|
Greek city of Kremna in Pisidia
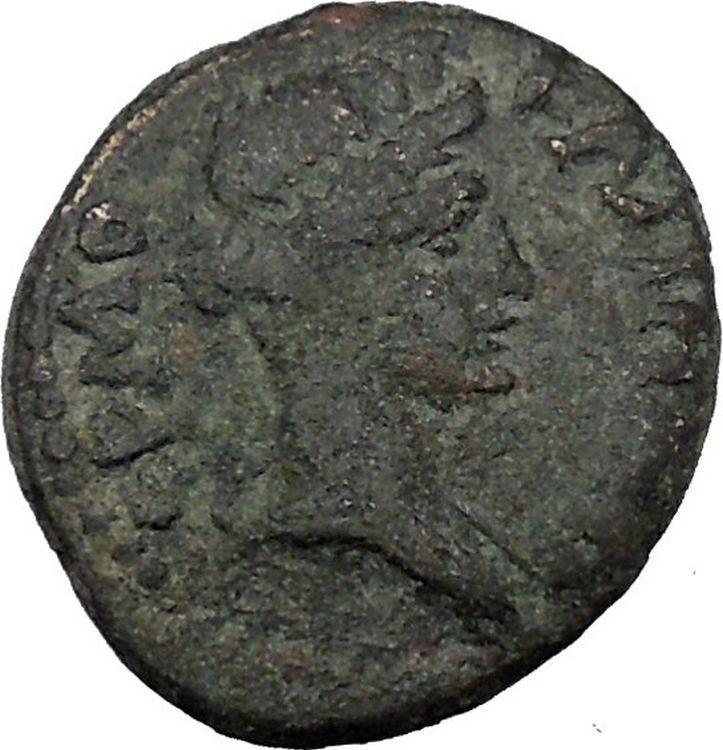
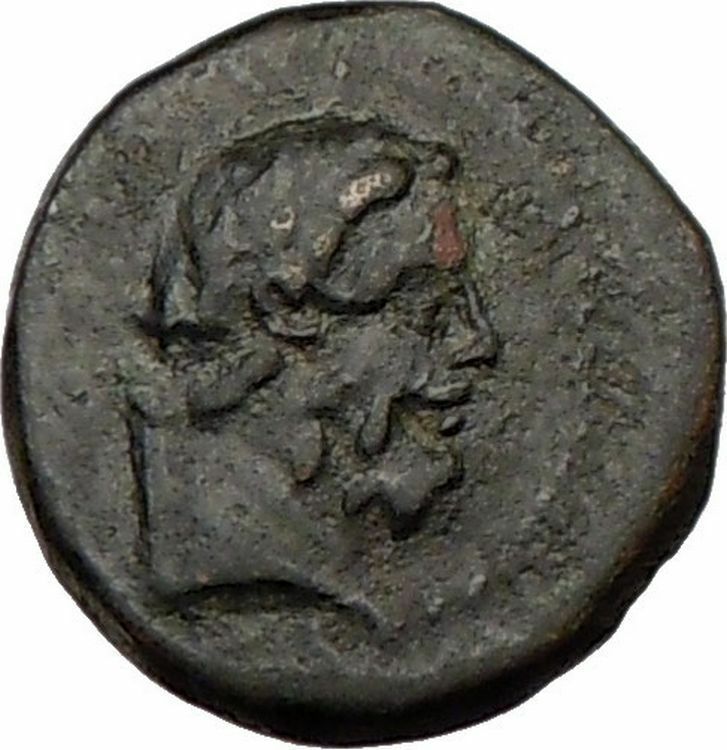
Amyntas – King of Galatia: 36-25 B.C.
Bronze 17mm (4.54 grams) Struck circa 36-25 B.C.
Reference: Aulock, Pisidien II 1014-47; RPC 3519
Laureate head of Zeus right.
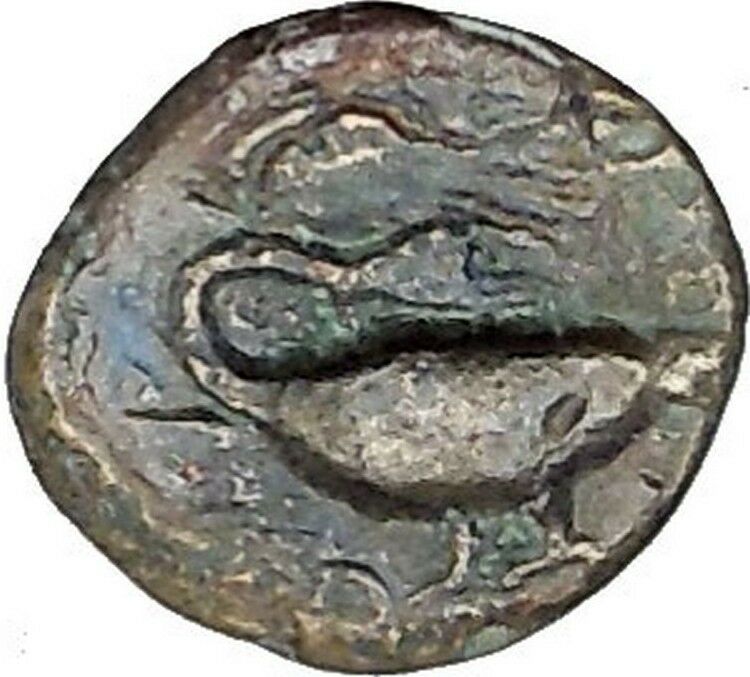
. Winged thunderbolt; KPH below; Z (date) above.
Amyntas was a secretary of Deiotaros. He was in the military service commanding an auxiliary force in the Roman army of Brutus and Cassius. Having gained the favor of Mark Antony, because he had gone over to his side before the Battle of Philippi, Antony granted him an extensive kingdom which included Galatia, Lycaonia and parts of neighboring territories. Having deserted Antony in a timely manner to Augustus, he secured the patronage of Augustus. After having perished in battle in 25 B.C., his kingdom became a Roman province.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 In the ancient Greek religion, Zeus was the “Father of Gods and men” who ruled the Olympians of Mount Olympus as a father ruled the family. He was the god of sky and thunder in Greek mythology. His Roman counterpart is Jupiter and Etruscan counterpart is Tinia. In the ancient Greek religion, Zeus was the “Father of Gods and men” who ruled the Olympians of Mount Olympus as a father ruled the family. He was the god of sky and thunder in Greek mythology. His Roman counterpart is Jupiter and Etruscan counterpart is Tinia.
Zeus was the child of Cronus and Rhea, and the youngest of his siblings. In most traditions he was married to Hera, although, at the oracle of Dodona, his consort was Dione: according to the Iliad, he is the father of Aphrodite by Dione. He is known for his erotic escapades. These resulted in many godly and heroic offspring, including Athena, Apollo and Artemis, Hermes, Persephone (by Demeter), Dionysus, Perseus, Heracles, Helen of Troy, Minos, and the Muses (by Mnemosyne); by Hera, he is usually said to have fathered Ares, Hebe and Hephaestus.
As Walter Burkert points out in his book, Greek Religion, “Even the gods who are not his natural children address him as Father, and all the gods rise in his presence.” For the Greeks, he was the King of the Gods, who oversaw the universe. As Pausanias observed, “That Zeus is king in heaven is a saying common to all men”. In Hesiod’s Theogony Zeus assigns the various gods their roles. In the Homeric Hymns he is referred to as the chieftain of the gods.
His symbols are the thunderbolt, eagle, bull, and oak. In addition to his Indo-European inheritance, the classical “cloud-gatherer” also derives certain iconographic traits from the cultures of the Ancient Near East, such as the scepter. Zeus is frequently depicted by Greek artists in one of two poses: standing, striding forward, with a thunderbolt leveled in his raised right hand, or seated in majesty.
Amyntas (Ancient Greek: Ἀμύντας), Tetrarch of the Trocmi was a King of Galatia and of several adjacent countries between 36 BC and 25 BC, mentioned by Strabo as contemporary with himself. He was the son of Brogitarus, king of Galatia, and Adobogiona, daughter of king Deiotarus Philoromaeus.
Amyntas seems to have first possessed Lycaonia, where he maintained more than 300 flocks. To this he added the territory of Derbe by the murder of its prince, Antipater of Derbe, the friend of Cicero, and Isaura and Cappadocia by Roman favour. Originally he had been the king of Cappadocia Deiotarus secretary (γραμματεύς), and was made by Amyntas commander in chief (στρατηγός) of the Galatian auxiliaries sent to help Brutus and Cassius against the Triumvires, but deserted to Mark Anthony just before the battle of Philippi (42 BC).
After the death of Deiotarus, he was made king of Cappadocia in 37 BC as a client ruler of Mark Anthony. Plutarch enumerates him among the adherents of Mark Antony at Actium and is mentioned as deserting to Octavian, just before the battle (31 BC).
While pursuing his schemes of aggrandizement, and endeavoring to reduce the refractory highlanders around him, Amyntas made himself master of Homonada or Hoinona, and slew the prince of that place; but his death was avenged by his widow, and Amyntas fell a victim in 25 BC to an ambush which she laid for him. On his death Galatia became a Roman province.
He was the father of Artemidoros of the Trocmi, a Galatian nobleman, who married a princess of the Tectosagi, the daughter of Amyntas, Tetrarch of the Tectosagii. They were the parents of Gaius Julius Severus, a nobleman from Acmonia in Galatia, who was in turn the father of Gaius Julius Bassus, proconsul of Bithynia in 98, and Gaius Julius Severus, a Tribune of the Legio VI Ferrata.
Cremna (Greek Κρῆμνα) was a town in Pisidia. It was first taken by Amyntas, commander of the Galatian auxiliary army of Brutus and Cassius, who became king of Galatia and Pisidia on going over to the side of Mark Antony. Octavian allowed him to remain king until his death in 25 BC. After this it became a Roman colony, as Strabo says; and there are imperial coins with the epigraph COL. IVL. AVG. CREMNA, which stands for Colonia Iulia Augusta [Felix] Cremnena. Its first coins appear to have been minted under Hadrian. Ptolemy mentions the Cremna Colonia, and according to him it is in the same longitude as Sagalassus.
The donatio given by the emperor Aurelian (270-275) promised a period of great prosperity for Cremna; but in 276 the town was taken by an Isaurian robber, named Lydius, who used it as a base for looting the region, giving rise to the only visit of a Roman Emperor to the region, that of Marcus Claudius Tacitus. Later, the town was inserted in the Roman province of Pamphylia Secunda. The name of only one of its bishops is known: Theodorus, present at the Second Council of Nicaea in 787. No longer a residential bishopric, Cremna is today listed by the Catholic Church as a titular see.
At some time in the high Middle Ages the ancient site of the town was abandoned, the population transferring itself to the present village of Çamlık.
The ancient site of Cremna was identified in the district of Bucak in 1874, and excavations began in 1970. It stands on a hill dominating the ancient Cestrus River (today Aksu); very few of the site’s old buildings are still standing, generally consisting of heaps of stone.
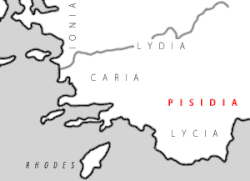 Pisidia was a region of ancient Asia Minor located north of Lycia, bordering Caria, Lydia, Phrygia and Pamphylia, and corresponding roughly to the modern-day province of Antalya in Turkey. Among Pisidia’s settlements were Termessus, Selge, Cremna, Sagalassos, Etenna, Antiochia, Neapolis, Tyriacum, Laodiceia Katakekaumene and Philomelium. Pisidia was a region of ancient Asia Minor located north of Lycia, bordering Caria, Lydia, Phrygia and Pamphylia, and corresponding roughly to the modern-day province of Antalya in Turkey. Among Pisidia’s settlements were Termessus, Selge, Cremna, Sagalassos, Etenna, Antiochia, Neapolis, Tyriacum, Laodiceia Katakekaumene and Philomelium.
Geography
Although close to Mediterranean Sea on the map, the warm climate of the south cannot pass the height of the Taurus Mountains. Owing to the climate, there is no timberland but crop plants grow in areas provided with water from the mountains, whose annual average rainfall is c. 1000 mm on the peaks and 500 mm on the slopes. This water feeds the plateau. The Pisidian cities, mostly founded on the slopes, benefited from this fertility. The irrigated soil of the land is very suitable for growing fruit and for husbandry.
History
Early history
The area of Pisidia has been inhabited since the Paleolithic age, with some settlements known from historical times ranging in age from the eighth to third millennium BC. The ancestors of the classical Pisidians were likely present in the region before the 14th century BC, when Hittite records refer to a mountain site of Salawassa, identified with the later site of Sagalassos. At that time, Pisidia appears to have been part of the region the Hittites called Arzawa. The Pisidian language is poorly known, but is assumed to be a member of the Anatolian branch of Indo-European languages.
Herodotus mentioned the Pisidic people in the text which they were called “Lakuna” but this was one of the names given to Pisidic tribes, which occupied a little mountainous region north to the Antalya Bay. Pisidians are known to be among the nations which helped the Persians in their war against Greece.
There can be little doubt that the Pisidians and Pamphylians were the same people, but the distinction between the two seems to have been established at an early period. Herodotus, who does not mention the Pisidians, enumerates the Pamphylians among the nations of Asia Minor, while Ephorus mentions them both, correctly including the one among the nations on the interior, the other among those of the coast. Pamphylia early received colonies from Greece and other lands, and from this cause, combined with the greater fertility of their territory, became more civilized than its neighbor in the interior. Pisidia remained a wild, mountainous region, and one of the most difficult for outside powers to rule.
As far back as the Hittite period, Pisidia was host to independent communities not under the Hittite yoke. Known for its warlike factions, it remained largely independent of the Lydians, and even the Persians, who conquered Anatolia in the 6th century BC, and divided the area into satrapies for greater control, were unable to cope with constant uprisings and turmoil.
Hellenistic period
Alexander the Great had somewhat better fortune, conquering Sagalassos on his way to Persia, though the city of Termessos defied him. After Alexander died, the region became part of territories of Antigonus Monophthalmus, and possibly Lysimachus of Thrace, after which Seleucus I Nicator, founder of the Seleucid Dynasty of Syria, took control of Pisidia. Under the Selucids Greek colonies were founded at strategically important places and the local people Hellenised. Even so, the Hellenistic kings were never in complete control, in part because Anatolia was contested between the Selucids, the Attalids of Pergamon, and the Galatians, invading Celts from Europe. The cities in Pisidia were among the last in western Anatolia to fully adopt Greek culture and to coin their own money.
Pisidia officially passed from the Selucids to the Attalids as a result of the Treaty of Apamea, forced on Antiochos III of Syria by the Romans in 188 BC. After Attalos III, the last king of Pergamon, bequeathed his kingdom to Rome in 133 BC as the province of Asia, Pisidia was given to the Kingdom of Cappadocia, which proved unable to govern it. The Pisidians cast their lot with pirate-dominated Cilicia and Pamphylia until Roman rule was restored in 102 BC.
In 39 BC Marcus Antonius entrusted Pisidia to the Galatian client king Amyntas and charged him with putting down the bandit Homonadesians of the Taurus Mountains, who threatened the roads connecting Pisidia to Pamphylia. After Amyntas was killed in the struggle 25 BC, Rome made Pisidia part of the new province of Galatia. The Homonadesians were finally wiped out in 3 BC.
Roman and Byzantine period
During the Roman period Pisidia was colonized with veterans of its legions to maintain control. For the colonists, who came from poorer parts of Italy, agriculture must have been the area’s main attraction. Under Augustus, eight such colonies were established in Pisidia, and Antioch and Sagalassos became the most important cities. The province was gradually Latinised. Latin remained the formal language of the area until the end of the 3rd century.
Pisidia became an important early Christian centre. Paul the Apostle preached in Antioch on his first journey and visited the area again in his second and third journeys. After the Emperor Constantine’s legalization of Christianity in 311, Antioch played an important role as the Christian metropolitan see as well as being the capital of the civil province of Pisidia. Most Pisidian cities were heavily fortified at that time due to civil wars and foreign invasions.
The area was devastated by an earthquake in 518, a plague around 541-543, and another earthquake and Arab raids in the middle of the 7th century. After the Muslim conquest of Syria disrupted the trade routes, the area declined in importance. In the 8th century the raids increased. In the 11th century the Seljuk Turks captured the area and founded the Seljuk Sultanate in Central Anatolia. Pisidia frequently changed hands between the Byzantine Empire and the Turks until 1176, when Sultan Kılıçarslan defeated Manuel Komnenos in the Battle of Myriocephalon (thousand heads), which ended Byzantine rule and cemented Turkish rule of the area.
|





 In the ancient Greek religion, Zeus was the “Father of Gods and men” who ruled the Olympians of Mount Olympus as a father ruled the family. He was the god of sky and thunder in Greek mythology. His Roman counterpart is Jupiter and Etruscan counterpart is Tinia.
In the ancient Greek religion, Zeus was the “Father of Gods and men” who ruled the Olympians of Mount Olympus as a father ruled the family. He was the god of sky and thunder in Greek mythology. His Roman counterpart is Jupiter and Etruscan counterpart is Tinia. Pisidia was a region of ancient Asia Minor located north of Lycia, bordering Caria, Lydia, Phrygia and Pamphylia, and corresponding roughly to the modern-day province of Antalya in Turkey. Among Pisidia’s settlements were Termessus, Selge, Cremna, Sagalassos, Etenna, Antiochia, Neapolis, Tyriacum, Laodiceia Katakekaumene and Philomelium.
Pisidia was a region of ancient Asia Minor located north of Lycia, bordering Caria, Lydia, Phrygia and Pamphylia, and corresponding roughly to the modern-day province of Antalya in Turkey. Among Pisidia’s settlements were Termessus, Selge, Cremna, Sagalassos, Etenna, Antiochia, Neapolis, Tyriacum, Laodiceia Katakekaumene and Philomelium.




