|
Greek city of Metropolis in Thessaly
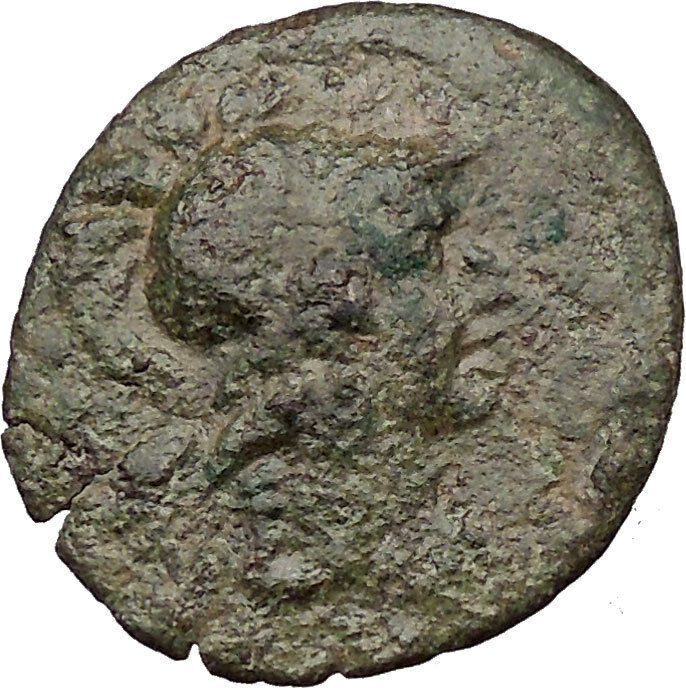
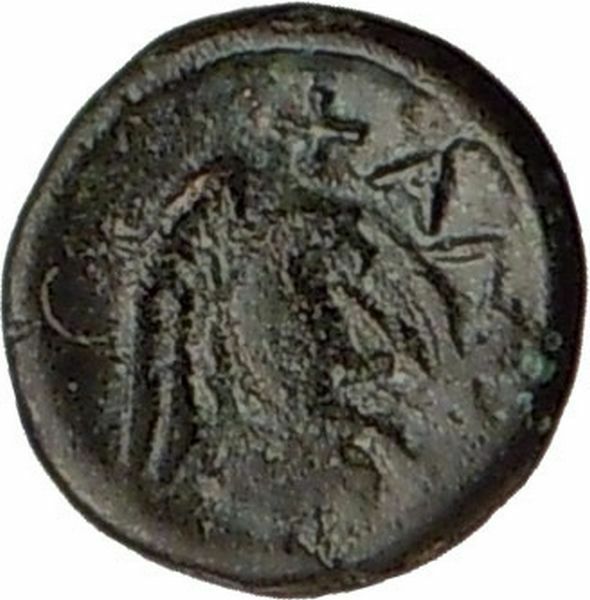
Bronze Trichalkon 19mm (6.79 grams) Struck 3rd Century (circa 300-200 B.C.)
Reference: BCD Thessaly II 478; HGC 4, 255.
Laureate head of Apollo right.
ΜΗΤΡΟΠΟΛΙΤΩΝ, Aphrodite Kastnia standing left, holding dove; to left, Eros standing left, reaching up towards the bird.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
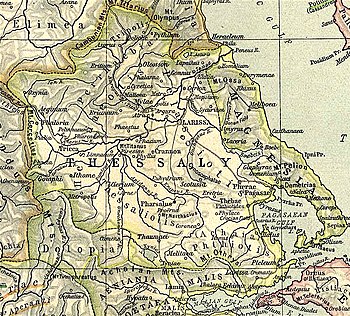 Metropolis (Ancient Greek: Μητρόπολις) was a town and polis (city-state) of Histiaeotis (or of Thessaliotis) in ancient Thessaly, described by Stephanus of Byzantium as a town in Upper Thessaly. Strabo says that Metropolis was founded by three insignificant towns, but that a larger number was afterwards added, among which was Ithome. He further says, that Ithome was within a quadrangle, formed by the four cities Tricca, Metropolis, Pelinnaeum, and Gomphi. The position of Metropolis is also determined by its being on Caesar’s march from Gomphi to Pharsalus. Metropolis (Ancient Greek: Μητρόπολις) was a town and polis (city-state) of Histiaeotis (or of Thessaliotis) in ancient Thessaly, described by Stephanus of Byzantium as a town in Upper Thessaly. Strabo says that Metropolis was founded by three insignificant towns, but that a larger number was afterwards added, among which was Ithome. He further says, that Ithome was within a quadrangle, formed by the four cities Tricca, Metropolis, Pelinnaeum, and Gomphi. The position of Metropolis is also determined by its being on Caesar’s march from Gomphi to Pharsalus.
Livy relates how the town repulsed an attack by the Aetolians after the retreat of Philip V of Macedon (198 BCE). Whilst the Aetolians were devastating the fields round Metropolis the townsmen who had mustered in force to defend their walls inflicted a repulse upon them. The Aetolians then continued on to attack nearby Callithera. It was taken by Titus Quinctius Flamininus on his descending into this part of Thessaly, after the Battle of the Aous.
We learn from an inscription that the territory of Metropolis adjoined that of Cierium (the ancient Arne), and that the adjustment of their boundaries was a frequent subject of discussion between the two peoples. Metropolis is mentioned in the sixth century by Hierocles. The remains of Metropolis are at the small village about 5 miles (8.0 km) southwest of Karditsa formerly called Paleokastro, but since renamed Mitropoli (Μητρόπολη) to reflect its association with the historic town.
The city was of a circular form, and in the centre of the circle are the vestiges of a circular citadel, part of the wall of which still exists in the yard of the village church, where is a collection of the sculptured or inscribed remains found upon the spot. Among other sculptures noticed by William Martin Leake during his visit in the early nineteenth century, one in low relief, representing a figure seated upon a rock, in long drapery, and a mountain rising in face of the figure, at the foot of which there is a man in a posture of adoration, while on the top of the mountain there are other men, one of whom holds a hog in his hands. Leake conjectured with great probability that the seated figure represents the Aphrodite of Metropolis, to whom Strabo says that hogs were offered in sacrifice.
Metropolis minted silver coins dated to c. 400-34
 In Greek and Roman mythology, Apollo, is one of the most important and diverse of the Olympian deities. The ideal of the kouros (a beardless youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the sun; truth and prophecy; archery; medicine and healing; music, poetry, and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son of Zeus and Leto, and has a twin sister, the chaste huntress Artemis. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both ancient Greek and Roman religion, as well as in the modern Greco-Roman Neopaganism. In Greek and Roman mythology, Apollo, is one of the most important and diverse of the Olympian deities. The ideal of the kouros (a beardless youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the sun; truth and prophecy; archery; medicine and healing; music, poetry, and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son of Zeus and Leto, and has a twin sister, the chaste huntress Artemis. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both ancient Greek and Roman religion, as well as in the modern Greco-Roman Neopaganism.
As the patron of Delphi (Pythian Apollo), Apollo was an oracular god – the prophetic deity of the Delphic Oracle. Medicine and healing were associated with Apollo, whether through the god himself or mediated through his son Asclepius, yet Apollo was also seen as a god who could bring ill-health and deadly plague as well as one who had the ability to cure. Amongst the god’s custodial charges, Apollo became associated with dominion over colonists, and as the patron defender of herds and flocks. As the leader of the Muses (Apollon Musagetes) and director of their choir, Apollo functioned as the patron god of music and poetry. Hermes created the lyre for him, and the instrument became a common attribute of Apollo. Hymns sung to Apollo were called paeans.
In Hellenistic times, especially during the third century BCE, as Apollo Helios he became identified among Greeks with Helios, god of the sun, and his sister Artemis similarly equated with Selene, goddess of the moon. In Latin texts, on the other hand, Joseph Fontenrose declared himself unable to find any conflation of Apollo with Sol among the Augustan poets of the first century, not even in the conjurations of Aeneas and Latinus in Aeneid XII (161-215). Apollo and Helios/Sol remained separate beings in literary and mythological texts until the third century CE.
Aphrodite is the Greek goddess of love, beauty, and sexuality. Her Roman equivalent is the goddess Venus. Historically, her cult in Greece was imported from, or influenced by, the  cult of Astarte in Phoenicia. cult of Astarte in Phoenicia.
According to Hesiod’s Theogony, she was born when Cronus cut off Uranus’ genitals and threw them into the sea, and from the sea foam (aphros) arose Aphrodite.
Because of her beauty other gods feared that jealousy would interrupt the peace among them and lead to war, and so Zeus married her to Hephaestus, who was not viewed as a threat. Aphrodite had many lovers, both gods like Ares, and men like Anchises. Aphrodite also became instrumental in the Eros and Psyche legend, and later was both Adonis’ lover and his surrogate mother. Many lesser beings were said to be children of Aphrodite.
Aphrodite is also known as Cytherea (Lady of Cythera) and Cypris (Lady of Cyprus) after the two cult-sites, Cythera and Cyprus, which claimed her birth. Myrtles, doves, sparrows, horses, and swans are sacred to her. The Greeks further identified the Ancient Egyptian goddess Hathor with Aphrodite. Aphrodite also has many other local names, such as Acidalia, Cytherea and Cerigo, used in specific areas of Greece. Each goddess demanded a slightly different cult but Greeks recognized in their overall similarities the one Aphrodite. Attic philosophers of the fourth century separated a celestial Aphrodite (Aprodite Urania) of transcendent principles with the common Aphrodite of the people (Aphrodite Pandemos).
|





 Metropolis (Ancient Greek: Μητρόπολις) was a town and polis (city-state) of Histiaeotis (or of Thessaliotis) in ancient Thessaly, described by Stephanus of Byzantium as a town in Upper Thessaly. Strabo says that Metropolis was founded by three insignificant towns, but that a larger number was afterwards added, among which was Ithome. He further says, that Ithome was within a quadrangle, formed by the four cities Tricca, Metropolis, Pelinnaeum, and Gomphi. The position of Metropolis is also determined by its being on Caesar’s march from Gomphi to Pharsalus.
Metropolis (Ancient Greek: Μητρόπολις) was a town and polis (city-state) of Histiaeotis (or of Thessaliotis) in ancient Thessaly, described by Stephanus of Byzantium as a town in Upper Thessaly. Strabo says that Metropolis was founded by three insignificant towns, but that a larger number was afterwards added, among which was Ithome. He further says, that Ithome was within a quadrangle, formed by the four cities Tricca, Metropolis, Pelinnaeum, and Gomphi. The position of Metropolis is also determined by its being on Caesar’s march from Gomphi to Pharsalus. In Greek and Roman mythology, Apollo, is one of the most important and diverse of the Olympian deities. The ideal of the kouros (a beardless youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the sun; truth and prophecy; archery; medicine and healing; music, poetry, and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son of Zeus and Leto, and has a twin sister, the chaste huntress Artemis. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both ancient Greek and Roman religion, as well as in the modern Greco-Roman Neopaganism.
In Greek and Roman mythology, Apollo, is one of the most important and diverse of the Olympian deities. The ideal of the kouros (a beardless youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the sun; truth and prophecy; archery; medicine and healing; music, poetry, and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son of Zeus and Leto, and has a twin sister, the chaste huntress Artemis. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both ancient Greek and Roman religion, as well as in the modern Greco-Roman Neopaganism. cult of Astarte in Phoenicia.
cult of Astarte in Phoenicia.




