opposition as there were only a few revolts he had to suppress as a result of the nationalist party.
On September 9, Abbadon, the leader of the rebellion, invited Gaius into the fortress to speak with him. It proved to be a trick, and Gaius was wounded in the confrontation. He had to be carried away by his outraged lieutenants. His forces promptly laid siege to the city and captured the fortress after intense fighting. At first the wound did not seem serious and he was able to complete the pacification of Armenia, a relatively easy task.
By the next year (3 AD), he was entirely prostrated by the effects of his wound, had resigned his command, and withdrawn to Syria from where he informed Augustus that he had no further desire to take part in public life. The eastern campaign had proven severe: his health was weak and his mental balance unstable. At the age of twenty-three, the young man whom the Emperor considered his heir and sole hope of prosperity had abandoned his prospects of reputation and power in a wild fit of despair and fear. Augustus did his best to cheer him up and convince him to return to Italy. It was in vain: Gaius died in a little Lycian town on 21 February 4 AD.
Post mortem
 The Maison Carrée (French: “square house”) was dedicated in Nemausus to Gaius and Lucius. The Maison Carrée (French: “square house”) was dedicated in Nemausus to Gaius and Lucius.
While Gaius was in Armenia, his brother Lucius had been sent by Augustus to complete his military training in Spain. While there, he fell ill and died on 20 August 2 AD in Massalia, Gaul. In the span of 18 months, the planned future of Rome was shaken. The death of both Gaius and Lucius, the Emperor’s two most favored heirs, led Augustus to adopt his stepson Tiberius, and his sole remaining grandson Postumus as his new heirs on 26 June 4 AD.
Many honors were heaped upon him by citizens and city officials of the Empire, including Colonia Obsequens Iulia Pisana (Pisa), where it was decreed that proper rites must be observed by matrons to lament his passing. Temples, public baths, and shops shut their doors as women wept inconsolably. To commemorate his brief life, a cenotaph was erected on the Limyrus River in Lycia. Posthumously, the Senate voted honors for the young Caesars, and arranged for the golden spears and shields the boys had received on achieving the age of military service, to be hung in the Senate House. The caskets containing their ashes were stored in the Mausoleum of Augustus alongside those of their father Agrippa and other members of the imperial family.
Both Tacitus and Cassius Dio suggested foul play may have been involved in the death of Gaius and Lucius and that Gaius’s step grandmother Livia may have had a hand in their deaths. Livia’s presumed motive may have been to orchestrate the accession of her own son Tiberius as heir to Augustus.
 Augustus – Roman Emperor: 27 B.C. – 14 A.D. Augustus – Roman Emperor: 27 B.C. – 14 A.D.
| As Octavian: Member of Second Triumvirite, 43-33 B.C. | As Octavian, Imperator, 31-27 B.C. | As Augustus 27 B.C. – 14 A.D. |
| Grand-nephew and adopted son of Julius Caesar | Husband of Scribonia and Livia | Father of Julia (by Scribonia) | Brother of Octavia | Brother-in-law of Mark Antony | Father-in-law of Marcellus, Agrippa and Tiberius | Adoptive father of Tiberius and Nero Claudius Drusus | Uncle of Antonia | Grand-uncle of Germanicus, Claudius and Livilla | Grandfather of Gaius Caesar, Lucius Caesar, Agrippa Postumus, Julia the Younger and Agrippina Senior | Great-grandfather of Nero Caesar, Drusus Caesar, Caligula, Agrippina Junior, Drusilla and Julia Livilla | Great-great-grandfather of Nero |
Augustus (Latin: Imperātor Caesar Dīvī Fīlius Augustus; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August 14 AD) was the founder of the Roman Empire and its first Emperor, ruling from 27 BC until his death in AD 14.
He was born Gaius Octavius into an old and wealthy equestrian branch of the plebeian Octavii family. His maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC, and Octavius was named in Caesar’s will as his adopted son and heir, then known as Octavianus (Anglicized as Octavian). He, Mark Antony, and Marcus Lepidus formed the Second Triumvirate to defeat the assassins of Caesar. Following their victory at Philippi, the Triumvirate divided the Roman Republic among themselves and ruled as military dictators. The Triumvirate was eventually torn apart under the competing ambitions of its members. Lepidus was driven into exile and stripped of his position, and Antony committed suicide following his defeat at the Battle of Actium by Octavian in 31 BC.
After the demise of the Second Triumvirate, Augustus restored the outward façade of the free Republic, with governmental power vested in the Roman Senate, the executive magistrates, and the legislative assemblies. In reality, however, he retained his autocratic power over the Republic as a military dictator. By law, Augustus held a collection of powers granted to him for life by the Senate, including supreme military command, and those of tribune and censor. It took several years for Augustus to develop the framework within which a formally republican state could be led under his sole rule. He rejected monarchical titles, and instead called himself Princeps Civitatis (“First Citizen of the State”). The resulting constitutional framework became known as the Principate, the first phase of the Roman Empire.
The reign of Augustus initiated an era of relative peace known as the Pax Romana (The Roman Peace). The Roman world was largely free from large-scale conflict for more than two centuries, despite continuous wars of imperial expansion on the Empire’s frontiers and one year-long civil war over the imperial succession. Augustus dramatically enlarged the Empire, annexing Egypt, Dalmatia, Pannonia, Noricum, and Raetia; expanding possessions in Africa; expanding into Germania; and completing the conquest of Hispania.
Beyond the frontiers, he secured the Empire with a buffer region of client states and made peace with the Parthian Empire through diplomacy. He reformed the Roman system of taxation, developed networks of roads with an official courier system, established a standing army, established the Praetorian Guard, created official police and fire-fighting services for Rome, and rebuilt much of the city during his reign.
Augustus died in AD 14 at the age of 75. He may have died from natural causes, although there were unconfirmed rumors that his wife Livia poisoned him. He was succeeded as Emperor by his adopted son (also stepson and former son-in-law) Tiberius.
|









 Gaius Caesar (Latin: Gaius Julius Caesar; 20 BC – 21 February AD 4) was consul in AD 1 and the grandson of Augustus, the first emperor of the Roman Empire. Although he was born to Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa and Julia the Elder, Augustus’ only daughter, Gaius and his younger brother, Lucius Caesar were raised by their grandfather as his adopted sons and joint-heirs to the empire. He would experience an accelerated political career befitting a member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, with the Roman Senate allowing him to advance his career without first holding a questorship or praetorship, offices that ordinary senators were required to hold as part of the cursus honorum.
Gaius Caesar (Latin: Gaius Julius Caesar; 20 BC – 21 February AD 4) was consul in AD 1 and the grandson of Augustus, the first emperor of the Roman Empire. Although he was born to Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa and Julia the Elder, Augustus’ only daughter, Gaius and his younger brother, Lucius Caesar were raised by their grandfather as his adopted sons and joint-heirs to the empire. He would experience an accelerated political career befitting a member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, with the Roman Senate allowing him to advance his career without first holding a questorship or praetorship, offices that ordinary senators were required to hold as part of the cursus honorum. Map of Armenia and the Roman client states in eastern Asia Minor.
Map of Armenia and the Roman client states in eastern Asia Minor.  The Maison Carrée (French: “square house”) was dedicated in Nemausus to Gaius and Lucius.
The Maison Carrée (French: “square house”) was dedicated in Nemausus to Gaius and Lucius.  Augustus – Roman Emperor: 27 B.C. – 14 A.D.
Augustus – Roman Emperor: 27 B.C. – 14 A.D.




