|
France under Louis XV – French King: 1 September 1715 – 10 May 1774
Cambrai
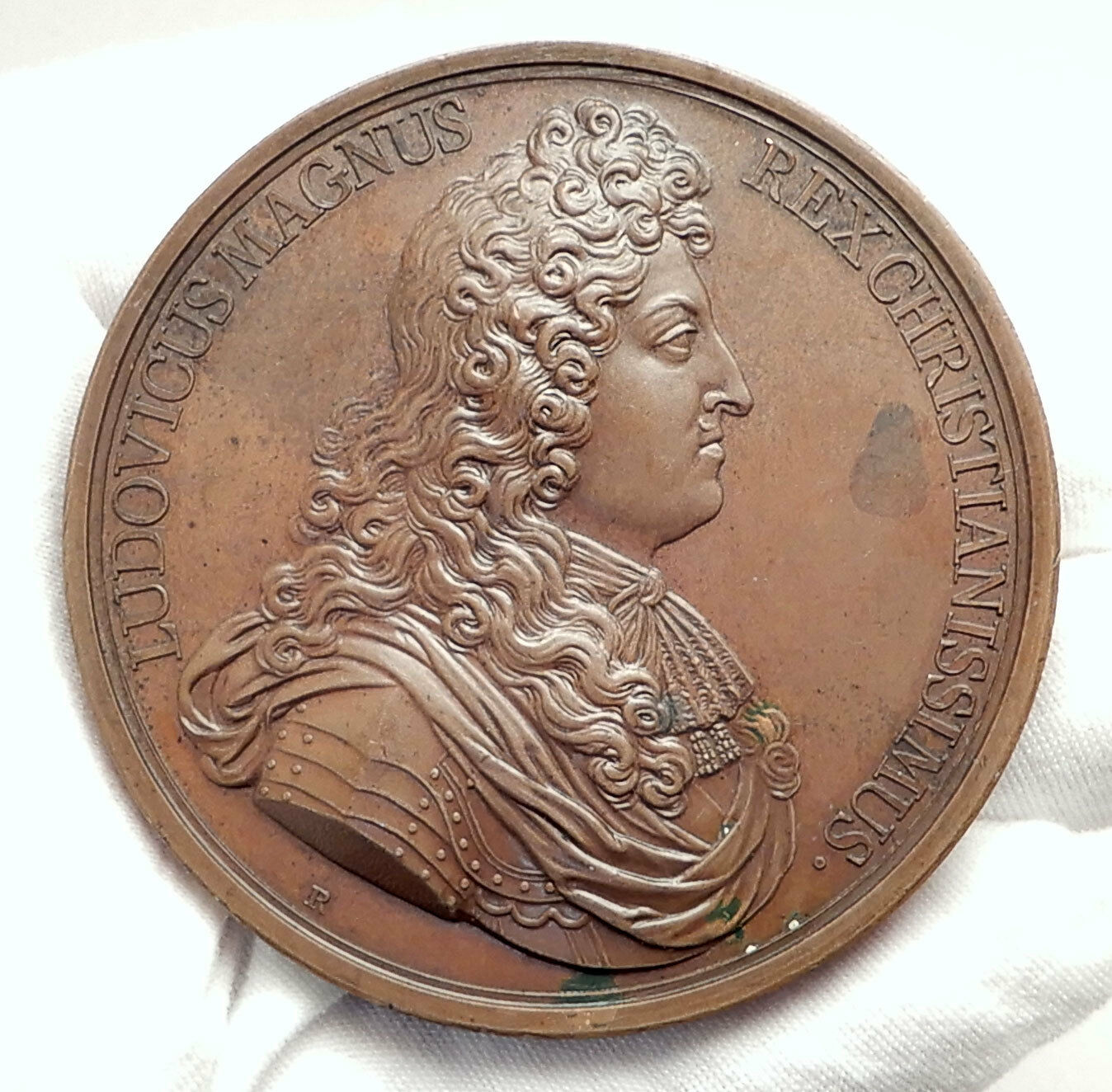
Undated Silver Jeton / Token / Medal 30mm (9.57 grams)
LUD.XV.REX CHRISTIANISS DV VIVIERF, Louis facing right.
CIVITAS CAMERA ACENSIS, Cambrai Coat-of-arms within plaque on crowned eagle.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
![The bell tower of the town hall, where Martin and Martine [fr] mark the hours](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/da/Campanile_hôtel_de_ville_Cambrai.JPG/270px-Campanile_hôtel_de_ville_Cambrai.JPG) Cambrai, formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a commune in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river. Cambrai, formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a commune in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river.
 A sub-prefecture of the department, Cambrai is a town which had 32,558 inhabitants in 2017. It is in the heart of the urban unit of Cambrai which, with 46,897 inhabitants, ranks as 7th largest of the department. Its urban area a more extensive range, included 66,177 inhabitants in 2017. With Lille and the towns of the former Nord-Pas de Calais Mining Basin, it is also part of the Metropolitan area of Lille which has more than 3.8 million inhabitants. A sub-prefecture of the department, Cambrai is a town which had 32,558 inhabitants in 2017. It is in the heart of the urban unit of Cambrai which, with 46,897 inhabitants, ranks as 7th largest of the department. Its urban area a more extensive range, included 66,177 inhabitants in 2017. With Lille and the towns of the former Nord-Pas de Calais Mining Basin, it is also part of the Metropolitan area of Lille which has more than 3.8 million inhabitants.
Towards the end of the Roman Empire, Cambrai replaced Bavay as the “capital” of the land of the Nervii. At the beginning of the Merovingian era, Cambrai became the seat of an immense archdiocese covering all the right bank of the Scheldt and the centre of a small ecclesiastical principality, roughly coinciding with the shire of Brabant, including the central part of the Low Countries. The bishopric had some limited secular power and depended on the Holy Roman Empire until annexation to France in 1678. Fénelon, nicknamed the “Swan of Cambrai”, was the most renowned of the archbishops.
The fertile lands which surround it and the textile industry gave it prosperity in the Middle Ages, but in modern times it is less industrialised than its neighbours of Nord-Pas-de-Calais.
Cambrai was the Duke of Wellington’s headquarters, for the British Army of Occupation, from 1815 to 1818. Occupied and partly destroyed by the German army during World War I, Cambrai saw unfold in its vicinity the Battle of Cambrai (20 November 1917 – 3 December 1917) where tanks were massively and successfully used for the first time. A second Battle of Cambrai took place between 8 and 10 October 1918 as part of the Hundred Days Offensive. World War II was followed by reconstructions and a rapidly developing economy and population, abruptly reversed by the 1973 oil crisis.
Cambrai today is a lively city and, despite the past destruction, maintains a rich monumental heritage. Cambrai is affirmed as the urban centre of Cambrésis. Its economic life is strengthened by its position on the main local highway and river.
Jetons or jettons are tokens or coin-like medals produced across Europe from the 13th through the 17th centuries. They were produced as counters for use in calculation on a counting board, a lined board similar to an abacus. They also found use as a money substitute in games, similar to modern casino chips or poker chips.
Thousands of different jetons exist, mostly of religious and educational designs, as well as portraits, the last of which most resemble coinage, somewhat similar to modern, non-circulation commemorative coins. The spelling “jeton” is from the French; the English spell it “jetton”.
 Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved, was a monarch of the House of Bourbon who ruled as King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defined as his 13th birthday) on 15 February 1723, the kingdom was ruled by Philippe II, Duke of Orleans, as Regent of France. Cardinal Fleury was his chief minister from 1726 until the Cardinal’s death in 1743, at which time the young king took sole control of the kingdom. Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved, was a monarch of the House of Bourbon who ruled as King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defined as his 13th birthday) on 15 February 1723, the kingdom was ruled by Philippe II, Duke of Orleans, as Regent of France. Cardinal Fleury was his chief minister from 1726 until the Cardinal’s death in 1743, at which time the young king took sole control of the kingdom.
His reign of almost 59 years (from 1715-1774) was the second longest in the history of France, exceeded only by his predecessor and great-grandfather, Louis XIV who ruled for 72 years (from 1643-1715). In 1748, Louis returned the Austrian Netherlands, won at the Battle of Fontenoy of 1745. He ceded New France in North America to Spain and Great Britain at the conclusion of the disastrous Seven Years’ War in 1763. He incorporated the territories of the Duchy of Lorraine and the Corsican Republic into the Kingdom of France. He was succeeded in 1774 by his grandson Louis XVI, who was executed by guillotine during the French Revolution. Two of his other grandsons, Louis XVIII and Charles X, occupied the throne of France after the fall of Napoleon I. Historians generally give his reign very low marks, especially as wars drained the treasury and set the stage for the governmental collapse and French Revolution in the 1780s.
  France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called Metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people. France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called Metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people.
During the Iron Age, what is now Metropolitan France was inhabited by the Gauls, a Celtic people. The Gauls were conquered in 51 BC by the Roman Empire, which held Gaul until 486. The Gallo-Romans faced raids and migration from the Germanic Franks, who dominated the region for hundreds of years, eventually creating the medieval Kingdom of France. France emerged as a major European power in the Late Middle Ages, with its victory in the Hundred Years’ War (1337 to 1453) strengthening French state-building and paving the way for a future centralized absolute monarchy. During the Renaissance, France experienced a vast cultural development and established the beginning of a global colonial empire. The 16th century was dominated by religious civil wars between Catholics and Protestants (Huguenots).
France became Europe’s dominant cultural, political, and military power under Louis XIV. French philosophers played a key role in the Age of Enlightenment during the 18th century. In 1778, France became the first and the main ally of the new United States in the American Revolutionary War. In the late 18th century, the absolute monarchy was overthrown in the French Revolution. Among its legacies was the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, one of the earliest documents on human rights, which expresses the nation’s ideals to this day. France became one of modern history’s earliest republics until Napoleon took power and launched the First French Empire in 1804. Fighting against a complex set of coalitions during the Napoleonic Wars, he dominated European affairs for over a decade and had a long-lasting impact on Western culture. Following the collapse of the Empire, France endured a tumultuous succession of governments: the monarchy was restored, it was replaced in 1830 by a constitutional monarchy, then briefly by a Second Republic, and then by a Second Empire, until a more lasting French Third Republic was established in 1870. By the 1905 law, France adopted a strict form of secularism, called laïcité, which has become an important federative principle in the modern French society.
France reached its territorial height during the 19th and early 20th centuries, when it ultimately possessed the second-largest colonial empire in the world. In World War I, France was one of the main winners as part of the Triple Entente alliance fighting against the Central Powers. France was also one of the Allied Powers in World War II, but came under occupation by the Axis Powers in 1940. Following liberation in 1944, a Fourth Republic was established and later dissolved in the course of the Algerian War. The Fifth Republic, led by Charles de Gaulle, was formed in 1958 and remains to this day. Following World War II, most of the empire became decolonized.
Throughout its long history, France has been a leading global center of culture, making significant contributions to art, science, and philosophy. It hosts Europe’s third-largest number of cultural UNESCO World Heritage Sites (after Italy and Spain) and receives around 83 million foreign tourists annually, the most of any country in the world. France remains a great power with significant cultural, economic, military, and political influence. It is a developed country with the world’s sixth-largest economy by nominal GDP and eight-largest by purchasing power parity. According to Credit Suisse, France is the fourth wealthiest nation in the world in terms of aggregate household wealth. It also possesses the world’s second-largest exclusive economic zone (EEZ), covering 11,035,000 square kilometres (4,261,000 sq mi).
French citizens enjoy a high standard of living, and the country performs well in international rankings of education, health care, life expectancy, civil liberties, and human development. France is a founding member of the United Nations, where it serves as one of the five permanent members of the UN Security Council. It is a member of the Group of 7, North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the World Trade Organization (WTO), and La Francophonie. France is a founding and leading member state of the European Union (EU).
|





![The bell tower of the town hall, where Martin and Martine [fr] mark the hours](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/da/Campanile_hôtel_de_ville_Cambrai.JPG/270px-Campanile_hôtel_de_ville_Cambrai.JPG) Cambrai, formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a commune in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river.
Cambrai, formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a commune in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the Escaut river. A sub-prefecture of the department, Cambrai is a town which had 32,558 inhabitants in 2017. It is in the heart of the urban unit of Cambrai which, with 46,897 inhabitants, ranks as 7th largest of the department. Its urban area a more extensive range, included 66,177 inhabitants in 2017. With Lille and the towns of the former Nord-Pas de Calais Mining Basin, it is also part of the Metropolitan area of Lille which has more than 3.8 million inhabitants.
A sub-prefecture of the department, Cambrai is a town which had 32,558 inhabitants in 2017. It is in the heart of the urban unit of Cambrai which, with 46,897 inhabitants, ranks as 7th largest of the department. Its urban area a more extensive range, included 66,177 inhabitants in 2017. With Lille and the towns of the former Nord-Pas de Calais Mining Basin, it is also part of the Metropolitan area of Lille which has more than 3.8 million inhabitants. Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved, was a monarch of the House of Bourbon who ruled as King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defined as his 13th birthday) on 15 February 1723, the kingdom was ruled by Philippe II, Duke of Orleans, as Regent of France. Cardinal Fleury was his chief minister from 1726 until the Cardinal’s death in 1743, at which time the young king took sole control of the kingdom.
Louis XV (15 February 1710 – 10 May 1774), known as Louis the Beloved, was a monarch of the House of Bourbon who ruled as King of France from 1 September 1715 until his death in 1774. He succeeded his great-grandfather Louis XIV at the age of five. Until he reached maturity (then defined as his 13th birthday) on 15 February 1723, the kingdom was ruled by Philippe II, Duke of Orleans, as Regent of France. Cardinal Fleury was his chief minister from 1726 until the Cardinal’s death in 1743, at which time the young king took sole control of the kingdom. 
 France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called Metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people.
France, officially the French Republic (French: République française), is a sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. The European part of France, called Metropolitan France, extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean. France spans 640,679 square kilometres (247,368 sq mi) and has a total population of 67 million. It is a unitary semi-presidential republic with the capital in Paris, the country’s largest city and main cultural and commercial centre. The Constitution of France establishes the state as secular and democratic, with its sovereignty derived from the people.





