|
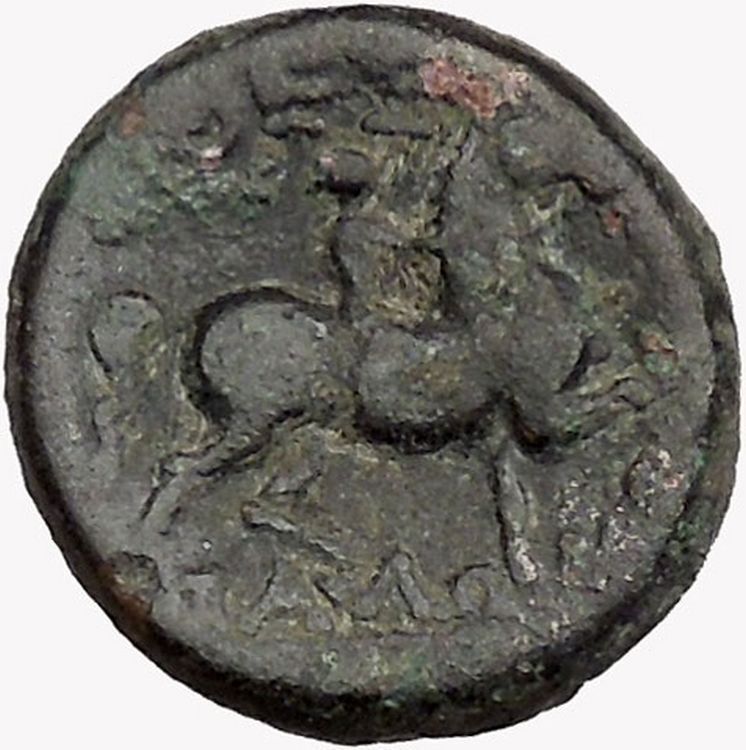
Greek city of Laodikeia (ad Lycum) in Phrygia
Pseudo-autonomous issue 81-96 A.D.
Bronze 15mm (2.7 grams) Struck circa 81-96 A.D.
Kornelios Dioskourides, magistrate
Reference: RPC II 1293; BMC 77; SNG Copenhagen 572
ΛΑΟΔΙΚΕΩΝ, helmeted and draped bust of Athena to right, wearing aegis.
ΔΙΑ Κ ΔΙΟ[ΣΚΟΥΡΙΔΟΥ], Nike advancing left, holding wreath and palm frond.
An important city in the valley of the Lykos, north-west of Kilossai, Laodikeia was founded by Antiochos II, on the site of an earlier town, and named after that king’s wife, Laodike.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 Athena or Athene (Latin: Minerva), also referred to as Pallas Athena, is the goddess of war, civilization, wisdom, strength, strategy, crafts, justice and skill in Greek mythology. Minerva, Athena’s Roman incarnation, embodies similar attributes. Athena is also a shrewd companion of heroes and the goddess of heroic endeavour. She is the virgin patron of Athens. The Athenians built the Parthenon on the Acropolis of her namesake city, Athens, in her honour (Athena Parthenos). Athena’s cult as the patron of Athens seems to have existed from the earliest times and was so persistent that archaic myths about her were recast to adapt to cultural changes. In her role as a protector of the city (polis), many people throughout the Greek world worshiped Athena as Athena Polias (“Athena of the city”). Athens and Athena bear etymologically connected names. Athena or Athene (Latin: Minerva), also referred to as Pallas Athena, is the goddess of war, civilization, wisdom, strength, strategy, crafts, justice and skill in Greek mythology. Minerva, Athena’s Roman incarnation, embodies similar attributes. Athena is also a shrewd companion of heroes and the goddess of heroic endeavour. She is the virgin patron of Athens. The Athenians built the Parthenon on the Acropolis of her namesake city, Athens, in her honour (Athena Parthenos). Athena’s cult as the patron of Athens seems to have existed from the earliest times and was so persistent that archaic myths about her were recast to adapt to cultural changes. In her role as a protector of the city (polis), many people throughout the Greek world worshiped Athena as Athena Polias (“Athena of the city”). Athens and Athena bear etymologically connected names.
 In Greek mythology, Nike was a goddess who personified victory, also known as the Winged Goddess of Victory. The Roman equivalent was Victoria. Depending upon the time of various myths, she was described as the daughter of Pallas (Titan) and Styx (Water) and the sister of Kratos (Strength), Bia (Force), and Zelus (Zeal). Nike and her siblings were close companions of Zeus, the dominant deity of the Greek pantheon. According to classical (later) myth, Styx brought them to Zeus when the god was assembling allies for the Titan War against the older deities. Nike assumed the role of the divine charioteer, a role in which she often is portrayed in Classical Greek art. Nike flew around battlefields rewarding the victors with glory and fame. In Greek mythology, Nike was a goddess who personified victory, also known as the Winged Goddess of Victory. The Roman equivalent was Victoria. Depending upon the time of various myths, she was described as the daughter of Pallas (Titan) and Styx (Water) and the sister of Kratos (Strength), Bia (Force), and Zelus (Zeal). Nike and her siblings were close companions of Zeus, the dominant deity of the Greek pantheon. According to classical (later) myth, Styx brought them to Zeus when the god was assembling allies for the Titan War against the older deities. Nike assumed the role of the divine charioteer, a role in which she often is portrayed in Classical Greek art. Nike flew around battlefields rewarding the victors with glory and fame.
Nike is seen with wings in most statues and paintings. Most other winged deities in the Greek pantheon had shed their wings by Classical times. Nike is the goddess of strength, speed, and victory. Nike was a very close acquaintance of Athena, and is thought to have stood in Athena’s outstretched hand in the statue of Athena located in the Parthenon. Nike is one of the most commonly portrayed figures on Greek coins.
Names stemming from Nike include amongst others: Nicholas, Nicola, Nick, Nikolai, Nils, Klaas, Nicole, Ike, Niki, Nikita, Nika, Niketas, and Nico.
Laodicea on the Lycus was the ancient metropolis of Phrygia Pacatiana (also attributed to Caria and Lydia), built on the river Lycus (Çürüksu), in Anatolia near the modern village of Eskihisar (Eski Hissar), Denizli Province, Turkey.
.JPG/285px-Laodicea_(2).JPG)
History
Laodicea is situated on the long spur of a hill between the narrow valleys of the small rivers Asopus and Caprus, which discharge their waters into the Lycus. The town was originally called Diospolis, “City of Zeus”, and afterwards Rhodas, and Laodicea, the building of which is ascribed to Antiochus II Theos, in 261-253 BC, in honor of his wife Laodice, was probably founded on the site of the older town. It was approximately 17 km west of Colossae, and 10 km south of Hierapolis. It was approximately 160 km east of Ephesus and, according to Strabo, it was on a major road. It was in Phrygia, although some ancient authors place Laodicea in differing provincial territories – not surprising because the precise limits of these territories were both ill-defined and inconstant – e.g. Ptolemy and Philostratus call it a town of Caria, while Stephanus of Byzantium describes it as belonging to Lydia.
.JPG/220px-Laodicea_(10).JPG) Western Theatre with Heirapolis/Pammukale in the distance Western Theatre with Heirapolis/Pammukale in the distance
At first Laodicea was not a place of much importance, but it soon acquired a high degree of prosperity. In 220 BC, Achaeus was its king. In 188 BC, the city had passed to the Kingdom of Pergamon, and after 133 BC fell under Roman control. It suffered greatly during the Mithridatic Wars,[6] but quickly recovered under the dominion of Rome; and towards the end of the Roman Republic and under the first emperors, Laodicea, benefiting from its advantageous position on a trade route, became one of the most important and flourishing commercial cities of Asia Minor, in which large money transactions and an extensive trade in black wool were carried on.
The place often suffered from earthquakes, especially from the great shock in the reign of Nero (60 AD), in which it was completely destroyed. But the inhabitants declined imperial assistance to rebuild the city and restored it from their own means. The wealth of its inhabitants created among them a taste for the arts of the Greeks, as is manifest from its ruins; and that it did not remain behind in science and literature is attested by the names of the sceptics Antiochus and Theiodas, the successors of Aenesidemus and by the existence of a great medical school. Its wealthy citizens embellished Laodicea with beautiful monuments. One of the chief of them, Polemon, became King of Armenian Pontus – called after him “Polemoniacus” – and of the coast round Trebizond. The city minted its own coins, the inscriptions of which show evidence of the worship of Zeus, Æsculapius, Apollo, and the emperors.
It received from Rome the title of free city. During the Roman period Laodicea was the chief city of a Roman conventus, which comprised twenty-four cities besides itself; Cicero records holding assizes there ca. 50 BC.
Antiochus the Great transported 2,000 Jewish families to Phrygia from Babylonia. Many of Laodicea’s inhabitants were Jews, and Cicero records that Flaccus confiscated the considerable sum of 9 kg of gold which was being sent annually to Jerusalem for the Temple (Pro Flacco 28-68).
The Byzantine writers often mention it, especially in the time of the Comneni. In 1119, Emperor John the Beautiful and his lead military aid John Axuch captured Laodicea from the Seljuk Turks in the first major military victory of his reign.
It was fortified by the emperor Manuel I Comnenus. In 1206-1230, it was ruled by Manuel Maurozomes. The city was destroyed during the invasions of the Turks and Mongols.
Christian Laodicea
See also: Early centers of Christianity#Anatolia
It was probably owing to its large Jewish community, that at a very early period it became one of the chief seats of Christianity, and the see of a bishop. Laodicea receives passing mention in the epistle to the Colossians and is one of the Seven churches of Asia mentioned in the Book of Revelation. The Laodicean Church had probably been founded by the Colossian Epaphras, who shared the care of it with Nymphas, in whose house the faithful used to assemble. Paul asks the Colossians to communicate to the Church of Laodicea the letter which he sends to them, and to read publicly that which should come to them from Laodicea, that is, no doubt, a letter which he had written, or was to write, to the Laodiceans. An apocryphal epistle purporting to be from Paul to the Laodiceans is extant in Latin and Arabic (see Epistle to the Laodiceans). Some of the Greek manuscripts end the First Epistle to Timothy with these words: “Written at Laodicea, metropolis of Phrygia Pacatiana”.
The first bishops attributed to the See of Laodicea are very uncertain: Archippus (Colossians 4:17); St. Nymphas; Diotrephes (III John, 9). Next comes St. Sagaris, martyr (c. 166). Sisinnius is mentioned in the Acts of the martyr St. Artemon, a priest of his Church. Nunechius assisted at the Council of Nicaea (325). Eugenius, known by an inscription, was probably his successor. The Arian Cecropius was transferred by Constantius to the See of Nicomedia. When Phrygia was divided into two parts, Laodicea became the metropolis of Phrygia Pacatiana: it figures under this title in all the Notitiae Episcopatuum. Some twenty incumbents are known besides those already enumerated; the last occupied the see in 1450. The city remains a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church, Laodicensis in Phrygia; the seat has been vacant since 1968.
There are extant, in Greek, sixty canons of a Council of Laodicea. That this assembly was actually held, we have the testimony of Theodoret. There has been much discussion as to the date: some have even thought that the council must have preceded that of Nicaea (325), or at least that of Constantinople (381). It seems safer to consider it as subsequent to the latter. The canons are, undoubtedly, only a resume of an older text, and indeed appear to be derived from two distinct collections. They are of great importance in the history of discipline and liturgy; some Protestants have invoked one of them in opposition to the veneration of angels.
The ruins
.JPG/220px-Laodicea_(40).JPG) Temple “A” Temple “A”
The existing remains attest its former greatness. The ruins near Denizli (Denisli) are well preserved and are being substantially renovated (2012). Its many buildings include stadium, baths, temples, gymnasium, theatres, bouleuterion, etc.. On the east the line of the ancient wall may be distinctly traced, with the remains of the Ephesus gate; there are streets traversing the town, flanked by colonnades and numerous pedestals. North of the town, towards the Lycus, are many sarcophagi, with their covers lying near them, partly imbedded in the ground, and all having been long since rifled.
Particularly interesting are the remains of an aqueduct starting several kilometres away at the Baspinar spring in Denizli, and possibly having another more distant source. Unusually, to cross the valley to the south of Laodicea, instead of the usual open channel carried above the level of the city on lofty arches as was the usual practice of the Romans, an inverted siphon was employed consisting of a double pressurised pipeline, descending into the valley and back up to the city. The low arches supporting the siphon commence near the summit of a low hill to the south where the header tank was located, and thence continue to the first terminal distribution tank (castellum aquae) at the edge of the hill of the city, whose remains are visible to the east of the stadium and South Baths complex. The water was heavily charged with calcareous matter, as several of the arches are covered with a thick incrustation where leaks occurred at later times. The siphon consisted of large carved stone pipes; some of these also are much incrusted, and some completely choked up. The terminal tank has many clay pipes of various diameters for water distribution on the north, east and south sides which, because of the choking by sinter, were replaced in time. To the west of the terminal is a small fountain next to the vaulted gate. The aqueduct appears to have been destroyed by an earthquake, as the remaining arches lean bodily on one side, without being much broken. A second distribution terminal and sedimentation tank is visible 400m north of the first, to which it was connected via another siphon of travertine blocks, and this one is bigger and supplied most of the city.
The stadium, which is in a good state of preservation, is near the southern extremity of the city. The seats are arranged along two sides of a narrow valley, which appears to have been taken advantage of for this purpose, and to have been closed up at both ends. Towards the west are considerable remains of a subterranean passage, by which chariots and horses were admitted into the arena, with a long inscription over the entrance.
.JPG/220px-Laodicea_(17).JPG) West Baths West Baths
The city ruins bear the stamp of Roman extravagance and luxury, rather than of the stern and massive solidity of the Greeks. Strabo attributes the celebrity of the place to the fertility of the soil and the wealth of some of its inhabitants: amongst whom Hiero, having adorned the city with many beautiful buildings, bequeathed to it more than 2000 talents at his death.
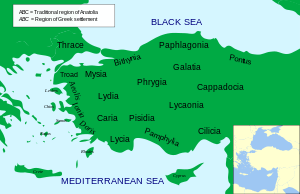 In antiquity, Phrygia was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Turkey, centered on the Sakarya River. In antiquity, Phrygia was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Turkey, centered on the Sakarya River.
During the heroic age of Greek mythology, several legendary kings were Phrygians: Gordias whose Gordian Knot would later be cut by Alexander the Great, Midas who turned whatever he touched to gold, and Mygdon who warred with the Amazons. According to Homer’s Iliad, the Phrygians were close allies of the Trojans and participants in the Trojan War against the Achaeans. Phrygian power reached its peak in the late 8th century BC under another, historical, king: Midas, who dominated most of western and central Anatolia and rivaled Assyria and Urartu for power in eastern Anatolia. This later Midas was, however, also the last independent king of Phrygia before its capital Gordium was sacked by Cimmerians around 695 BC. Phrygia then became subject to Lydia, and then successively to Persia, Alexander and his Hellenistic successors, Pergamon, Rome and Byzantium. Phrygians were gradually assimilated into other cultures by the early medieval era, and after the Turkish conquest of Anatolia the name Phrygia passed out of usage as a territorial designation.
|





 Athena or Athene (Latin: Minerva), also referred to as Pallas Athena, is the goddess of war, civilization, wisdom, strength, strategy, crafts, justice and skill in Greek mythology. Minerva, Athena’s Roman incarnation, embodies similar attributes. Athena is also a shrewd companion of heroes and the goddess of heroic endeavour. She is the virgin patron of Athens. The Athenians built the Parthenon on the Acropolis of her namesake city, Athens, in her honour (Athena Parthenos). Athena’s cult as the patron of Athens seems to have existed from the earliest times and was so persistent that archaic myths about her were recast to adapt to cultural changes. In her role as a protector of the city (polis), many people throughout the Greek world worshiped Athena as Athena Polias (“Athena of the city”). Athens and Athena bear etymologically connected names.
Athena or Athene (Latin: Minerva), also referred to as Pallas Athena, is the goddess of war, civilization, wisdom, strength, strategy, crafts, justice and skill in Greek mythology. Minerva, Athena’s Roman incarnation, embodies similar attributes. Athena is also a shrewd companion of heroes and the goddess of heroic endeavour. She is the virgin patron of Athens. The Athenians built the Parthenon on the Acropolis of her namesake city, Athens, in her honour (Athena Parthenos). Athena’s cult as the patron of Athens seems to have existed from the earliest times and was so persistent that archaic myths about her were recast to adapt to cultural changes. In her role as a protector of the city (polis), many people throughout the Greek world worshiped Athena as Athena Polias (“Athena of the city”). Athens and Athena bear etymologically connected names. In Greek mythology, Nike was a goddess who personified victory, also known as the Winged Goddess of Victory. The Roman equivalent was Victoria. Depending upon the time of various myths, she was described as the daughter of Pallas (Titan) and Styx (Water) and the sister of Kratos (Strength), Bia (Force), and Zelus (Zeal). Nike and her siblings were close companions of Zeus, the dominant deity of the Greek pantheon. According to classical (later) myth, Styx brought them to Zeus when the god was assembling allies for the Titan War against the older deities. Nike assumed the role of the divine charioteer, a role in which she often is portrayed in Classical Greek art. Nike flew around battlefields rewarding the victors with glory and fame.
In Greek mythology, Nike was a goddess who personified victory, also known as the Winged Goddess of Victory. The Roman equivalent was Victoria. Depending upon the time of various myths, she was described as the daughter of Pallas (Titan) and Styx (Water) and the sister of Kratos (Strength), Bia (Force), and Zelus (Zeal). Nike and her siblings were close companions of Zeus, the dominant deity of the Greek pantheon. According to classical (later) myth, Styx brought them to Zeus when the god was assembling allies for the Titan War against the older deities. Nike assumed the role of the divine charioteer, a role in which she often is portrayed in Classical Greek art. Nike flew around battlefields rewarding the victors with glory and fame..JPG/285px-Laodicea_(2).JPG)
.JPG/220px-Laodicea_(10).JPG) Western Theatre with Heirapolis/Pammukale in the distance
Western Theatre with Heirapolis/Pammukale in the distance .JPG/220px-Laodicea_(40).JPG) Temple “A”
Temple “A” .JPG/220px-Laodicea_(17).JPG) West Baths
West Baths  In antiquity, Phrygia was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Turkey, centered on the Sakarya River.
In antiquity, Phrygia was a kingdom in the west central part of Anatolia, in what is now Turkey, centered on the Sakarya River.




