|
Greek city of Adramytion in Mysia
Bronze 21mm (9.34 grams) Struck circa 133-67 B.C.
Time of Mithradates VI the Great
Reference: Sear 3807; B.M.C.15.3,7-8; S&B 69; SNG BN 16
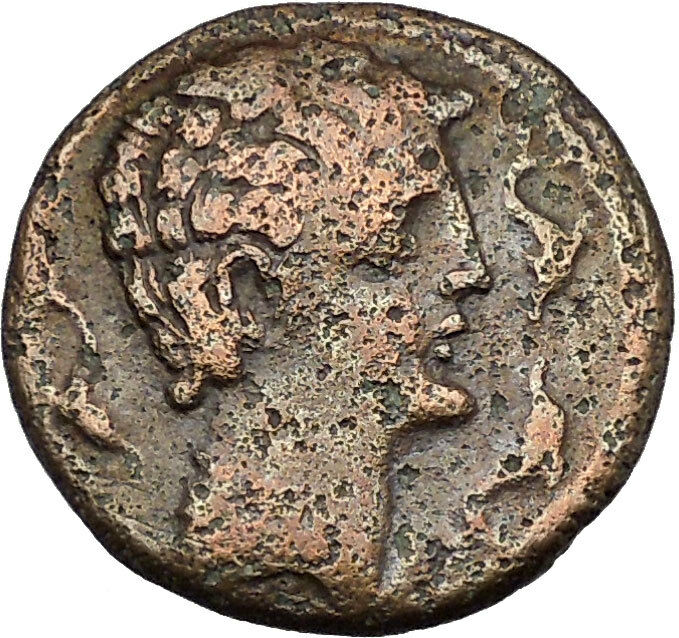
Laureate head of Apollo left; bow and quiver over shoulder.
Cornucopia between caps (pilei) of the Dioskouroi surmounted by stars; AΔPA – MY / TH – NΩN across field.
A coastal town situated north-west of Pergamon, Adramytteion is said to have been founded by Adramys, brother of King Kroisos of Lydia.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 Mithridates VI or Mithradates VI (Greek: Μιθραδάτης), from Old Persian Mithradatha, “gift of Mithra”; 134-63 BC, also known as Mithradates the Great (Megas) and Eupator Dionysius, was king of Pontus and Armenia Minor in northern Anatolia (now Turkey) from about 120-63 BC. Mithridates is remembered as one of the Roman Republic’s most formidable and successful enemies, who engaged three of the prominent generals from the late Roman Republic in the Mithridatic Wars: Lucius Cornelius Sulla, Lucullus and Pompey. He was also the greatest ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus. Mithridates VI or Mithradates VI (Greek: Μιθραδάτης), from Old Persian Mithradatha, “gift of Mithra”; 134-63 BC, also known as Mithradates the Great (Megas) and Eupator Dionysius, was king of Pontus and Armenia Minor in northern Anatolia (now Turkey) from about 120-63 BC. Mithridates is remembered as one of the Roman Republic’s most formidable and successful enemies, who engaged three of the prominent generals from the late Roman Republic in the Mithridatic Wars: Lucius Cornelius Sulla, Lucullus and Pompey. He was also the greatest ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus.
 In Greek and Roman mythology, Apollo, is one of the most important and diverse of the Olympian deities. The ideal of the kouros (a beardless youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the sun; truth and prophecy; archery; medicine and healing; music, poetry, and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son of Zeus and Leto, and has a twin sister, the chaste huntress Artemis. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both ancient Greek and Roman religion, as well as in the modern Greco-Roman Neopaganism. In Greek and Roman mythology, Apollo, is one of the most important and diverse of the Olympian deities. The ideal of the kouros (a beardless youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the sun; truth and prophecy; archery; medicine and healing; music, poetry, and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son of Zeus and Leto, and has a twin sister, the chaste huntress Artemis. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both ancient Greek and Roman religion, as well as in the modern Greco-Roman Neopaganism.
As the patron of Delphi (Pythian Apollo), Apollo was an oracular god – the prophetic deity of the Delphic Oracle. Medicine and healing were associated with Apollo, whether through the god himself or mediated through his son Asclepius, yet Apollo was also seen as a god who could bring ill-health and deadly plague as well as one who had the ability to cure. Amongst the god’s custodial charges, Apollo became associated with dominion over colonists, and as the patron defender of herds and flocks. As the leader of the Muses (Apollon Musagetes) and director of their choir, Apollo functioned as the patron god of music and poetry. Hermes created the lyre for him, and the instrument became a common attribute of Apollo. Hymns sung to Apollo were called paeans.
In Hellenistic times, especially during the third century BCE, as Apollo Helios he became identified among Greeks with Helios, god of the sun, and his sister Artemis similarly equated with Selene, goddess of the moon. In Latin texts, on the other hand, Joseph Fontenrose declared himself unable to find any conflation of Apollo with Sol among the Augustan poets of the first century, not even in the conjurations of Aeneas and Latinus in Aeneid XII (161-215). Apollo and Helios/Sol remained separate beings in literary and mythological texts until the third century CE.
_-_Google_Art_Project.jpg/260px-Peter_Paul_Rubens_-_Abundance_(Abundantia)_-_Google_Art_Project.jpg) The cornucopia (from Latin cornu copiae) or horn of plenty is a symbol of abundance and nourishment, commonly a large horn-shaped container overflowing with produce, flowers or nuts. The horn originates from classical antiquity, it has continued as a symbol in Western art, and it is particularly associated with the Thanksgiving holiday in North America. The cornucopia (from Latin cornu copiae) or horn of plenty is a symbol of abundance and nourishment, commonly a large horn-shaped container overflowing with produce, flowers or nuts. The horn originates from classical antiquity, it has continued as a symbol in Western art, and it is particularly associated with the Thanksgiving holiday in North America.
Mythology offers multiple explanations of the origin of the cornucopia. One of the best-known involves the birth and nurturance of the infant Zeus, who had to be hidden from his devouring father Kronus. In a cave on Mount Ida on the island of Crete, baby Zeus was cared for and protected by a number of divine attendants, including the goat Amalthea (“Nourishing Goddess”), who fed him with her milk. The suckling future king of the gods had unusual abilities and strength, and in playing with his nursemaid accidentally broke off one of her horns, which then had the divine power to provide unending nourishment, as the foster mother had to the god.
In another myth, the cornucopia was created when Heracles (Roman Hercules) wrestled with the river god Achelous and wrenched off one of his horns; river gods were sometimes depicted as horned. This version is represented in the Achelous and Hercules mural painting by the American Regionalist artist Thomas Hart Benton.
The cornucopia became the attribute of several Greek and Roman deities, particularly those associated with the harvest, prosperity, or spiritual abundance, such as personifications of Earth (Gaia or Terra); the child Plutus, god of riches and son of the grain goddess Demeter; the nymph Maia; and Fortuna, the goddess of luck, who had the power to grant prosperity. In Roman Imperial cult, abstract Roman deities who fostered peace (pax Romana) and prosperity were also depicted with a cornucopia, including Abundantia, “Abundance” personified, and Annona, goddess of the grain supply to the city of Rome. Pluto, the classical ruler of the underworld in the mystery religions, was a giver of agricultural, mineral and spiritual wealth, and in art often holds a cornucopia to distinguish him from the gloomier Hades, who holds a drinking horn instead.
Edremit is a district in Balıkesir Province, Turkey, as well as the central city of that district, on the west coast of Turkey, not far from the Greek island Lesbos. It is situated at the tip of the gulf with the same name (Gulf of Edremit), with its town center a few kilometers inland, and is an important center of trade, along with the other towns that are situated on the same gulf (namely Ayvalık, Gömeç, Burhaniye and Havran). It is also one of the largest district centers of Balıkesir Province.
Coordinates:  39°35′N 27°01′E 39°35′N 27°01′E
The Greek name for Edremit is Adramyttion (Άδραμύττιον) and the Latin name is Adramyttium, mentioned in the New Testament (Acts 27:2), as a city of Asia Minor on the coast of Mysia, which was called Aeolis in classical antiquity. The ship in which Apostle Paul embarked at Caesarea belonged to this city (Acts 27:2). He was conveyed in it only to Myra, in Lycia, whence he sailed in an Alexandrian ship to Italy. It was a rare thing for a ship to sail from any port of Judea direct for Italy. In the 19th century, the name Adramyti was used. However the ancient city was not Edremit itself ; it is in Ören, Burhaniye.
Edremit’s economy relies largely on the production of olives, as well as on tourism. Kaz Dağı National Park, extending around the ancient Mount Ida (mentioned in Homer’s epic poems such as the Iliad), is situated within the boundaries of Edremit district and is an important tourist attraction with its natural scenery and a number of picturesque small villages around it. In ethno-cultural terms, the population of Edremit is a mixture of Balkan Turks, descendants of immigrants from Aegean Islands, some Circassians, as well as native Tahtacı Turkmens, who pursue their own traditions and life-style to this day. A private museum of ethnography in the village of Tahtakuşlar is one of the rare institutions in Turkey focusing on Tahtacı culture. The district of Edremit, especially around Kazdağı, is largely covered with forests.
|





 Mithridates VI or Mithradates VI (Greek: Μιθραδάτης), from Old Persian Mithradatha, “gift of Mithra”; 134-63 BC, also known as Mithradates the Great (Megas) and Eupator Dionysius, was king of Pontus and Armenia Minor in northern Anatolia (now Turkey) from about 120-63 BC. Mithridates is remembered as one of the Roman Republic’s most formidable and successful enemies, who engaged three of the prominent generals from the late Roman Republic in the Mithridatic Wars: Lucius Cornelius Sulla, Lucullus and Pompey. He was also the greatest ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus.
Mithridates VI or Mithradates VI (Greek: Μιθραδάτης), from Old Persian Mithradatha, “gift of Mithra”; 134-63 BC, also known as Mithradates the Great (Megas) and Eupator Dionysius, was king of Pontus and Armenia Minor in northern Anatolia (now Turkey) from about 120-63 BC. Mithridates is remembered as one of the Roman Republic’s most formidable and successful enemies, who engaged three of the prominent generals from the late Roman Republic in the Mithridatic Wars: Lucius Cornelius Sulla, Lucullus and Pompey. He was also the greatest ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus. In Greek and Roman mythology, Apollo, is one of the most important and diverse of the Olympian deities. The ideal of the kouros (a beardless youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the sun; truth and prophecy; archery; medicine and healing; music, poetry, and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son of Zeus and Leto, and has a twin sister, the chaste huntress Artemis. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both ancient Greek and Roman religion, as well as in the modern Greco-Roman Neopaganism.
In Greek and Roman mythology, Apollo, is one of the most important and diverse of the Olympian deities. The ideal of the kouros (a beardless youth), Apollo has been variously recognized as a god of light and the sun; truth and prophecy; archery; medicine and healing; music, poetry, and the arts; and more. Apollo is the son of Zeus and Leto, and has a twin sister, the chaste huntress Artemis. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as Apulu. Apollo was worshiped in both ancient Greek and Roman religion, as well as in the modern Greco-Roman Neopaganism._-_Google_Art_Project.jpg/260px-Peter_Paul_Rubens_-_Abundance_(Abundantia)_-_Google_Art_Project.jpg) The cornucopia (from Latin cornu copiae) or horn of plenty is a symbol of abundance and nourishment, commonly a large horn-shaped container overflowing with produce, flowers or nuts. The horn originates from classical antiquity, it has continued as a symbol in Western art, and it is particularly associated with the Thanksgiving holiday in North America.
The cornucopia (from Latin cornu copiae) or horn of plenty is a symbol of abundance and nourishment, commonly a large horn-shaped container overflowing with produce, flowers or nuts. The horn originates from classical antiquity, it has continued as a symbol in Western art, and it is particularly associated with the Thanksgiving holiday in North America.
 39°35′N 27°01′E
39°35′N 27°01′E




