|
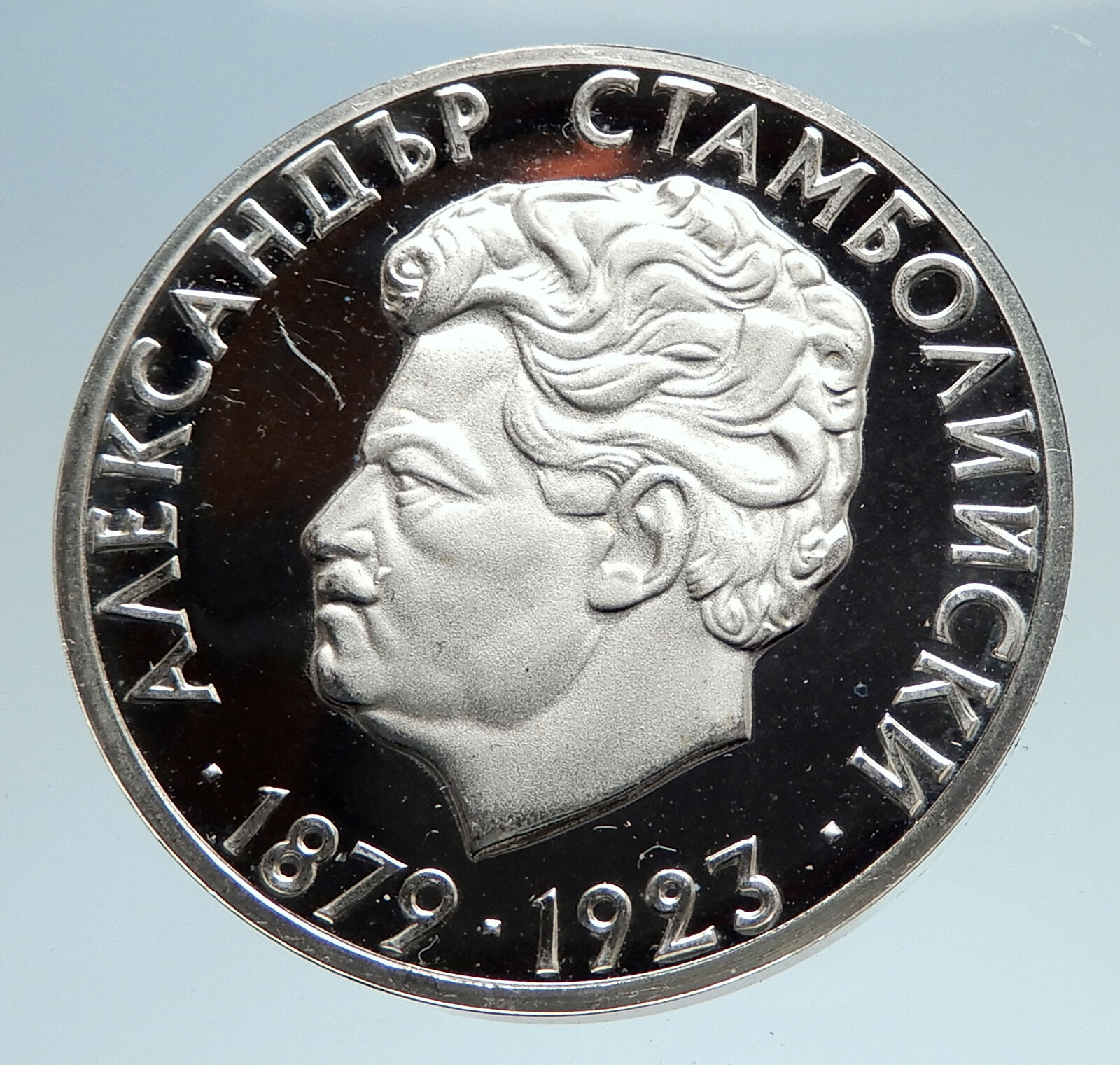
Bulgaria – 10th Olympic Congress – Commemorative issue
1975 Silver 10 Leva 40mm (29.98 grams) 0.900 Silver (0.86666 oz. ASW)
Reference: KM# 93.1 (Edge Lettering in
Latin) | Mintage: 50,000
Certification: NGC
PF 66 CAMEO 2863147-014
НАРОДНА РЕПУБЛИКА БЪЛГАРИЯ 1975 10 ЛЕВА, National coat-of-arms of eople’s Republic of Bulgaria.
ДЕСЕТИ ОЛИМПИЙСКИ КОНГРЕС 1973 (Translation: Tenth Olympic Congress), Design from anancient Roman 2nd century coin from Philippopolis in Thrace featuring two nude wrestler athletes for the ancient Olympic-style games above the modern Olympic games rings.
Edge:
Latin: Citius Altius Fortius
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
 An Olympic Congress is a large gathering of representatives from the different constituencies of the Olympic Movement, organised by the International Olympic Committee (IOC). As detailed in chapter 1, rule 4 of the Olympic Charter, the IOC President is responsible for convening a Congress, presiding over its proceedings and for determining its procedures. Olympic Congresses are not regular events in the IOC’s calendar. As the Olympic Charter states, “The Olympic Congress gathers representatives of the constituents of the Olympic Movement, at intervals determined by the IOC”. An Olympic Congress is a large gathering of representatives from the different constituencies of the Olympic Movement, organised by the International Olympic Committee (IOC). As detailed in chapter 1, rule 4 of the Olympic Charter, the IOC President is responsible for convening a Congress, presiding over its proceedings and for determining its procedures. Olympic Congresses are not regular events in the IOC’s calendar. As the Olympic Charter states, “The Olympic Congress gathers representatives of the constituents of the Olympic Movement, at intervals determined by the IOC”.
As the role of an Olympic Congress is consultative, all recommendations from the Congress must be submitted to the IOC Session for formal adoption. The first Olympic Congress was held in Paris, France in 1894. It was this Congress which founded and established the IOC and laid the groundwork for its statutes. The process of revival of the Olympic Games also began at the Paris Congress of 1894.
After 1894, and until 1930, there were eight Congresses covering various issues related to the burgeoning Olympic Movement. The last Congress before the Second World War was held in Berlin in 1930. After this time, there was then an interruption of more than forty years until the 10th Olympic Congress was held in Varna, Bulgaria in 1973. Successive Congresses were held in Baden-Baden, Germany in 1981 and then in Paris, France in 1994.

Bulgaria (Bulgarian: България, tr. Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria (Bulgarian: Република България, tr. Republika Bǎlgariya, IPA: [rɛˈpublikɐ bɐɫˈɡarijɐ]), is a country in southeastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. With a territory of 110,994 square kilometres (42,855 sq mi), Bulgaria is Europe’s 16th-largest country.
 Organised prehistoric cultures began developing on current Bulgarian lands during the Neolithic period. Its ancient history saw the presence of the Thracians, Ancient Greeks, Persians, Celts, Romans, Goths, Alans and Huns. The emergence of a unified Bulgarian state dates back to the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681 AD, which dominated most of the Balkans and functioned as a cultural hub for Slavs during the Middle Ages. With the downfall of the Second Bulgarian Empire in 1396, its territories came under Ottoman rule for nearly five centuries. The Russo-Turkish War of 1877-78 led to the formation of the Third Bulgarian State. The following years saw several conflicts with its neighbours, which prompted Bulgaria to align with Germany in both world wars. In 1946 it became a one-party socialist state as part of the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc. In December 1989 the ruling Communist Party allowed multi-party elections, which subsequently led to Bulgaria’s transition into a democracy and a market-based economy. Organised prehistoric cultures began developing on current Bulgarian lands during the Neolithic period. Its ancient history saw the presence of the Thracians, Ancient Greeks, Persians, Celts, Romans, Goths, Alans and Huns. The emergence of a unified Bulgarian state dates back to the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681 AD, which dominated most of the Balkans and functioned as a cultural hub for Slavs during the Middle Ages. With the downfall of the Second Bulgarian Empire in 1396, its territories came under Ottoman rule for nearly five centuries. The Russo-Turkish War of 1877-78 led to the formation of the Third Bulgarian State. The following years saw several conflicts with its neighbours, which prompted Bulgaria to align with Germany in both world wars. In 1946 it became a one-party socialist state as part of the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc. In December 1989 the ruling Communist Party allowed multi-party elections, which subsequently led to Bulgaria’s transition into a democracy and a market-based economy.

Bulgaria’s population of 7.2 million people is predominantly urbanised and mainly concentrated in the administrative centres of its 28 provinces. Most commercial and cultural activities are centred on the capital and largest city, Sofia. The strongest sectors of the economy are heavy industry, power engineering, and agriculture, all of which rely on local natural resources.
The country’s current political structure dates to the adoption of a democratic constitution in 1991. Bulgaria is a unitary parliamentary republic with a high degree of political, administrative, and economic centralisation. It is a member of the European Union, NATO, and the Council of Europe; a founding state of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE); and has taken a seat at the UN Security Council three times.
|









 An Olympic Congress is a large gathering of representatives from the different constituencies of the Olympic Movement, organised by the International Olympic Committee (IOC). As detailed in chapter 1, rule 4 of the Olympic Charter, the IOC President is responsible for convening a Congress, presiding over its proceedings and for determining its procedures. Olympic Congresses are not regular events in the IOC’s calendar. As the Olympic Charter states, “The Olympic Congress gathers representatives of the constituents of the Olympic Movement, at intervals determined by the IOC”.
An Olympic Congress is a large gathering of representatives from the different constituencies of the Olympic Movement, organised by the International Olympic Committee (IOC). As detailed in chapter 1, rule 4 of the Olympic Charter, the IOC President is responsible for convening a Congress, presiding over its proceedings and for determining its procedures. Olympic Congresses are not regular events in the IOC’s calendar. As the Olympic Charter states, “The Olympic Congress gathers representatives of the constituents of the Olympic Movement, at intervals determined by the IOC”. 
 Organised prehistoric cultures began developing on current Bulgarian lands during the Neolithic period. Its ancient history saw the presence of the Thracians, Ancient Greeks, Persians, Celts, Romans, Goths, Alans and Huns. The emergence of a unified Bulgarian state dates back to the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681 AD, which dominated most of the Balkans and functioned as a cultural hub for Slavs during the Middle Ages. With the downfall of the Second Bulgarian Empire in 1396, its territories came under Ottoman rule for nearly five centuries. The Russo-Turkish War of 1877-78 led to the formation of the Third Bulgarian State. The following years saw several conflicts with its neighbours, which prompted Bulgaria to align with Germany in both world wars. In 1946 it became a one-party socialist state as part of the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc. In December 1989 the ruling Communist Party allowed multi-party elections, which subsequently led to Bulgaria’s transition into a democracy and a market-based economy.
Organised prehistoric cultures began developing on current Bulgarian lands during the Neolithic period. Its ancient history saw the presence of the Thracians, Ancient Greeks, Persians, Celts, Romans, Goths, Alans and Huns. The emergence of a unified Bulgarian state dates back to the establishment of the First Bulgarian Empire in 681 AD, which dominated most of the Balkans and functioned as a cultural hub for Slavs during the Middle Ages. With the downfall of the Second Bulgarian Empire in 1396, its territories came under Ottoman rule for nearly five centuries. The Russo-Turkish War of 1877-78 led to the formation of the Third Bulgarian State. The following years saw several conflicts with its neighbours, which prompted Bulgaria to align with Germany in both world wars. In 1946 it became a one-party socialist state as part of the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc. In December 1989 the ruling Communist Party allowed multi-party elections, which subsequently led to Bulgaria’s transition into a democracy and a market-based economy.





